Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Vacuum Tower Telescope
Solar telescope on Tenerife operated by KIS From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Vacuum Tower Telescope is an evacuated-optics solar telescope located at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It is operated by the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik (KIS).[1][2]
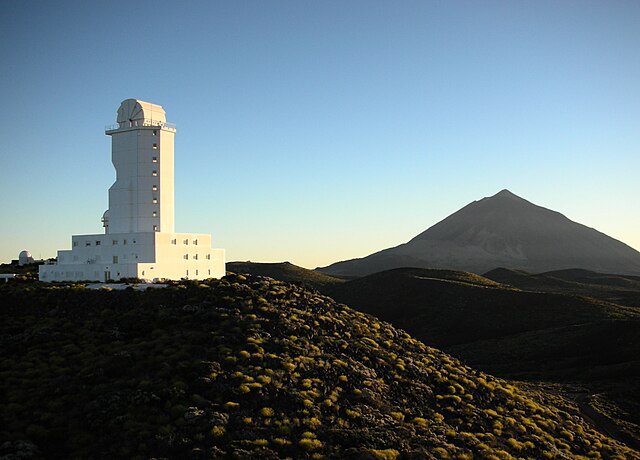


It was built between 1983 and 1986, with first light in 1988.[3] It has a 70-centimetre-diameter (28 in) primary mirror and a focal length of 46 metres (151 ft). Thanks to an adaptive optics system KAOS (Kiepenheuer-institute Adaptive Optic System), in operation since spring 2000,[4][5] it is able to resolve details down to 0.2 arc seconds (150 km) on the Sun's surface.[6][7][8]
Remove ads
Description
The VTT and the GREGOR are operated by four German institutes: the Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik (Freiburg, chair), the Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung (Lindau), and the Universitäts-Sternwarte Göttingen. The telescope is used for scientific observations from mid-April through mid-December. Typically 30 to 40 observing campaigns are carried out every year.
Remove ads
History
In the early seventies, the 40-centimetre Newton telescope, built at the Kiepenheuer-Institut, was installed at the Observatorio del Teide. In 1982, the Federal Republic of Germany joined the international Agreement on the Cooperation in Astrophysical Research between Spain, Great Britain, Sweden and Denmark. Construction work for the German solar telescopes started in 1983, including the Vacuum Tower Telescope (VTT), and the Gregory-Coudé-Telescope (GCT) of the Universitäts-Sternwarte Göttingen. The VTT was developed at the Kiepenheuer-Institut in Freiburg during the mid-seventies. The telescope was installed in 1986 and the scientific operations started in 1988. Since then, the VTT has been constantly improved and has been the workhorse for our[whose?] researchers. The GCT was put into operation in 1985 and dismantled in 2002, in order to make room for the new 1.5-metre GREGOR telescope.
Remove ads
Results
The VTT instrumentation is designed for high-quality measurements of plasma flows and magnetic fields. Some instruments can be combined for simultaneous observations in different parts of the solar spectrum, from the near-infrared to the near-UV. This possibility is a unique feature for a solar telescope and allows it to reveal the three-dimensional structure of the solar atmosphere. With the help of adaptive optics and suitable image-reconstruction techniques, it is now possible to observe physical properties of small-scale objects on the solar surface with sizes of only 150 km, at the theoretical limit of the telescope.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads