Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Television channel frequencies
Tables of radio frequencies assigned to television channels From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
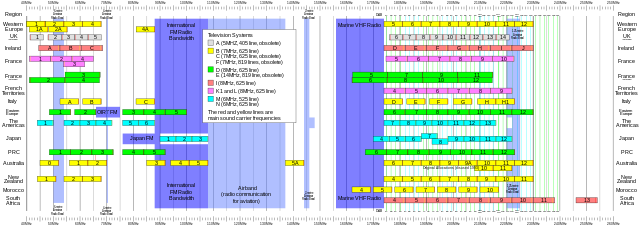
The following tables show the frequencies assigned to analog broadcast television channels in various regions of the world, along with the ITU letter designator for the transmission system used. The frequencies shown are for the channel limits and for the analog video and audio carriers. The channel itself usually occupies 6, 7 or 8 megahertz of bandwidth depending on the television transmission system in use. For example, North American channel 1 occupies the spectrum from 44 to 50 MHz. See Broadcast television systems for a table of signal characteristics, including bandwidth, by ITU letter designator. Analog television broadcasts have been phased out in most regions, having been replaced by digital television broadcasts.
Remove ads
International normalization for analog TV systems

International broadcasting television frequencies are divided in two part of the spectrum; the Very high frequency or "VHF" band and the Ultra high frequency or "UHF" band.
VHF
Summarize
Perspective
Americas (most countries), South Korea, Taiwan, Myanmar, and the Philippines
During World War II, the frequencies originally assigned as channels 13 to 18 were appropriated by the U.S. military, which still uses them to this day. It was also decided to move the allocation for FM radio from the 42-50 MHz band to a larger 88-106 MHz band (later extended to the current 88-108 MHz FM band). This required a reassignment of the VHF channels to the plan currently in use.[1]
Assignments since February 25, 1946
- System M 525 lines (most countries in the Americas and Caribbean, South Korea, Taiwan and the Philippines)
- System N 625 lines (used in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay)
- FM channel 200, 87.9 MHz, overlaps TV 6. This is used only by K200AA.
- TV 6 analog audio can be heard on FM 87.75 on most broadcast radio receivers as well as on a European TV tuned to channel E4A or channel IC, but at lower volume than wideband FM broadcast stations, because of the lower deviation.
- Channel 1 audio is the same as European Channel E2 audio and the video is the same as European Channel E2A. Channel 2 video is the same as European Channel E3 video.
Japan
- The frequency spacing for each channel is 6 MHz as the countries above, except between channels 7 and 8 (which overlap).
- Channels 1 through 3 are reallocated for the expansion of the FM band.
United Kingdom, Ireland, and Hong Kong
Ireland
- Channel A was never used terrestrially. The only System I Band I transmitter on Channel B was RTÉ One from the Maghera, Co. Clare transmitter during 1963–1999. Channel A was initially intended for use at Maghera but Channel B was used instead because of the risk of interference to (overspill) reception of BBC 405 line transmissions.[2] It was moved to Channel E due to interference from distant transmitters on channel E3 and Italian channel IA via certain atmospheric conditions and other reasons. Channel C was used by a relay transmitter in Glanmire, Co. Cork.
- Channel B video is the same as Italian Channel IA video and Channel C audio is the same as Channel E4 audio.
- There are currently no Band I Channels used in Ireland (except on cable TV, and these have mostly been phased out for DOCSIS use) and no plans to resume using them.
- Most Irish Cable TV systems do not follow the above channel plan as their analogue (video) carriers are usually at multiples of 8 MHz (i.e. 176, 184, 192 MHz etc. in Band III)
Western Europe; Greenland; and most countries in Asia, Africa, and Oceania
- Channels 1 and 1A were used for early experimental broadcasts and are no longer allocated.[3]
- Channels 15 and 16 are allocated for use in the African Broadcasting Area only.[4]
- Channel 2A was only ever used in Austria for the Sendeturm Jauerling to avoid interferences with neighboring Eastern European TV stations.
- Channel 3 in Belgium, RTBF 1 broadcast from the Liège transmitter with 100 kW until the switchover to DVB-T.
- Channel 12 was reserved by the military in some countries (like Germany (West Germany only)) so only relay transmitters operated on this frequency.
- Channel 4A audio carrier's frequency is very close to US Channel 6 audio carrier and overlaps the FM band in Europe.
France
- Channel 1 used an earlier 441-line system and was discontinued in 1956.
French overseas departments and territories and former French African colonies
Italy
- Channels A through H are indicated in many European TVs as Channels 13–20.
- Channels B, C, D, H, H1, and H2 are identical to Channels E4, E4A, E5, E10, E11, and E12, respectively.
- Channel A video carrier is the same as Channel E2 audio carrier and thus it used to be common that the audio from a distant TV station on channel E2 received via Sporadic E interferes with Channel A video and vice versa.
- Channel C audio carrier's frequency falls into the FM band in Europe, and is also identical to American A6 channel audio.
Eastern Europe, North Korea
East Germany (former DDR)
In its very early days DFF made some test transmissions using the D/K standard (6.5 MHz audio) before reverting (around 1957) to System B/G (5.5 MHz audio) but using some unique frequencies.[6]
- [7]
- From 1960 onwards (West) European standard channels were adopted.
Morocco
Australia
* Channels 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 5A were discontinued with the changeover to digital television.
** With the transition to digital television in 2001, Channels 10 and 11 (209.25 and 216.25 respectively)[8] were moved up by 1 MHz to allow a full 7 MHz separation for a new channel 9A, and Channel 12 was added. Some existing services were affected, notably AMV11 in the Upper Murray region of Victoria, and VTV-11 in Western Victoria.
New Zealand and Indonesia
- VHF analog TV ceased in New Zealand on 1 December 2013.
- Channels 10 and 11 weren't added until the late 1980s.
- VHF analog TV channel 1A is only used in Indonesia.
- VHF is currently no longer used for television in Indonesia (except in some regions until 2022) and only UHF is used for both analog and digital television, as in the UK.
Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, and South Africa
China
Vietnam
Remove ads
UHF
Summarize
Perspective
Americas (most countries), South Korea, Taiwan, Burma (Myanmar) and the Philippines
For frequencies used in the Americas (most countries), South Korea, Taiwan and the Philippines, refer to Pan-American television frequencies.
- Notes
- The frequencies used by UHF channels 70 through 83 were reallocated to the Land Mobile Radio System (Public Safety and Trunked Radio) and mobile phones in a CCIR worldwide convention in 1982, and thus were never used for digital TV but are highlighted in cyan and listed here for theoretical use.
- In certain metropolitan areas of the United States, Channels 14 through 20 have been allocated to Land Mobile Radio (LMR) use.[12]
- Channels 52 through 69 in the United States have been reallocated now that conversion to digital TV was completed on June 12, 2009. These channels are highlighted in yellow. Channels 70 through 83 in the United States and Canada were re-allocated to AMPS cellular phone use in 1983.
- On August 22, 2011, the United States' Federal Communications Commission announced a freeze on all future applications for broadcast stations requesting to use channel 51,[13] to prevent adjacent-channel interference to the A-Block of the 700 MHz band. Later that year (on December 16, 2011), Industry Canada and the CRTC followed suit in placing a moratorium on future television stations using Channel 51 for broadcast use, to prevent adjacent-channel interference to the A-Block of the 700 MHz band.[14]
- Not all countries listed use ATSC, which has a single VSB carrier wave. Other countries use COFDM modulation for DVB-T (Taiwan, Colombia, Panama) or ISDB-Tb (Philippines and Latin America), which has dozens of carriers within the channel. Burma (Myanmar) uses DVB-T2 on 8 MHz channel spacing on Western Europe / Asia DTV frequency along with Southeast Asian countries (except Philippines).[15]
- ISDB-Tb frequency DTV channel 14 uses 473.142857 MHz, but ATSC 3.0, DVB-T/DVB-T2, and DTMB, use 473.0 MHz.
- Channel 37 is reserved for radio astronomy in the United States, Canada, Bermuda, Belize, and the Bahamas, thus there are no television stations assigned to it. Mexico also informally observes a ban on transmitters using this channel.
- Due to the FCC repack in the United States, all TV stations that had been broadcasting from channels 38 to 51 were required to move on or below channel 36 by July 3, 2020. As a result, channels 38-51 are highlighted in magenta.[16] These frequencies would later be used by U.S. mobile carriers like T-Mobile on Band 71.[17]
Japan
Frequency spacing for each channel in Japan is the same as in the countries listed above, but the channel numbers are 1 lower than in those countries; for example, channel 13 in Japan is on the same frequency as channel 14 in North and South America (most countries), South Korea, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
Channels 13-62 are used for analog and digital TV broadcasting.
United Kingdom, Ireland, Hong Kong, Macau, Falkland Islands and Southern Africa
- Channels 21 to 60 used for DVB-T Digital TV broadcasting in the UK, with the exception of Channel 38, which is used for programme making and special events. Channels 61 to 69 used for 4G LTE.
- Channel 69 was not used for TV broadcasting in the UK, it was used by the MOD and until 2012 for programme making and special events.
- PAL I was withdrawn from broadcasting use in the UK during 2012 and 2013.
Western Europe, Greenland, most countries in Asia and Africa, and most of Oceania
France, Eastern Europe, Former Soviet Union, French overseas territories and former French colonies in Africa, North Korea, Vietnam
- Some cable television providers in Vietnam may use System G.[19]
DVB-T/DVB-T2/DTMB/ISDB-T Digital television frequencies (Western Europe, Eastern Europe most countries Asia, Africa and Oceania)
Australia
Channels 52–69 had been progressively phased out since the introduction of digital television and rationalisation of the spectrum
Mainland China
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads