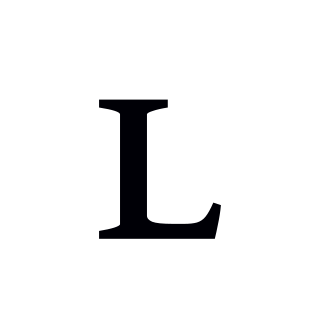Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Voiced velar lateral approximant
Consonantal sound represented by ⟨ʟ⟩ in IPA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A voiced velar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used as a distinct consonant in a very small number[1] of spoken languages in the world. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that has represented this sound since 1989 is ⟨ʟ⟩, a small capital letter l.
Velar laterals often involve a prestopped realization [ᶢʟ].[2]
According to Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996), the extremely short duration of /ʟ/ in intervocalic position (20–30 ms) in some of the languages in New Guinea, such as Kanite and Melpa, warrants calling it a voiced velar lateral tap. The IPA has no specific symbol for this sound, but it may be represented with a breve for extra-short, such as ⟨ʟ̆⟩, to indicate a tapped consonant.
It is reported that some dialects of English may have a voiced uvular lateral approximant,[3] which can be represented in the IPA as ⟨ʟ̠⟩ (a retracted ⟨ʟ⟩), though evidence of this consonant is limited.
Remove ads
Features
Features of a voiced velar lateral approximant:
- Its manner of articulation is approximant, which means it is produced by narrowing the vocal tract at the place of articulation, but not enough to produce a turbulent airstream.
- Its place of articulation is velar, which means it is articulated with the back of the tongue (the dorsum) at the soft palate.
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is not allowed to escape through the nose.
- It is a lateral consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream over the sides of the tongue, rather than down the middle.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air only with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
A velar lateral [ʟ] involves no contact of the tip of the tongue with the roof of the mouth: just like for a velar stop [ɡ], the only contact takes place between the back of the tongue and the velum. This contrasts with a velarized alveolar lateral approximant [ɫ] – also known as the dark l in English feel [fiːɫ] – for which the apex touches the alveolar ridge.[4]
Remove ads
Occurrence
Velar
Uvular
Remove ads
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads