Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
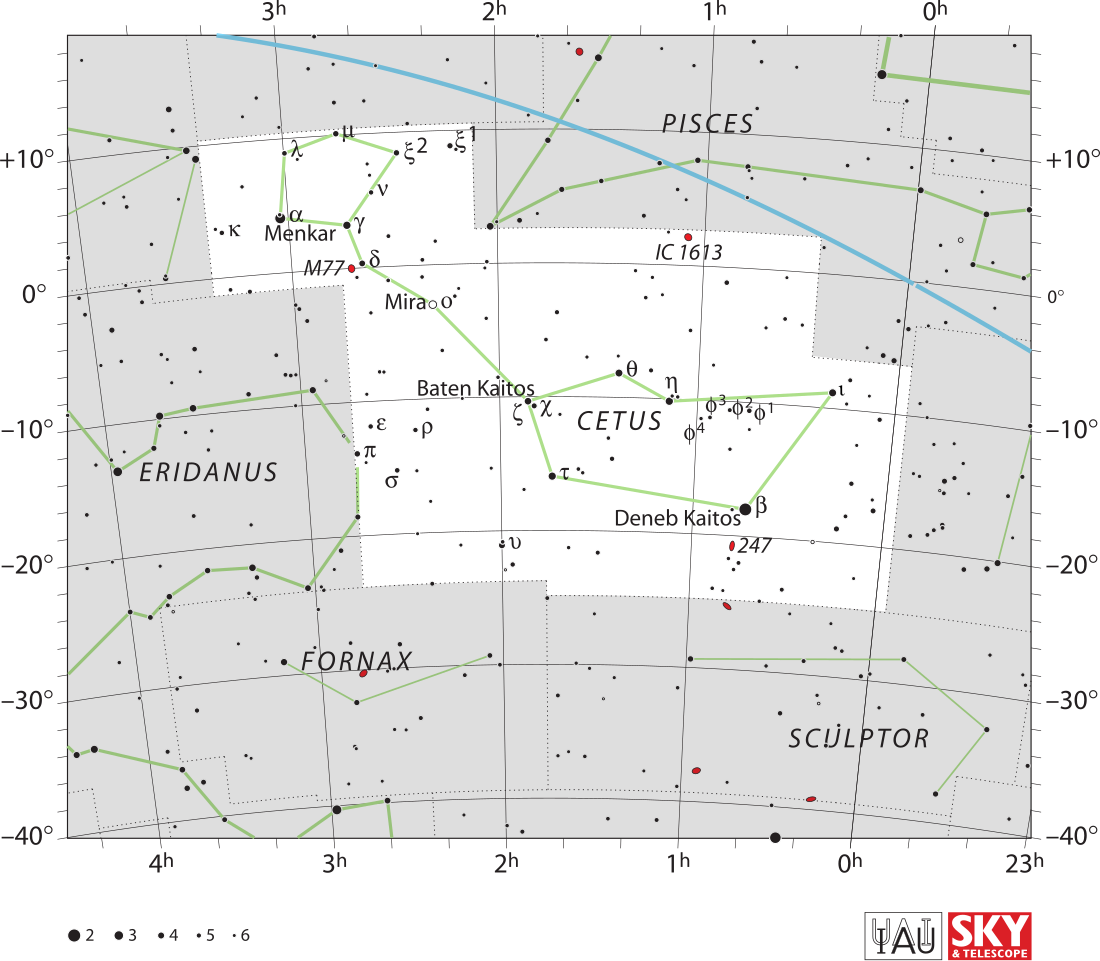
Xi1 Ceti
Star in the constellation Cetus From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Xi1 Ceti , Latinized from ξ1 Ceti, is a binary star[10] system located in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.36.[2] The distance to this system is approximately 340 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −4 km/s.[2] The proximity of the star to the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations.[11]
The spectroscopic binary nature of Xi1 Ceti was discovered in 1901 by William Wallace Campbell using the Mills spectrograph at the Lick Observatory.[12][6] The pair have a circular orbit with a period of 4.5 years and a separation of 3.8 AU.[5] It is a suspected eclipsing binary with an amplitude of 0.03 in magnitude, which would suggest the orbital plane has a high inclination.[13]
The primary, designated component A, is a mild barium[14] giant star with a stellar classification of G7III Ba0.4 Fe-1.[3] Morgan and Keenan in 1973 had classified it as a bright giant star with an anomalous underabundance of the CN molecule.[15] Evidence has been found for an overabundance of s-process elements,[5] although this is disputed.[7] The star has 3.8[5] times the mass and 18[1] times the radius of the Sun. The companion, component B, is a small white dwarf companion with 80% of the mass of the Sun and a class of DA4.[4] It was detected in 1985 by its ultraviolet emission.[8]
In Chinese, 天囷 (Tiān Qūn), meaning Circular Celestial Granary, refers to an asterism consisting of α Ceti, κ1 Ceti, λ Ceti, μ Ceti, ξ1 Ceti, ξ2 Ceti, ν Ceti, γ Ceti, δ Ceti, 75 Ceti, 70 Ceti, 63 Ceti and 66 Ceti. Consequently, the Chinese name for Xi1 Ceti itself is "the Fifth Star of Circular Celestial Granary", Tiān Qūn Wu.[16]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads