Xenon
chemical element with atomic number of 54 and heaviest stable noble gas From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Xenon is a non-metal chemical element. It has the chemical symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is one of the few elements that are a gas at the standard temperature and pressure.
Remove ads
History
Sir William Ramsay and M. W. Travers discovered this element in 1898. The element's name came from the Greek word xenos, which means 'stranger'.
Chemistry
Xenon belongs to the group of the noble gases. Noble gases are very unreactive. However, in 1962, chemists have found that xenon can react with fluorine under special conditions, such as high pressure and high temperature. It is not known why xenon behaves differently under these circumstances. There are also some compounds with oxygen. The gas is not very reactive, because if fulfills the octet rule. This means that a lot of energy is needed to remove an electron from xenon. This activation energy for xenon is 1172 kJ/mol. To remove a second electron from xenon, an energy of 2046.4 kJ/mol is needed.
Known oxidation states of xenon are 0, +1, +2, +4, +6 and +8. However, the most stable form is pure xenon, or the xenon's oxidation state of 0. Xenon has 8 stable isotopes and more than 30 unstable isotopes.
Remove ads
Uses
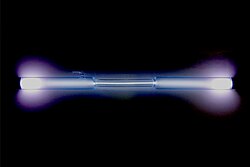
Xenon gas is used in electron tubes, bactericidal lamps, trobe lamps, and lamps used to excite ruby lasers. It has the atomic mass of 131.294 and is the 5th inert gas in the inner gas group.
Xenon is also a trace gas in the atmosphere, occurring at 87 ±1 nL/L (parts per billion) or approximately 1 in 11.5 million. It is also emitted from some mineral springs.

Related pages
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads