Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
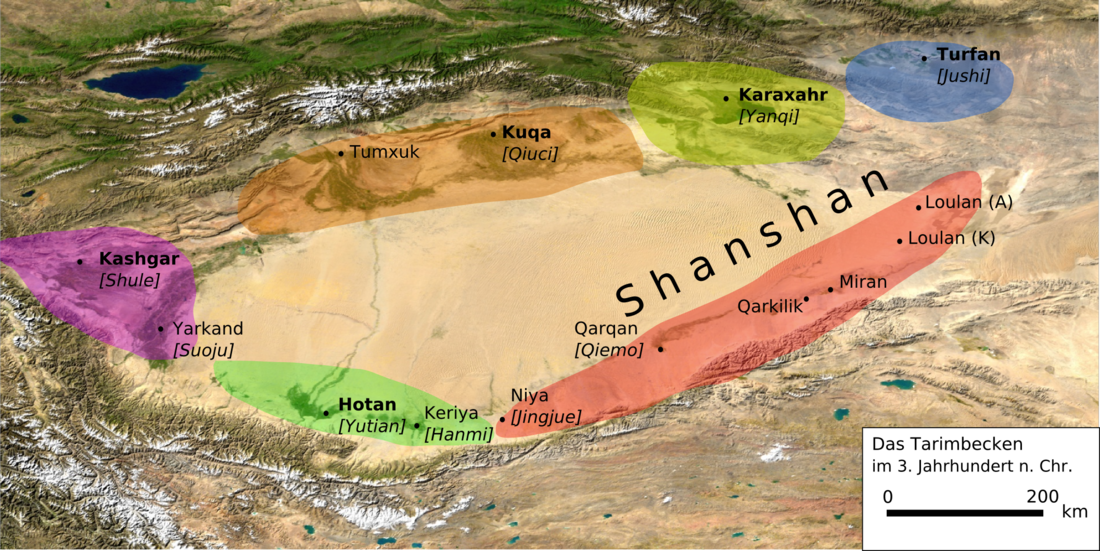
Shule Kingdom
Ancient Iranian oasis kingdom in contemporary China From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Shule Kingdom (Chinese: 疏勒) was an ancient oasis kingdom of the Taklamakan Desert on the Northern Silk Road, in the historical Western Regions of what is now Xinjiang in Northwest China. Its capital was Kashgar,[1] the source of Kashgar's water being a river of the same name. Much like the neighboring people of the Kingdom of Khotan, the people of Kashgar spoke Saka, one of the Eastern Iranian languages.[2]
Although a vassal of the Chinese Tang dynasty from the 7th century, Shule was conquered by the Tibetan Empire in the late 8th century and was eventually incorporated into the Kara-Khanid Khanate during the Islamicisation and Turkicisation of Xinjiang.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
The earliest mention of the Shule is around 120 BC, by the Western Han Chinese, when exploring their borders.[3] In 127 AD, Shule began to pay tribute to the Eastern Han.[3] In 168, following Hede's murder of the current ruler (name unknown), the Han declared war on the Shule, ending in the unsuccessful Siege of Zhenzhong in 170 AD.[3]
By the end of the Eastern Han period (220 AD), Shule had conquered the city-states of Zhenzhong, Yarkent, Jieshi, Qusha, Xiye, and Yinai.[3] In the 5th century, the Shule kingdom became a tributary of the Gokturks. They gained independence from the Gokturks in 630, when the Gokturks fell in battle to the Chinese Tang dynasty.[3] In 632 AD, it was vassalized by the Tang, as part of the Tang campaign against the oasis states.[4] Some sources say they were only made into a tributary, and the Tang had very loose suzerainty.[5][6][7] After being conquered by the Tang, it was part of the Protectorate General to Pacify the West between c. 640 and c. 790.[8] It was one of the Four Garrisons of Anxi stations between 649 and 670. After 670, one of the garrisons was changed, but Kashgar was still a seat of the four garrisons.[9]
In 670 AD, Shule was conquered by the Tibetan Empire. In 673, the Shule kingdom declared itself a vassal of the Tang,[10] but was not reconquered by the Tang Chinese until 692 AD.[11]
It is alleged and probably untrue that Qutayba ibn Muslim in 715 attacked Kashgar.[12][13]
Kara Khanid Muslim Turks absorbed Kashgar during the Islamicisation and Turkicisation of Xinjiang. According to Mahmud al-Kashgari, within Kashgar's vicinity, some non-Turkic languages like the Kanchaki and Sogdian were still used in some areas.[14] It is believed that the Saka language group was what Kanchaki belonged to.[15][16] The Tarim Basin was believed to be linguistically Turkified before the end of the 11th century.[17]
Remove ads
Economy
As it was on the Northern Silk Road, Shule mostly traded through the Yumen Pass[18] and the Pamir Mountains.[19]
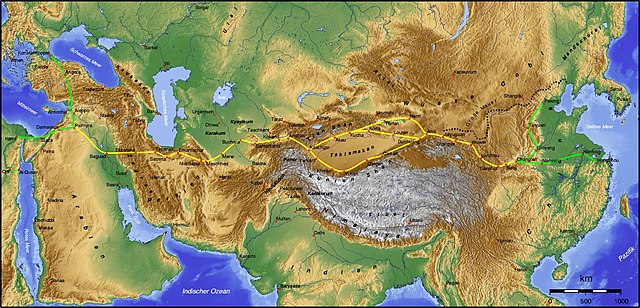
The Northern Silk Road that passed through Kashgar split off into the northern Tarim Basin route, which ran from Kashgar over Aksu, Kucha, Korla, through the Iron Gate Pass, over Karasahr, Jiaohe, Turpan, Gaochang and Kumul to Anxi. The southern Tarim Basin route ran from Kashgar over Yarkant, Karghalik, Pishan, Khotan, Keriya, Niya, Qarqan, Qarkilik, Miran and Dunhuang to Anxi.[20]
Remove ads
Genetics
Paternal haplogroups
Saka Shule had predominantly haplogroup Q1a, with R1a and N1a also present.[21]
Maternal haplogroups
Among the maternal haplogroups were H14a, H13a, U2e, U5a, M3a, D4j, C4a.[22]
Autosomal DNA
Genetically, the Saka Shule appear to be descended from steppe pastoralists associated with the Andronovo/Sintasha and Afanasevo cultures, but with significant contributions from other populations such as the bmac, Baikal HG and local Tarim mummies. During the Iron Age, the region received genetic flow from the Central Asian Saka. There is also a minor contribution from the Yellow farmer and AASI.[23]


Rulers
- Cheng (成) 70
- Dou Ti (兜題) 72
- Zhong (忠) 74
- Cheng Da (成大) 84
- An Guo (安國) 116
- Yi Fu (遺腹) 125
- Chen Pan (臣磐) 127
- He De (和得) 168
- A Mijue (阿彌厥) 605
- Pei Chuo (裴綽) 618
- Pei Amozhi (裴阿摩支) 627
- Pei Yijian (裴夷健) 698
- Pei Anding (裴安定) 728
- Pei Guoliang (裴國良) 753
- Pei Lengleng (裴冷冷) 784–789? / Tang general – Lu Yang (魯陽) 789
See also
References
Bibliography
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads