Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Straight sinus
Venous sinus draining the brain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
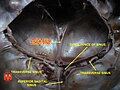
The straight sinus, also known as tentorial sinus or the sinus rectus, is an area within the skull beneath the brain. It receives blood from the inferior sagittal sinus and the great cerebral vein, and drains into the confluence of sinuses.
Remove ads
Structure
The straight sinus is situated within the dura mater, where the falx cerebri meets the midline of tentorium cerebelli.[1] It forms from the confluence of the inferior sagittal sinus and the great cerebral vein.[1][2] It may also drain blood from the superior cerebellar veins and veins from the falx cerebri.[1] In cross-section, it is triangular, contains a few transverse bands across its interior, and increases in size as it proceeds backward.[citation needed] It is usually around 5 cm long.[2]
Variation
The straight sinus is usually an unpaired structure.[2] However, there may be two straight sinuses, which may be one on top of the other or parallel.[2]
Remove ads
Function
The straight sinus allows blood to drain from the inferior center of the head outwards posteriorly. It receives blood from the inferior sagittal sinus, great cerebral vein, posterior cerebral veins, superior cerebellar veins and veins from the falx cerebri.[1]
Additional images
- Tentorium cerebelli from above.
- Straight sinus
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads