Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Timeline of ancient history
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This timeline of ancient history lists historical events of the documented ancient past from the beginning of recorded history until the Early Middle Ages. Prior to this time period, prehistory civilizations were pre-literate and did not have written language.
(Common Era years in astronomical year numbering) |
 |
Millennia: 4th millennium BC – 3rd millennium BC – 2nd millennium BC – 1st millennium BC – 1st millennium
Centuries: 34th BC – 33rd BC – 32nd BC – 31st BC – 30th BC – 29th BC – 28th BC – 27th BC – 26th BC – 25th BC – 24th BC – 23rd BC – 22nd BC – 21st BC – 20th BC – 19th BC – 18th BC – 17th BC – 16th BC – 15th BC – 14th BC – 13th BC – 12th BC – 11th BC – 10th BC – 9th BC – 8th BC – 7th BC – 6th BC – 5th BC – 4th BC – 3rd BC – 2nd BC – 1st BC – 1st AD – 2nd AD – 3rd AD – 4th AD — 5th AD
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2022) |
Remove ads
Early history
- Late 4th millennium BC: Sumerian cuneiform writing system[1][2] and Egyptian hieroglyphs are first used.[3]
- 3200 BC: Cycladic culture in Greece.
- 3200 BC: Caral–Supe civilization begins in Peru.
- 3200 BC: Rise of Proto-Elamite Civilization in Iran.
- 3180 BC: Skara Brae is built in Scotland.[4]
- 3100 BC: First Dynasty of Egypt.[5]
- c. 3000 BC: Stonehenge construction begins. In its first version, it consisted of a circular ditch and bank, with 56 wooden posts.[6]
- c. 3000 BC: Cucuteni–Trypillia culture is established in Romania and Ukraine.
- 3000 BC: Jiroft culture begins in Iran.
- 3000 BC: First known use of papyrus by Egyptians.[7]
- 3000 – 2500 BC: Earliest evidence of autochthonous iron production in West Africa.[8]
- 3000 – 2300 BC: The Pastoral Neolithic culture builds East Africa's earliest and largest monumental cemetery at Lothagam North Pillar Site.[9]
- 3000 BC: Domestication of the horse in the Yamnaya culture.
- 2800 BC: Kot Diji phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins.
- 2800 BC: Longshan culture begins in China.
- 2700 BC: Minoan civilization ancient palace city Knossos reaches 80,000 inhabitants.
- 2700 BC: Rise of Elam in Iran.
- 2700 BC: The Old Kingdom begins in Egypt.
- 2600 BC: Oldest known surviving literature: Sumerian texts from Abu Salabikh, including the Instructions of Shuruppak and the Kesh temple hymn.[10][11][12][13]
- 2600 BC: Mature Harappan phase of the Indus Valley civilization (in present-day Pakistan and India) begins.
- 2600 BC: Emergence of Mayan culture in the Yucatán Peninsula.[14]
- 2560 BC: King Khufu completes the Great Pyramid of Giza. The Land of Punt in the Horn of Africa first appears in Egyptian records around this time.
- 2500 – 1500 BC: Kerma culture begins in Nubia.
- Late 24th century BC: Akkadian Empire is founded, dating depends upon whether the Middle chronology or the Short chronology is used.[15]
- 2291 BC: Pharaoh Teti is thought to be the earliest known victim of assassination.[16]
- 2250 BC: Oldest known depiction of the Staff God, the oldest image of a god to be found in the Americas.
- 2200 – 2100 BC: 4.2-kiloyear event: a severe aridification phase, likely connected to a Bond event, which was registered throughout most of North Africa, Middle East and continental North America. Related droughts very likely caused the collapse of the Old Kingdom in Egypt and the Akkadian Empire in Mesopotamia.
- 2200 BC: Completion of Stonehenge.
- 2115 BC: Traditional date for the legendary foundation of Armenia by Hayk.[17][18]
- 2055 BC: The Middle Kingdom begins in Egypt.[19]
- 2000 BC: The last mammoth population, on Wrangel Island in Siberia, goes extinct.
- 1900 BC: Erlitou culture begins in China.
- c. 1850 BC: Alphabetic writing emerges.[20]
- 1800 BC: The Old Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh constitutes the earliest complete version of that narrative.[21][22]
- 1780 BC: Oldest Record of Code of Hammurabi.
- c. 1750 BC: Mycenaean civilization begins in mainland Greece.[23]
- 1700 – 1400 BC: The Proto-Sinaitic script is the oldest alphabet created in Egypt.
- 1700 BC: Indus Valley Civilization comes to an end but is continued by the Cemetery H culture; The beginning of Poverty Point culture in North America.
- 1600 BC: Minoan eruption destroys Akrotiri and causes damage to some Minoan sites in eastern Crete.[24][25][26]
- 1600 BC: The beginning of Shang dynasty in China;[27] evidence of a fully developed writing system, see Oracle bone script.
- c. 1550 BC: The New Kingdom begins in Egypt.[28]
- 1500 – 400 BC: Olmec civilization flourishes in Pre-Columbian Mexico, during Mesoamerica's Formative period.[29]
- 1500 BC: Composition of the Rigveda is completed.[30][31][32]
- c. 1500 BC: Nok culture begins in West Africa.[33]
- c. 1400 BC: Oldest known song with notation.
- c. 1209 BC: The Merneptah Stele is the first non-biblical reference to the Israelites.
- 1200 – 1150 BC: Late Bronze Age collapse occurs in Southwestern Asia and in the Eastern Mediterranean region.[34] This period is also the setting of the Iliad and the Odyssey epic poems (which were composed about four centuries later).
- 1200 BC: The Hallstatt culture begins.[35]
- c. 1180 BC: Disintegration of Hittite Empire.[36]
- 1100 BC: Use of Iron spreads.
- c. 1050 BC: The Phoenician alphabet is created.[37]
- c. 1046 BC: The Zhou force, led by King Wu of Zhou, overthrows the last king of Shang dynasty; Zhou dynasty established in China.[38][39]
- 1000 BC: The second stream of Bantu expansion reaches the great lakes region of Africa, creating a major population centre.[40][41]
- 890 BC: Approximate date for the composition of the Iliad and the Odyssey.
- 814 BC: Foundation of Carthage by the Phoenicians in Tunisia.[42][43]
- 808 BC: Formation of the Kingdom of Macedonia by King Karanos [44]
- 800 BC: Rise of Greek city-states.
- 788 BC: Iron Age begins in Sungai Batu (Old Kedah).
- c. 785 BC: Rise of the Kingdom of Kush.[45]
Remove ads
Classical antiquity
Summarize
Perspective
Classical antiquity is a term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea. It primarily refers to the timeframe of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome.[46] In the context of this list its use encompasses various other civilizations including, but not limited to, those of the Ancient Near East.
- 776 BC: First recorded Ancient Olympic Games.[47]
- 771 BC: Spring and Autumn period begins in China; Zhou dynasty's power is diminishing; the era of the Hundred Schools of Thought.
- 753 BC: Founding of Rome (traditional date).
- 745 BC: Tiglath-Pileser III becomes the new king of Assyria. With time he conquers neighboring countries and turns Assyria into an empire.
- c. 732 BC: Assyrian captivity begins, creating the Ten Lost Tribes.
- 728 BC: Rise of the Median Empire.
- 700 BC: The construction of Marib Dam in Arabia Felix, in modern Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
- 653 BC: Rise of Achaemenid dynasty.
- 650 – 550 BC: The Urewe culture dominates the African Great Lakes region. It was one of Africa's oldest iron smelting centres.[48][49]
- 621 BC: Draco replaces oral law with written law in Classical Athens, considered one of the earliest developments of the Athenian democracy.
- 612 BC: An alliance between the Babylonians, Medes, and Scythians succeeds in destroying Nineveh and causing subsequent fall of the Assyrian empire.
- 600 BC: Sixteen Mahajanapadas ("Great Realms" or "Great Kingdoms") emerge in India.
- 600 BC: Evidence of writing system appears in Oaxaca used by the Zapotec civilization.
- c. 600 BC: Rise of the Sao civilisation near Lake Chad.
- c. 600 BC: Early Cholas mentioned in Sangam literature.[50]
- 594 BC: Solon appointed Archon of Classical Athens and begins issuing citizenship and judicial reforms, giving Athenian citizens the right to participate in government.
- 563 BC: Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), founder of Buddhism is born as a prince of the Shakya clan, which ruled parts of Magadha, one of the Mahajanapadas.
- 551 BC: Confucius, founder of Confucianism, is born.
- 550 BC: Foundation of the Achaemenid Empire by Cyrus the Great.
- 549 BC: Mahavira, founder of Jainism, is born.
- 546 BC: Cyrus the Great overthrows Croesus, King of Lydia.
- 544 BC: Rise of Magadha as the dominant power under Bimbisara.
- 539 BC: The fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire and liberation of the Jews by Cyrus the Great.
- 530 BC: Death of Cyrus the Great.[51]
- 525 BC: Cambyses II of Persia conquers Ancient Egypt.
- c. 512 BC: Darius I (Darius the Great) of Persia, subjugates eastern Thrace, Macedonia submits voluntarily, and annexes the Libyan Kingdom, Persian Empire at largest extent.
- 509 BC: Expulsion of Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, founding of Roman Republic (traditional date).
- 508 BC: Athenian democracy instituted at the Republic of Athens.
- 500 BC: Pāṇini standardizes the grammar and morphology of Sanskrit in the text Aṣṭādhyāyī. Panini's standardized Sanskrit is known as Classical Sanskrit.
- 499 BC: King Aristagoras of Miletus incites all of Hellenic Asia Minor to rebel against the Persian Empire, beginning the Greco-Persian Wars.
- 490 BC: Greek city-states defeat Persian invasion at Battle of Marathon.
- 483 BC: Death of Gautama Buddha.
- 480 BC: Persian invasion of Greece by Xerxes I; Battles of Thermopylae and Salamis.
- 479 BC: Death of Confucius.
- 475 BC: Warring States period begins in China as the Zhou king became a mere figurehead; China is annexed by regional warlords.
- 470~469 BC: Birth of Socrates.
- 465 BC: Murder of Xerxes I.
- 460 BC: Birth of Democritus.
- 458 BC: Oresteia by Aeschylus, the only surviving trilogy of ancient Greek plays, is performed.
- 449 BC: The Greco-Persian Wars end.
- 447 BC: Building of the Parthenon at Athens started.
- 432 BC: Construction of the Parthenon is completed.
- 431 BC: Beginning of the Peloponnesian War between the Greek city-states.
- 429 BC: Sophocles's play Oedipus Rex is first performed.
- 427 BC: Birth of Plato.
- 424 BC: Nanda dynasty comes to power in Magadha.
- 404 BC: End of the Peloponnesian War.
- 400 BC: Zapotec culture flourishes around city of Monte Albán.
- 400 BC: Pandya dynasty is founded in South India.
- c. 400 BC: Rise of the Garamantes as an irrigation-based desert state in the Fezzan region of Libya.
- 399 BC: Trial of Socrates.
- 384 BC: Birth of Aristotle.
- 370 BC: Death of Democritus.
- 331 BC: Alexander the Great defeats Darius III of Persia in the Battle of Gaugamela, completing his conquest of Persia.
- 326 BC: Alexander the Great defeats Indian king Porus in the Battle of the Hydaspes River.
- 323 BC: Death of Alexander the Great at Babylon.
- 322 BC: Death of Aristotle.
- 321 BC: Chandragupta Maurya overthrows the Nanda dynasty of Magadha.
- 321 BC: Establishment of the Seleucid Empire by Seleucus I Nicator. The empire existed until 63 BC.
- 305 BC: Chandragupta Maurya seizes the satrapies of Paropamisadae (Kabul), Aria (Herat), Arachosia (Qanadahar) and Gedrosia (Baluchistan) from Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of Babylonia, in return for 500 elephants.
- c. 300 BC: Completion of Euclid's Elements.
- c. 300 BC: Pingala uses zero and binary numeral system.
- 300 BC: Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், Canka ilakkiyam) period in the history of ancient southern India (known as the Tamilakam)
- 300 BC: Construction of the Great Pyramid of Cholula, the world's largest pyramid by volume (the Great Pyramid of Giza built 2560 BC Egypt stands 146.5 meters, making it 91.5 meters taller), begins in Cholula, Puebla, Mexico.
- 273 BC: Ashoka becomes the emperor of the Maurya Empire.
- 261 BC: Kalinga War.
- 257 BC: An Dương Vương takes over Việt Nam (then Kingdom of Âu Lạc).
- 255 BC: Ashoka sends a Buddhist missionary led by his son Mahinda to Sri Lanka (then Lanka).
- 250 BC: Rise of Parthia (Ashkâniân), the second native dynasty of ancient Persia.
- 232 BC: Death of Emperor Ashoka; Decline of the Mauryan Empire.
- 230 BC: Emergence of Satavahana in South India.
- 221 BC: Qin Shi Huang unifies China, end of Warring States period; marking the beginning of Imperial rule in China which lasts until 1912. Construction of the Great Wall of China by the Qin dynasty begins.
- 216 BC: Battle of Cannae – Rome defeated in major battle in the second Punic War.
- 207 BC: Nanyue Kingdom extends from Guangzhou to North Việt Nam .
- 206 BC: Han dynasty established in China, after the death of Qin Shi Huang; China in this period officially becomes a Confucian state and opens trading connections with the West, i.e. the Silk Road.
- 202 BC: Scipio Africanus defeats Hannibal at Battle of Zama.
- 200 BC: El Mirador, largest early Maya city, flourishes.
- 200 BC: Paper is invented in the Han dynasty.
- c. 200 BC: Chera dynasty in South India.
- 185 BC: Shunga Empire founded.
- 167 – 160 BC: Maccabean Revolt.
- 149 – 146 BC: Third Punic War between Rome and Carthage. War ends with the complete destruction of Carthage, allowing Rome to conquer modern day Tunisia and Libya.
- 146 BC: Roman conquest of Greece, see Greece in the Roman era.
- c. 145 BC: Eucratides I dies; Greco-Bactrian Kingdom collapses. Remnants move southwards to form the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
- 121 BC: Roman armies enter Gaul for the first time.
- 111 BC: First Chinese domination of Vietnam in the form of the Nanyue Kingdom.
- c. 100 BC: Chola dynasty rises in prominence.
- 100 BC – 100 AD: Bantu-speaking communities in the African Great Lakes regions develop iron forging techniques that enable them to produce carbon steel.[52]
- 100 BC – 300 AD: The earliest Bantu settlements in the Swahili coast appear on the archaeological record in Kwale County in Kenya, Misasa in Tanzania and Ras Hafun in Somalia.[53]
- c. 82 BC: Burebista becomes the king of Dacia.
- 71 BC: Death of Spartacus. End of the Third Servile War, a major slave uprising against the Roman Republic.
- c. 63 BC: The Siege of Jerusalem leads to the conquest of Judea by the Romans.
- c. 60 – 44 BC: Burebista conquers territories from south Germany to Thrace, reaching the coast of the Aegean Sea.
- 49 BC: Roman Civil War between Julius Caesar and Pompey.
- 44 BC: Julius Caesar murdered by Marcus Junius Brutus and others.
- 44 BC: Burebista is assassinated in the same year like Julius Caesar and his empire breaks into 4 and later 5 kingdoms in modern-day Romania.
- 31 - 30 BC: Battle of Actium. The Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt.
- 30 BC: Cleopatra ends her reign as the last active ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt.
- 27 BC: End of the Roman Republic and formation of the Roman Empire: Augustus is given titles of Princeps and Augustus by Roman Senate – beginning of Pax Romana. Formation of influential Praetorian Guard to provide security to Emperor.
- 27 – 22 BC: Amanirenas, the kandake (Queen) of the Kingdom of Kush, leads Kushite armies against the Romans.[54][55][56]
- 18 BC: Three Kingdoms period begins in Korea. Herod's Temple is reconstructed.
- 6 BC: Earliest theorized date for birth of Jesus of Nazareth. Roman succession: Gaius Caesar and Lucius Caesar groomed for the throne.
- 4 BC: Widely accepted date (Ussher) for birth of Jesus.
- c. 1 – 50 AD: The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, a Graeco-Roman manuscript is written. It describes an established Indian Ocean Trade route.[57]
- 9 AD: Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, the Imperial Roman army's bloodiest defeat.
- 14 AD: Death of Roman Emperor Augustus Caesar (Octavian), ascension of his adopted son Tiberius to the throne.
- 30 – 33 AD: Crucifixion of Jesus, exact date unknown.[58][59][60][61]
- 37 AD: Death of Emperor Tiberius, ascension of his nephew Caligula to the throne.
- 40 AD: Rome conquers Mauretania.
- 41 AD: Emperor Caligula is assassinated by the Roman senate. His uncle Claudius succeeds him.
- 43 AD: The Roman Empire enters Great Britain for the first time.
- 54 AD: Emperor Claudius dies and is succeeded by his grand nephew Nero.
- 68 AD: Emperor Nero commits suicide, prompting the Year of the Four Emperors in Rome.
- 70 AD: Destruction of Jerusalem by the armies of Titus.
- 79 AD: Destruction of Pompeii by the volcano Vesuvius.
- 98 AD: After a two-year rule, Emperor Nerva dies of natural causes, his adopted son Trajan succeeds him.
- 100 – 940: Kingdom of Aksum forms in the Horn of Africa.
- 106 – 117: Roman Empire at largest extent under Trajan after having conquered modern-day Romania, Iraq and Armenia.
- 117: Trajan dies of natural causes. His adopted son Hadrian succeeds him. Hadrian pulls out of Iraq and Armenia.
- 122: Construction of Hadrian's Wall begins.
- 126: Hadrian completes the Roman Pantheon.
- 138: Hadrian dies of natural causes. His adopted son Antoninus Pius succeeds him.
- 161: Death of Antoninus Pius. His rule was the only one in which Rome did not fight in a war.
- 161: Marcus Aurelius becomes emperor of the Roman Empire.
- 180: Reign of Marcus Aurelius officially ends. End of the Pax Romana.
- 180 – 181: Commodus becomes Roman Emperor.
- 192: Kingdom of Champa in Tay Nguyen.
- 200s: The Buddhist Srivijaya Empire established in Maritime Southeast Asia.
- 220: Three Kingdoms period begins in China after the fall of Han dynasty.
- 226: Fall of the Parthian Empire and Rise of the Sasanian Empire.
- 244 - 260: Defeat of Gordian III (238–244), Philip the Arab (244–249), and Emperor Valerian (253–260), by Shapur I of Persia (Valerian was captured by the Persians).
- 266: Emperor Wu of Jin established the First Jin dynasty providing a temporary unity of China after the devastating Three Kingdoms period.
- 284: Diocletian becomes emperor of Rome and splits the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western Roman Empires.
- 285: Diocletian begins a large-scale persecution of Christians.
- 292: The capital of the Roman empire is officially moved from Rome to Mediolanum (modern day Milan).
- 300 – 1000: Growth of Azanian and Zanj settlements in the Swahili coast. Local industry and international trade flourish.[53]
- 301: Diocletian's Edict on Maximum Prices.
- 301: Armenia first to adopt Christianity as state religion.
- 313: Edict of Milan declared that the Roman Empire would tolerate all forms of religious worship.
- 316: Emperor Min of Jin executed, with northern China then controlled by various kingdoms founded by non-Han people. The Jin dynasty continues to rule the south.
- 325: Constantine the Great organizes the First Council of Nicaea.
- 330: Constantinople is officially named and becomes the capital of the eastern Roman Empire.
- 335: Samudragupta becomes the emperor of the Gupta Empire.
- 337: Emperor Constantine the Great dies, leaving his sons Constantius II, Constans, and Emperor Constantine II as the emperors of the Roman empire.
- 350: Constantius II is left sole emperor with the death of his two brothers.
- 354: Birth of Augustine of Hippo.[62]
- 361: Constantius II dies, his cousin Emperor Julian succeeds him.
- 378: Battle of Adrianople, Roman army is defeated by the Germanic tribes.
- 380: Roman Emperor Theodosius I declares the Arian faith of Christianity heretical.
- 395: Theodosius I outlaws all religions other than Catholic Christianity.
- 406: Romans are expelled from Britain.
- 407 – 409: Visigoths and other Germanic tribes cross into Roman-Gaul for the first time.
- 410: Visigoths sack Rome in 410 for the first time since 390 BC.
- 415: Germanic tribes enter Spain.
- 420: The general Liu Yu usurps the Jin in southern China, beginning the Liu Song dynasty.
- 429: Vandals enter North Africa from Spain for the first time.
- 439: Vandals have conquered the land stretching from Morocco to Tunisia by this time.
- 439: The Northern Wei dynasty unites northern China, beginning the Northern and Southern dynasties period.
- 455: Vandals sack Rome, capture Sicily and Sardinia.
- c. 455: Skandagupta repels a Huna people attack on India.
- 476: Romulus Augustulus, last Western Roman Emperor is forced to abdicate by Odoacer, a chieftain of the Germanic Heruli; Odoacer returns the imperial regalia to Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno in Constantinople in return for the title of dux of Italy; most frequently cited date for the end of ancient history.
Remove ads
End of ancient history in Europe
The date used as the end of the ancient era is arbitrary. The transition period from Classical Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages is known as Late Antiquity. Late Antiquity is a periodization used by historians to describe the transitional centuries from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages, in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world: generally from the end of the Roman Empire's Crisis of the Third Century (c. ACE 284) to the Islamic conquests and the re-organization of the Byzantine Empire under Heraclius. The Early Middle Ages are a period in the history of Europe following the fall of the Western Roman Empire spanning roughly five centuries from CE 500 to 1000. Not all historians agree on the ending dates of ancient history, which frequently falls somewhere in the 5th, 6th, or 7th century. Western scholars usually date the end of ancient history with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in CE 476, the death of the emperor Justinian I in CE 565, or the coming of Islam in CE 632 as the end of classical antiquity.
Horizontal timeline

- Dates are approximate, consult particular article for details
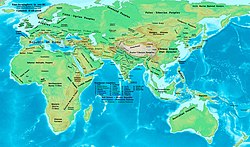
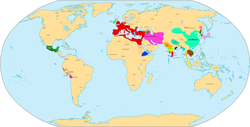
Maps
- Eastern Hemisphere in 500 BC.
- Eastern Hemisphere in 323 BC.
- Eastern Hemisphere in 200 BC.
- Eastern Hemisphere in 100 BC.
- World in CE 1.
- World in CE 100.
- Eastern Hemisphere in CE 200.
- World in CE 300.
- Eastern Hemisphere in CE 486.
See also
References
Citations and notes
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads