Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tungsten borides
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Tungsten borides are compounds of tungsten and boron. Their most remarkable property is high hardness. The Vickers hardness of WB or WB2 crystals is ~20 GPa[1][2] and that of WB4 is ~30 GPa for loads exceeding 3 N.[3]

Synthesis
Single crystals of WB2−x, x = 0.07–0.17 (about 1 cm diameter, 6 cm length) were produced by the floating zone method,[1] and WB4 crystals can be grown by arc-melting a mixture of elemental tungsten and boron.[3]
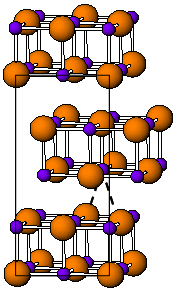
Structure
WB2 has the same hexagonal structure as most diborides (AlB2, MgB2, etc.).[4] WB has several forms, α (tetragonal), β (orthorhombic) and δ (tetragonal).[2]
Properties
δ-WB and WB2 crystals have metallic resistivities of 0.1 and 0.3 mΩ·cm, respectively. The oxidation of W2B, WB and WB2 is significant at temperatures above 600 °C. The final oxidation products contain WO3 and probably amorphous B2O3 or H3BO3. The melting temperatures of W2B, WB and WB2 are 2670, 2655 and 2365 °C, respectively.[2]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
