Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Shorty (crater)
Lunar crater From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Shorty is a feature on the Moon, an impact crater in the Taurus–Littrow valley.[2] Astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt visited it in 1972, on the Apollo 17 mission.[2][3] It is the location of the famous "orange soil", which geologists believe to be small bits of rapidly-cooled molten rock ejected in a lava fountain.[2] It is about 110 meters (120 yards) in diameter and up to 14 m (15 yd) deep.[4]
Shorty Crater is about 14 m deep. Based on our investigations at the site and later examination of photographs, the impact that formed it penetrated, in order, regolith on the avalanche deposit, the avalanche deposit, regolith on a basalt flow, a basalt flow overlying and protecting the orange and black glass layers, the orange and black glass layers, regolith on a second basalt flow, and, finally, the upper portion of that second flow. Orange and black glass clods and basalt boulders are spread throughout the ejecta blanket surrounding Shorty.
— Apollo 17 Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt as quoted on the LROC Instrument website[4]

To the east of Shorty are Victory, Camelot, and the Apollo 17 landing site. To the southeast is Brontë. To the southwest are Lara and Nansen.
The crater was named after the character "Shorty" in Richard Brautigan's 1967 novel Trout Fishing in America, as well as to honor the genre of the short story with particular reference to J. D. Salinger.[5]
- Apollo 17 panoramic camera image
- Exploring Shorty crater during the Apollo 17 mission to the Moon. The orange soil was found to the right of the rover, at the base of the small hill at the crater rim.
- Orange soil found next to Shorty, which turned out to be titanium-rich pyroclastic glass (sample 74220 in the table below)[4]
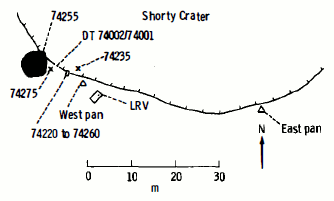
- Planimetric map of Station 4 including the rim of Shorty
Remove ads
Samples
The following samples were collected from Shorty crater (Station 4), as listed in Table 7-I of the Apollo 17 Preliminary Science Report.[6] The "Rock Type" is from the table, and the "Lithology" is from the Lunar Sample Compendium of the Lunar and Planetary Institute or NASA's Lunar Sample Catalog.
| Sample | In Situ Photo | Rock Type | Lithology | Photo |
| 74001/74002 |  | Double Drive Tube | Regolith breccia[7] | - |
| 74115 to 74119 |  | Friable clods | Regolith breccia[8] | - |
| 74220 |  | - | Soil[9] (the orange soil) | |
| 74235 | - | Basalt vitrophyre | High-Ti Mare Basalt[10] | |
| 74240 |  | - | Soil[9] | - |
| 74245 | - | Fine or devitrified basalt | Aphanitic High-Ti Basalt[11] | - |
| 74246 | - | Dark matrix breccia | Soil Breccia[12] | - |
| 74247 | - | Fine or devitrified basalt | High-Ti Basalt[13] | - |
| 74248 | - | Fine or devitrified basalt | High-Ti Basalt[14] | - |
| 74249 | - | Fine basalt | High-Ti Basalt[15] | - |
| 74250 |  | - | Soil[16] | - |
| 74255 |  | Coarse basalt | Ilmenite Basalt[17] | - |
| 74260 |  | - | Soil[9] | - |
| 74270 |  | - | Soil[16] | - |
| 74275 |  | Fine basalt | High-Ti Mare Basalt[18] | |
| 74285 |  | Medium basalt | High-Ti Mare Basalt[19] | - |
| 74286 |  | Medium basalt | High-Ti Mare Basalt[20] | - |
| 74287 |  | Fine basalt | High-Ti Mare Basalt[21] | - |
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads