Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
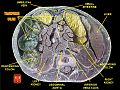
Transverse colon
Longest section of the large intestine From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In human anatomy, the transverse colon is the longest and most movable part of the colon.
Remove ads
Anatomical position
It crosses the abdomen from the ascending colon at the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure) with a downward convexity to the descending colon where it curves sharply on itself beneath the lower end of the spleen forming the left colic flexure (splenic flexure). In its course, it describes an arch, the concavity of which is directed backward and a little upward. Toward its splenic end there is often an abrupt U-shaped curve which may descend lower than the main curve.
It is almost completely invested by the peritoneum, and is connected to the inferior border of the pancreas by a large and wide duplicature of that membrane, the transverse mesocolon.
It is in relation, by its upper surface, with the liver and gall-bladder, the greater curvature of the stomach, and the lower end of the spleen; by its under surface, with the small intestine; by its anterior surface, with the posterior layer of the greater omentum and the abdominal wall; its posterior surface is in relation from right to left with the descending portion of the duodenum, the head of the pancreas, and some of the convolutions of the jejunum and ileum.
Remove ads
Function
The transverse colon absorbs water and salts.
Additional images
- Inner diameters of different sections of the large intestine, with transverse colon (at top) measuring on average 5.8 cm (range 5.0-6.5 cm).[1]
- Intestines
- Schematic figure of the bursa omentalis, etc. The human embryo of eight weeks
- Front view of the thoracic and abdominal viscera
- Digestive system
- Transverse colon
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads