Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tungsten hexabromide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Tungsten hexabromide, also known as tungsten(VI) bromide, is a chemical compound of tungsten and bromine with the formula WBr6. It is an air-sensitive dark grey powder that decomposes above 200 °C to tungsten(V) bromide and bromine.[1][3]
Remove ads
Production and reactions

Tungsten hexabromide is mainly produced by the reaction of metallic tungsten and bromine at temperatures around 100 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere:[1][2]
- W + 3 Br2 → WBr6
Another method of producing this compound is by the reaction of tungsten hexacarbonyl and bromine at room temperature, releasing carbon monoxide.[4] It can also be produced by the metathesis reaction of boron tribromide and tungsten hexachloride.[5]
WBr6 is reduced with elemental antimony at elevated temperatures, consecutively producing, WBr5, WBr4, W4Br10, W5Br12, then finally WBr2 at 350 °C. This reaction produces antimony tribromide as a side product.[4][6] Any of these bromides can be reverted to the hexabromide by oxidation with bromine at 160 °C.[7]
Tungsten hexabromide is hydrolyzed in water, producing tungsten pentoxide and releasing bromine.[1]
Tungsten(VI) oxytetrabromide is produced by the reaction of tungsten hexabromide and tungsten(VI) oxide:[7]
- 2 WBr6 + WO3 → 3 WOBr4
Remove ads
Structure
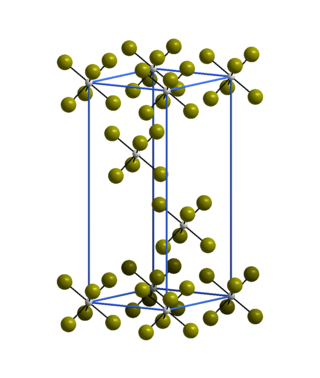
The trigonal crystal structure of WBr6 consists of isolated WBr6 octahedra and is isostructural with α-WCl6.[2]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads