Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Symmetric relation
Type of binary relation From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A symmetric relation is a type of binary relation. Formally, a binary relation R over a set X is symmetric if:[1]
| Transitive binary relations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
in general (it might, or might not, hold). For example, that every equivalence relation is symmetric, but not necessarily antisymmetric, is indicated by All definitions tacitly require the homogeneous relation be transitive: for all if and then |
where the notation aRb means that (a, b) ∈ R.
An example is the relation "is equal to", because if a = b is true then b = a is also true. If RT represents the converse of R, then R is symmetric if and only if R = RT.[2]
Symmetry, along with reflexivity and transitivity, are the three defining properties of an equivalence relation.[1]
Remove ads
Examples
In mathematics
- "is equal to" (equality) (whereas "is less than" is not symmetric)
- "is comparable to", for elements of a partially ordered set
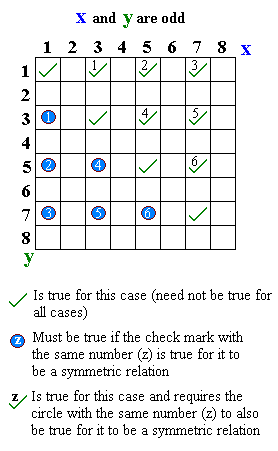
- "... and ... are odd":
Outside mathematics
- "is married to" (in most legal systems)
- "is a fully biological sibling of"
- "is a homophone of"
- "is a co-worker of"
- "is a teammate of"
Relationship to asymmetric and antisymmetric relations

By definition, a nonempty relation cannot be both symmetric and asymmetric (where if a is related to b, then b cannot be related to a (in the same way)). However, a relation can be neither symmetric nor asymmetric, which is the case for "is less than or equal to" and "preys on").
Symmetric and antisymmetric (where the only way a can be related to b and b be related to a is if a = b) are actually independent of each other, as these examples show.
| Symmetric | Not symmetric | |
| Antisymmetric | equality | divides, less than or equal to |
| Not antisymmetric | congruence in modular arithmetic | // (integer division), most nontrivial permutations |
| Symmetric | Not symmetric | |
| Antisymmetric | is the same person as, and is married | is the plural of |
| Not antisymmetric | is a full biological sibling of | preys on |
Remove ads
Properties
- A symmetric and transitive relation is always quasireflexive.[a]
- One way to count the symmetric relations on n elements, that in their binary matrix representation the upper right triangle determines the relation fully, and it can be arbitrary given, thus there are as many symmetric relations as n × n binary upper triangle matrices, 2n(n+1)/2.[3]
Note that S(n, k) refers to Stirling numbers of the second kind.
Notes
- If xRy, the yRx by symmetry, hence xRx by transitivity. The proof of xRy ⇒ yRy is similar.
References
See also
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads