Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
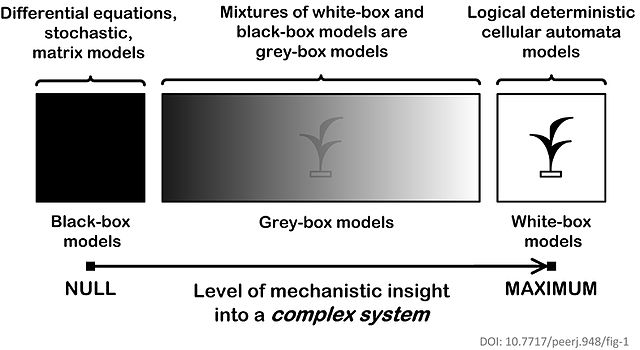
White box (software engineering)
System whose internals can be viewed but not altered From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A white box (or glass box, clear box, or open box) is a subsystem whose internals can be viewed but usually not altered.[1] The term is used in systems engineering, software engineering, and in intelligent user interface design,[2][3] where it is closely related to recent[when?] interest in explainable artificial intelligence.[4][5]
Having access to the subsystem internals in general makes the subsystem easier to understand, but also easier to hack; for example, if a programmer can examine source code, weaknesses in an algorithm are much easier to discover.[citation needed] That makes white-box testing much more effective than black-box testing but considerably more difficult from the sophistication needed on the part of the tester to understand the subsystem.
The notion of a "Black Box in a Glass Box" was originally used as a metaphor for teaching complex topics to computing novices.[6]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

