Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Timeline of the development of tectonophysics (after 1952)
Chronological listing of significant events in the history of tectonophysics From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The evolution of tectonophysics is closely linked to the history of the continental drift and plate tectonics hypotheses. The continental drift/ Airy-Heiskanen isostasy hypothesis had many flaws and scarce data. The fixist/ Pratt-Hayford isostasy, the contracting Earth and the expanding Earth concepts had many flaws as well.
The idea of continents with a permanent location, the geosyncline theory, the Pratt-Hayford isostasy, the extrapolation of the age of the Earth by Lord Kelvin as a black body cooling down, the contracting Earth, the Earth as a solid and crystalline body, is one school of thought. A lithosphere creeping over the asthenosphere is a logical consequence of an Earth with internal heat by radioactivity decay, the Airy-Heiskanen isostasy, thrust faults and Niskanen's mantle viscosity determinations.
Remove ads
Making sense of the puzzle pieces


- 1953, the Great Global Rift, running along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, was discovered by Bruce Heezen (Lamont Group) (Puzzle pieces: Seismic-refraction and Sonar survey of the rifts). (Ewing & Ewing 1959), (Heezen 1960), (Heezen & Tharp 1961), (Heezen & Tharp 1964), (Heezen & Tharp 1966)
- Their world ocean floor map was published 1977. Austrian painter Heinrich Berann worked on it.
- Nowadays the seafloor maps have a better resolution by the SEASAT, Geosat/ERM and ERS-1/ERM (European Remote-Sensing Satellite/Exact Repeat Mission) missions. (McAdoo 2006)
- World map of earthquake epicenters, oceanic ones mainly (Rothé 1954).
- 1954–1963: Alfred Rittmann was elected IAV President (IAV at that time) for three periods.
- 1956, S. K. Runcorn becomes a drifter. (Frankel 1987, p. 221), (Runcorn 1956)
- Statistics by Ronald Fisher. (Frankel 1987, p. 221), (Runcorn 1956)
- Jan Hospers work (magnetic poles and geographical poles coincide the last 23 Ma).
- Self-exciting dynamo theory of Elsasser-Bullard.
- S. W. Carey, plate tectonics (Carey 1958). But he believed here in an Expanding Earth.
- 1958, Henry William Menard notes that most mid-ocean ridges are halfway between the two continental edges ((Menard 1958) cited in (Bullard 1975)).
- 1959, analysis of Vanguard satellite orbit suggests "large-scale convection currents in the mantle" (O'Keefe, Eckeis & Squires 1959).
- Seafloor spreading
- December 1960, Harry H. Hess (preprint and a report for the Navy): Sonar and seafloor spreading (personal communication formally published in 1962 (Puzzle pieces: his World War II seafloor profiles, (Carey 1958), (Vening Meinesz 1948) and the Great Global Rift). (Hess 1962), (Hess 1960b), (Hess 1960a), (Hess 1959)
- 1961, Robert S. Dietz (Dietz 1961).
- Dott (1961), the Permian tillite at Squantum, Massachusetts, was reclassified as turbidite. It was used as argument by anti-drifters.
- P. M. S. Blakett (1960), Blakett's former lecturer S. K. Runcorn (1962), Runcorn's former student E. Irving: Paleomagnetism.
- References: (Frankel 1987, p. 221), (Blackett, Clegg & Stubbs 1960), (Runcorn 1959), (Runcorn 1962a), (Irving & Green 1958), (Irving 1960), (Creer, Irving & Runcorn 1957)
- 1962, S.K. Runcorn applies the Rayleigh's theory of convection: convection occurs if viscosity under the crust is less than 1026-1027 CGS units. (Runcorn 1962b)
- 1962, Subduction in the Aleutian Islands, Robert R. Coats (USGS). (Coats 1962)
- Wunderlich, H.G. (March 1962). "50 Jahre Kontinentalverschiebungstheorie – von Wegener bis Runcorn" [50 Years Continental Drift Hypothesis – Wegener to Runcorn]. Geologische Rundschau. 52 (1): 504–513. Bibcode:1962GeoRu..52..504W. doi:10.1007/BF01840095. S2CID 128754334.
- The uncertainty of the distance between Europe and North America is too great to confirm the continental drift hypothesis. It states wrongly that the lock-and-key form of South America and Africa is less good if the continental shelf is taken into account. Note: the truth is that neither A. Wegener nor C. Schuchert used the east coastline of South America and west coastline of Africa, really; these coastlines don't fit (Bullard 1975).
Remove ads
Plate tectonics


- Publication of the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis. (Frankel 1987, p. 228), (Vine 1963)
- Frederick Vine is working under Drummond Matthews, University of Cambridge.
- Lawrence W. Morley's independent paper was not accepted.
- John Tuzo Wilson, a former fixist/contractionist up to around 1959. (Frankel 1987, p. 231)
- J. T. Wilson spends much of 1965 in Cambridge and Hess joined him in the second half. Wilson develops the transform fault concept. (Wilson 1962), (Wilson 1963a), (Wilson 1963b), (Wilson 1963c), (Wilson 1965a)
- Wilson cycle, (Wilson 1966).
- Frederick Vine, applies the transform fault concept, the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis and the seafloor spreading concept on the Juan de Fuca Ridge. He does not get a constant spreading rate as the Jaramillo reversal (Geomagnetic reversal) is unknown. (Vine & Wilson 1965)
- P.M.S. Blackett; E.C. Bullard; S.K. Runcorn, eds. (1965). "A Symposium on Continental Drift, 28th October, 1965". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 258 (1088): i–x, 1–323, A1 – A6. (Bullard, Everett & Smith 1965), (Wilson 1965b), (Heezen & Tharp 1965).
- Wells, finds on growth rings of Devonian corals the maximum Earth expansion during this time to be less than 0.6 mm/year (Wells 1963), (Marvin 1966, p. 60). Heezen, abandons the expanding Earth theory as it requires a radial expansion of 4–8 mm/year for the Atlantic Ocean alone (Heezen 1966).
- 1966, East South America and West Africa, rocks and their ages match where they were joint: South Africa / Santa de la Ventana, Argentina; Ghana / São Luís do Maranhão, Brazil.[3][4]
- Nowadays, the fit between Africa and South America is based on paleomagnetism, slightly different from the older "Bullard's Fit" (based on least-square fitting of 500 fathom (c. 900 m) contours across the Atlantic). (Bullard, Everett & Smith 1965), (Torsvik et al. 2001)
- Closure:
- November 1965, Geological Society of America, Brent Dalrymple (Brent Dalrymple, Richard Doell and Allan V. Cox – USGS) brought to Frederik Vine attention that there is the Jaramillo "reversal" (publ. mid-1966 !!!). (Frankel 1987, p. 234), (Doell & Dalrymple 1966)
- February 1966, Vine visits the Lamont group (Walt Pitman and Neil Opdyke) and tells them that their 'discovered' Emperor reversal was already named as Jaramillo reversal. And shows the reversal on the Walt Pitman's graphik (cm/ vertical), surprising Pitman, Opdyke and even himself (Ninkovich et al. 1966), (Vine 1966). Many anti-drifters changed their mind after the publication of these magnetometer readings of sediment core (Eltanin-19), geomagnetic reversals (Le Grand 1990).
- The Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis is the first scientific test to confirm the seafloor spreading concept. Earth Sciences paradigm shift, from fix continents to plate tectonics (Wilson 1968):
- Magnetometer readings of sediment cores, geomagnetic reversals: ratio of cm (vertical).
- Magnetic profiles of seafloor, geomagnetic reversals: ratio of km (horizontal).
- Radiometric analysis of lava flows, geomagnetic reversals: ratio of Ma (time). (Frankel 1987, p. 235)
- Conference in New York in November 1966, sponsored by NASA ((Phinney 1968) cited in (Bullard 1975)).
- Maurice Ewing to Edward Bullard: "You don't believe all this rubbish, do you, Teddy?"
- Even Maurice Ewing (Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory) came to accept seafloor spreading by April 1967 and cited (along with his brother John Ewing) the case for Vine-Matthews-Morley Hypothesis as "strong support for the hypothesis of spreading."(Frankel 1987, p. 230)
- Ewing, John; Ewing, Maurice (23 June 1967). "Sediment Distribution on the Mid-Ocean Ridges with Respect to Spreading of the Sea Floor". Science. 156 (3782): 1590–1592. Bibcode:1967Sci...156.1590E. doi:10.1126/science.156.3782.1590. PMID 17797640. S2CID 8687894.
- Around 1967, Marshall Kay becomes a drifter. (Frankel 1987, p. 230)
- In 1967, W. Jason Morgan proposed that the Earth's surface consists of 12 rigid plates that move relative to each other (Morgan 1968). Two months later, in 1968, Xavier Le Pichon published a complete model based on 6 major plates with their relative motions (Le Pichon (1968), received 2 January 1968). The Englishmen Dan McKenzie and Robert Parker published the quantitative principles for plate tectonics (Euler's rotation theorem: Individual aseismic areas move as rigid plates on the surface of a sphere, quote: "a block on a sphere can be moved to any other conceivable orientation by a single rotation about a properly chosen axis.") (McKenzie & Parker 1967).
- Note I: although Morgan (1968) (received 30 August 1967, revised 30 November 1967 and published 15 March 1968) was published later than McKenzie & Parker (1967) (published 30 December 1967), priority belongs to Morgan. It is based on a presentation at the American Geophysical Union's 1967 meeting (title: Rises, Trenches, Great Faults, and Crustal Blocks).
- Note II: W. Jason Morgan shared with Fred Vine an office in the Princeton University for two years, and a scientific paper from H. W. Menard drifted his attention to plate tectonics. It was probably the long faults on Menard (1967) (cited in Morgan 1968) and the Euler's rotation theorem that gave him the idea.[5][6]
- End of the continental drift controversy in the USA: North Atlantic – Geology and Continental Drift, a Symposium (1969); American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG) ((Kay 1969) cited in (Krill 2011)).
Remove ads
Geodynamics



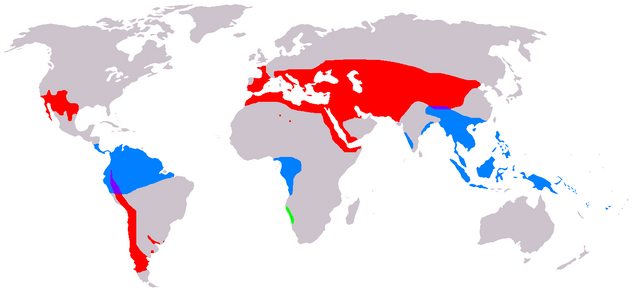
Green – Welwitschia
Blue – Gnetum
Red – Ephedra
Purple – Gnetum and Ephedra range overlap
- John F. Dewey applies Plate tectonics (Dewey 1970).
- Plate tectonics:
- Mantle plume controversy (Cowen & Lipps 1975, Jordan 2007): The relationship between subducted seafloor, flood basalts and continental rifting is uncovered. (Morgan 1971), (Morgan 1972), (Rampino & Stothers 1988), (Silver, Carlson & Olson 1988), (White 1989), (Segev 2002)
- Slab pull force, Slab suction force (Back-arc basin) and Ridge push force:
- Back-arc basin (Molnar & Atwater 1978), (Barker & Hill 1980), (Martinez et al. 1995)
- Similar to a landslide, seafloor sinks and subducts (Forsyth & Uyeda 1975), (Hager & O'Connell 1981), (Kerr 1995), (Anderson 2001), (Conrad & Lithgow-Bertelloni 2002)
- Wilson cycle: slab pull/ subduction opens a space on western South America and the sliding seafloor away from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on eastern South America occupies the new available space.
- Overview: viscous resistance, slab thickness, slab bending, trench migration and seismic coupling, slab width, slab edges and mantle return flow:
- Clinton P. Conrad; Susan Bilek; Carolina Lithgow-Bertelloni (2004). "Great earthquakes and slab pull: interaction between seismic coupling and plate-slab coupling" (PDF). Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 218 (1): 109–122. Bibcode:2004E&PSL.218..109C. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.506.2266. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00643-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 June 2011. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- Lallemand, S.; Heuret, A.; Boutelier, D. (2005). "On the relationships between slab dip, back-arc stress, upper plate absolute motion, and crustal nature in subduction zones". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 6 (9): Q09006. Bibcode:2005GGG.....6.9006L. doi:10.1029/2005GC000917.
- W. P. Schellart; D. R. Stegman; R. J. Farrington; J. Freeman & L. Moresi (16 July 2010). "Cenozoic Tectonics of Western North America Controlled by Evolving Width of Farallon Slab". Science. 329 (5989): 316–9. Bibcode:2010Sci...329..316S. doi:10.1126/science.1190366. PMID 20647465. S2CID 12044269.
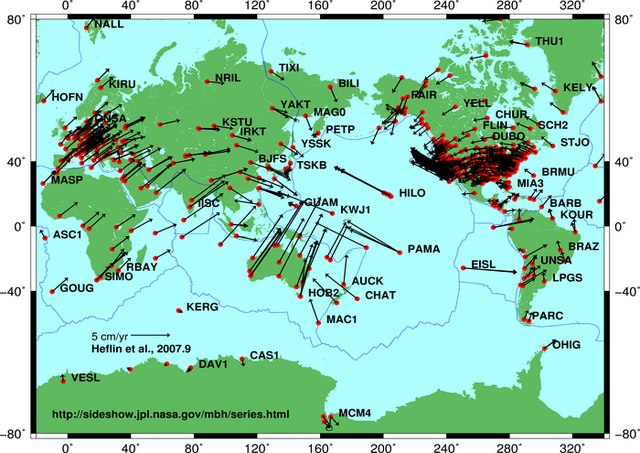
- Current plate motions. (Demets et al. 1990), (Argus et al. 2010), (Demets, Gordon & Argus 2010)
- Pacific Plate, lower mantle has a greater viscosity (Monastersky 1996a)
- Tibetan Plateau, collision generates heat (Nelson 1996), (Monastersky 1996b)
- Paleogeography (Irving (2005) and Krill (2011)):
- Order Cycadales, genus Bowenia
- Family Araucariaceae found in Norfolk Island, Australia, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, New Guinea, Argentina, Chile, and southern Brazil. Coal fossils found on the British Isles.
- Magnolia, subgenus Magnolia:
- Section Magnolia, found in the Neotropical realm
- Section Gwillimia, found in Asia including Borneo
- Section Blumiana, found in Asia, including Sumatra and Borneo
- Section Talauma, found in the Neotropical realm
- Section Manglietia, found in Asia
- Section Kmeria, found in Asia
- Section Rhytidospermum, found in Asia and Magnolia tripetala (L.) L. in Southeast USA
- Section Auriculata, Magnolia fraseri Walt. found in Southeast USA
- Section Macrophylla, Magnolia macrophylla Michx. found in Southeast USA
- Magnolia, subgenus Yulania:
- Section Yulania, found in Asia and Magnolia acuminata (L.) L. found in East USA
- Section Michelia, found in Asia including the Indomalayan realm
- Note: a bee fossil of the genus Melittosphex, is considered "an extinct lineage of pollen-collecting Apoidea sister to the modern bees", and dates from the early Cretaceous (c. 100 Ma).[7] Insect-pollinated flowering plants need bees (unranked taxon Anthophila, of the superfamily Apoidea). Beetles may have originated during the Lower Permian, up to 299 Ma.[8] Flies evolved c. 250 Ma, moths and wasps evolved c. 150 Ma.[9]
- Lockwood, John P.; Hazlett, Richard W. (2010). Volcanoes: Global Perspectives. Wiley. p. 552. ISBN 978-1-4051-6250-0.[10]
- Total estimated radiogenic heat release (from neutrino research): 19 Terawatts
- Total directly observed heat release through Earth's surface: 31 Terawatts
- Seismic anisotropy (Becker 2008), (Kreemer 2009), (Conrad & Behn 2010)
- Plate reconstruction: Torsvik, Trond Helge and Gaina, Carmen, Center for Geodynamics at NGU (Geological Survey of Norway), PGP (Physics of Geological Processes, University of Oslo, Norway); Müller, R. Dietmar, EarthByte Group, University of Sydney; Scotese, C.R., Ziegler, A.M. and Van der Voo, R., University of Michigan, University of Chicago and University of Texas, Arlington; Ziegler, P.A. and Stampfli, Gérard, University of Basel and University of Lausanne.[11][12][13]
- (Torsvik et al. 2010), (Ziegler 1990), (Stampfli & Borel 2004)
- Global plate reconstructions with velocity fields from 150 Ma to present in 10 Ma increments.
Remove ads
Overview
Summarize
Perspective
Many concepts had to be changed:
- Uniformitarianism instead of catastrophism.
- Empirical science instead of creationism.
- Plutonism instead of neptunism, but hydrothermal secondary mineralization occurs.
- Seafloor of sima instead of sial.
- Baron Kelvin got the age of the Earth too short.
- The concept of Earth crust and mantle.
- Airy-Heiskanen isostasy model instead of the Pratt-Hayford model.
- Thrust faults had to be accepted.
- The expanding Earth and the contracting Earth concept had to be given up.
The shifting and evolution of knowledge and concepts, were from:
- Eduard Suess (alpine geology: theory of thrusting as a modification of the geosyncline hypothesis), (Suess 1875);
- then to Alfred Wegener (continental drift), (Wegener 1912a), (Wegener 1929);
- then to Arthur Holmes (a model with convection), (Holmes 1944);
- then to Felix Andries Vening Meinesz (gravity anomalies along the oceanic trenches implied that the crust was moving) and A. Rittmann (subduction), (Vening Meinesz 1959), (Rittmann 1951);
- then to Samuel Warren Carey (plate tectonics), (Carey 1958); Harry Hammond Hess and Robert S. Dietz (seafloor spreading), (Hess 1962), (Dietz 1961);
- then to John Tuzo Wilson (seafloor spreading), (Wilson 1963b), (transform faults), (Wilson 1965a) and (Wilson cycle), (Wilson 1966);
- then to the confirmation of the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis, (Vine 1963) and paradigm shift, (Vine 1966) and (Wilson 1968);
- then to Jason Morgan, Dan McKenzie and Robert Parker (quantification of plate tectonics), (Morgan 1968), (McKenzie & Parker 1967); its uncertainty was quantified by Theodore C. Chang;
- and then to computer simulation with slab pull and "ridge-push" (Forsyth & Uyeda 1975), (Hager & O'Connell 1981), (Kerr 1995) and (Conrad & Lithgow-Bertelloni 2002) with nice works published by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, the EarthByte Group (R. Dietmar Müller) and the Center for Geodynamics (Trond Helge Torsvik and Carmen Gaina).[12][13]

Actually, there were two main "schools of thought" that pushed plate tectonics forward:
- The "alternative concepts to e.g. Harold Jeffreys group", James Hutton, Eduard Suess, Alfred Wegener, Alexander du Toit, Arthur Holmes and Felix Andries Vening Meinesz (together with J.H.F. Umbgrove, B.G. Escher and Ph.H. Kuenen). Holmes, Vening Meinesz and Umbgrove had some experience in Burma or Indonesia (Pacific Ring of Fire).
- The alpine geology "school of thought": Suess (1875), Argand (1916), Argand (1922), Ampferer (1920), Schwinner (1941) and Rittmann (1951). With the theory of thrusting, nappes, thrust faults and subductions.
- The "Princeton University" group around H. H. Hess: Felix Andries Vening Meinesz, Harry Hammond Hess, John Tuzo Wilson, W. Jason Morgan and Frederick Vine. Overview of plate tectonics in: Kearey, Klepeis & Vine 2009.
- Vening Meinesz (together with J.H.F. Umbgrove, B.G. Escher and Ph.H. Kuenen) had more evidence that the established paradigm and the reality do not match. But as all geophysicists he could not really believe in crust motions in such a large scale and he knew Wegener's Continental drift hypothesis fate too. Hess (1962) accumulated even more evidence, but he prudently introduced them as geopoetry, quote: "Little of Umbgrove (1947) brilliant summary remains pertinent when confronted by the relatively small but crucial amount of information collected in the intervening years. Like Umbgrove, I shall consider this paper an essay in geopoetry."
- The IAV/ IAVEI board (i.e., B.G. Escher and A. Rittmann) probably never dumped the idea that the South Atlantic is under extension.
- And the anti-drifters were in a way right as well. Although convection would mix up the mantle and make it homogeneous. The seafloor cycle with subduction and upwelling is something between conduction and convection, it allows for its inhomogeneity in a quasi-steady state. The mantle and the continents are in a way passive, the heat sink of the earth is the seafloor. So that the heat generated in the earth gets neutralised.
Wegener's continental drift hypotheses is a logical consequence of: the theory of thrusting (alpine geology), the isostasy, the continents forms resulting from the supercontinent Gondwana break up, the past and present-day life forms on both sides of the Gondwana continent margins, and the Permo-Carboniferous moraine deposits in South Gondwana.
Graphics

Remove ads
See also
- Timeline of the development of tectonophysics (before 1954) – Chronological listing of significant events in the history of tectonophysics
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads