Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Timeline of European imperialism
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This Timeline of European imperialism covers episodes of imperialism outside of Europe by western nations since 1400; for other countries, see Imperialism § Imperialism by country.
Pre-1700

- 1402 Castillian invasion of Canary Islands.
- 1415 Portuguese conquest of Ceuta.
- 1420-1425 Portuguese settlement of Madeira.
- 1433-1436 Portuguese settlement of Azores.
- 1445 Portuguese construction of trading post on Arguin Island.
- 1450 Portuguese construction of trading post on Gorée Island.
- 1462 Portuguese settlement of Cape Verde islands.
- 1470 Portuguese settlement of Bioko island.
- 1474 Portuguese settlement of Annobón island.
- 1482 Portuguese construction of Elmina Castle.
- 1492 – first cross-Atlantic trip of Columbus for Spain.
- 1493 Portuguese settlement of São Tomé and Príncipe.
- 1510 Portuguese conquest of Goa.
- 1511 Portuguese conquest of Malacca City.
- 1517 Portuguese conquest of Colombo.
- 1519-21 Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire.
- 1532-36 Spanish conquest of the Inca empire.
- 1556 Portuguese colonization of Timor.
- 1557 Portuguese construction of trading post in Macau.
- 1556-1599 Spanish conquest of Philippines.
- 1598: Dutch established colony on uninhabited island of Mauritius; they abandon it in 1710.[1]
- 1608: Dutch opened their first trading post in India at Golconda.[2]
- 1613: Dutch East India Company expands operations in Java.[3]
- 1613–20: Netherlands becomes England's major rival in trade, fishing, and whaling. The Dutch form alliances with Sweden and the Hanseatic League; England counters with an alliance with Denmark.[4]
- 1623. The Amboyna massacre occurs in Japan with execution of English traders; England closes its commercial base opened in 1613 at Hirado. Trade ends for more than two centuries.
- 1664. French East India Company Chartered for trade in Asia and Africa.[5]
Colonization of North America

- 1565 – St. Augustine, Florida – Spanish[6][7]
- 1604 – Acadia – French[8]
- 1605 – Port-Royal – French; in Nova Scotia
- 1607 – Jamestown, Virginia – English; established by Virginia Company
- 1607 – Popham Colony – English; failed effort in Maine
- 1608 – Quebec, Canada – French
- 1610 – Cuper's Cove, First English settlement in Newfoundland; abandoned by 1820
- 1610 – Santa Fe, New Mexico – Spanish[9]
- 1612 – Bermuda – English; established by Virginia Company[10][11]
- 1615 – Fort Nassau – Dutch; became Albany New York
- 1620 – St. John's, Newfoundland – English; capital of Newfoundland
- 1620 – Plymouth Colony, absorbed by Massachusetts Bay– English; small settlement by Pilgrims
- 1621 – Nova Scotia – Scottish
- 1623 – Portsmouth, New Hampshire – English; becomes the Colony of New Hampshire
- 1625 – New Amsterdam – Dutch; becomes New York City
- 1630 – Massachusetts Bay Colony – English; The main Puritan colony.[12]
- 1632 – Williamsburgh – English; becomes the capital of Virginia.[13]
- 1633 – Fort Hoop – Dutch settlement; Now part of Hartford Connecticut
- 1633 – Windsor, Connecticut – English
- 1634 – Maryland Colony – English Catholic colony

- 1634 – Wethersfield, Connecticut – First English settlement in Connecticut, comprising migrants from Massachusetts Bay.[14]
- 1635 – Territory of Sagadahock – English
- 1636 – Providence Plantations – English; became Rhode Island* [15]
- 1636 – Connecticut Colony – English
- 1638 – New Haven Colony – English; later merged into Connecticut colony
- 1638 – Fort Christina – Swedish; now part of Wilmington Delaware
- 1638 – Hampton, New Hampshire – English[16]
- 1639 – San Marcos – Spanish
- 1640 – Swedesboro- Swedish
- 1651 – Fort Casimir – Dutch
- 1660 – Bergen – Dutch
- 1670 – Charleston, South Carolina – English[17]
- 1682 – Pennsylvania – English Quakers;[18]
- 1683? – Fort Saint Louis (Illinois)- French;[19]
- 1683 – East New Jersey – Scottish
- 1684 – Stuarts Town, Carolina – Scottish
- 1685 – Fort Saint Louis (Texas)- French
- 1698 – Pensacola, Florida – Spanish (colonized by Tomas Romero II)
- 1699 – Louisiana (New France) – French;[20]
Remove ads
1700 to 1799
- 1704: Gibraltar captured by British on 4 August; becomes British naval bastion into the 21st century[21]
- 1713: Treaty of Utrecht, ends War of the Spanish Succession and gives Britain territorial gains, especially Gibraltar, Acadia, Newfoundland, and the land surrounding Hudson Bay. The lower Great Lakes-Ohio area became a free trade zone.[22]
- 1756–1763 Seven Years' War, Britain, Prussia, and Hanover against France, Austria, the Russian Empire, Sweden, and Saxony. Major battles in Europe and North America; the East India Company also in involved in the Third Carnatic War (1756–1763) in India. Britain victorious and takes control of all of Canada; France seeks revenge.[23][24]
- 1775–1783: American Revolutionary War as Thirteen Colonies revolt; Britain has no major allies. It is the first successful colonial revolt in European history.[25]
- 1783: Treaty of Paris ends Revolutionary War; British give generous terms to US with boundaries as British North America on north, Mississippi River on west, Florida on south. Britain gives East and West Florida to Spain[26]
- 1784: Britain allows trade with America but forbid some American food exports to West Indies; British exports to America reach £3.7 million, imports only £750,000
- 1784: Pitt's India Act re-organised the British East India Company to minimise corruption; it centralised British rule by increasing the power of the Governor-General
Remove ads
1793 to 1870
- 1792: In India, British victory over Tipu Sultan in Third Anglo-Mysore War; cession of one half of Mysore to the British and their allies.[27]
- 1793–1815: Wars of the French Revolution, and Napoleonic wars; French conquests spread Ideas of the French Revolution, including abolition of serfdom, modern legal systems, and of Holy Roman Empire; stimulate rise of nationalism
- 1804–1865: Russia expand across Siberia to Pacific.[28]
- 1804–1813: Uprising in Serbia against the ruling Ottoman Empire
- 1807: Britain makes the international slave trade criminal; Slave Trade Act 1807; United States criminalizes the international slave trade at the same time.
- 1810–1820s: Spanish American wars of independence[29]
- 1810–1821: Mexican War of Independence[30]
- 1814–15: Congress of Vienna; Reverses French conquests; restores reactionaries to power. However, many liberal reforms persist; Russia emerges as a powerful factor in European affairs.[31]
- 1815–1817: Serbian uprising leading to Serbian autonomy
- 1819: Stamford Raffles founds Singapore as outpost of British Empire.[32]
- 1821–1823: Greek War of Independence
- 1822: Independence of Brazil proclaimed by Dom Pedro I[33]
- 1822–27: George Canning in charge of British foreign policy, avoids co-operation with European powers.[34]
- 1823: United States issues Monroe Doctrine to preserve newly independent Latin American states; issued in cooperation with Britain, whose goal is to prevent French & Spanish influence and allow British merchants access to the opening markets. American goal is to prevent the New World becoming a battlefield among European powers.[35]
- 1821–32: Greece wins Greek War of Independence against the Ottoman Empire; the 1832 Treaty of Constantinople is ratified at the London Conference of 1832.
- 1830: Start of the French conquest of Algeria[36]
- 1833: Slavery Abolition Act 1833 frees slaves in British Empire; the owners (who mostly reside in Britain) are paid £20 million.
- 1839–42: Britain wages First Opium War against China
- 1842: Britain forces China to sign the Treaty of Nanking. It opens trade, cedes territory (especially Hong Kong), fixes Chinese tariffs at a low rate, grants extraterritorial rights to foreigners, and provides both a most favoured nation clause, as well as diplomatic representation.[37]
- 1845: Oregon boundary dispute threatens war between Great Britain and the United States.[38]
- 1846: Oregon Treaty ends dispute with the United States. Border settled on the 49th parallel. The British territory becomes British Columbia and later joins Canada. The American territory becomes Oregon Territory and will later become the states of Oregon, Washington, and Idaho, as well as parts of Wyoming and Montana.[39][40]
- 1846: The Corn Laws are repealed; free trade in grain strengthens the British economy By increasing trade with exporting nations.[41]
- 1845: Republic of Texas voluntarily joins the United States. Annexation causes the Mexican–American War, 1846–48.
- 1848: United States victorious in Mexican–American War; annexes area from New Mexico to California
- 1848–49: Second Sikh war; the British East India Company subjugates the Sikh Empire, and annexes Punjab
- 1857: Indian Rebellion suppressed. It has major long-term impact on reluctance to grant independence to Indians.[42]
- 1858: The government of India transferred from East India Company to the crown; the government appoints a viceroy. He rules portions of India directly, and dominates local princes in the other portions. British rule guarantees that local wars will not happen inside India.[43][44]
- 1861–1867: French intervention in Mexico; United States demands French withdrawal after 1865; France removes its army, and its puppet Emperor is executed.
- 1862: Treaty of Saigon; France occupies three provinces in southern Vietnam.[45]
- 1863: France establishes a protectorate over Cambodia.
- 1867: British North America Act, 1867 creates the Dominion of Canada, a federation with internal self-government; foreign and defence matters are still handled by London.[46]
Remove ads
1870–1914
- 1874: Second Treaty of Saigon, France controls all of South Vietnam
- 1875–1900: Britain, France, Germany, Portugal and Italy join in the Scramble for Africa[47]
- 1876: Korea signs unequal treaty with Japan
- 1878: Austria occupies Bosnia-Herzegovina while Ottoman Empire is at war with Russia
- 1878: Ottoman Empire wins main possessions in Europe; Treaty of Berlin recognising the independence of Romania, Serbia and Montenegro and the autonomy of Bulgaria
- 1882: Korea signs equal treaties with the United States and others
- 1884: France makes Vietnam a country.
- 1885: King Leopold of Belgium establishes the Congo Free State, under his personal control. There is a role for the government of Belgium until the King's financial difficulties lead to a series of loans; it takes over in 1908.[48]

- 1893: France makes Laos a protectorate.[49]
- 1893: Overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom
- 1895: Creation of French West Africa (AOF)
- 1896–1910: Japan takes full control of Korea.[50]
- 1900: Fashoda Incident in Africa threatens war between France and Britain; Settled peacefully
- 1898: United States demands that Spain immediately reform its rule in Cuba; Spain procrastinates; US wins short Spanish–American War
- 1898: Annexation of the Republic of Hawaii as a United States territory via the Newlands Resolution[51]
- 1898: In the Treaty of Paris, the United States obtains the Philippines, Guam, Puerto Rico, and makes Cuba a protectorate.[52]
- 1899–1900: Anti-imperialist sentiment in the United States mobilizes but fails to stop the expansion.[53]
- 1900-08: King Leopold is denounced worldwide for his maltreatment of rubber workers in Congo. The campaign is led by journalist E.D. Morel.[54]
- 1908: Austria annexes Bosnia and Herzegovina; pays compensation and colonial issues. The chief pressure group was the Parti colonial, a coalition of 50 organizations with a combined total of 5,000 members.[55]
Remove ads
1914–1936
- 1917: Jones Act gives full American citizenship to Puerto Ricans.[56]
- 1918: Austrian Empire ends, Austria becomes a republic, Hungary remains a kingdom, Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Yugoslavia become independent
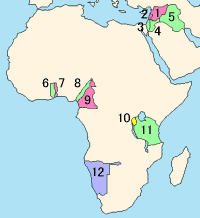
1. Syria, 2. Lebanon, 3. Palestine, 4. Transjordan, 5. Mesopotamia, 6. British Togoland, 7. French Togoland, 8. British Cameroons, 9. French Cameroun, 10. Ruanda-Urundi, 11. Tanganyika and 12. South West Africa
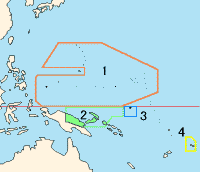
- 1919: German and Ottoman colonies came under the control of the League of Nations, which distributed them as "mandates" to Great Britain, France, Japan, Belgium, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand.[57]
- 1936: Italy in a few months (between spring 1935 and summer 1936) conquers one of two remaining independent territories in Africa: Ethiopia, merging it with Somalia, Eritrea, and Aussa to create Italian East Africa. Liberia becomes the sole unconquered nation in Africa.
Remove ads
Maps

See also
Notes
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads