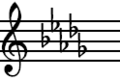B-flat minor
minor tonality based on B-flat From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
B♭ minor or B-flat minor is a minor scale based on B♭. Its key signature has five flats. It has the pitches of B♭ , C, D♭, E♭, F, G♭, A♭, and B♭.
Its relative major is D-flat major, and its parallel major is B-flat major. Its enharmonic equivalent is A-sharp minor.
B-flat minor is often seen as a "dark" key.[1] Tchaikovsky said that the oboe solo in B-flat minor in the second movement of his Symphony No. 4 was "the feeling that you get when you are all alone".
The old valveless horn could not play easily in B-flat minor. In fact, the only example found in 18th century music is a modulation in the first minuet of Franz Krommer's Concertino in D major, Opus 80.[2]
Remove ads
In classical music
- Frédéric Chopin's Piano Sonata No. 2, Nocturne Op. 9 No. 1, and Scherzo No. 2
- Sergei Rachmaninoff's Piano Sonata No. 2
- Dmitri Shostakovich's Symphony No. 13
- Peter Tchaikovsky's Piano Concerto No. 1
- Peter Tchaikovsky's Marche Slave
- Sir William Walton's Symphony No. 1
In popular music
- "Part-Time Lover"[3] – Stevie Wonder
- "Cannonball (Damien Rice song)"[4] - Damien Rice
- All eight songs on The Raveonettes' Whip It On album are in the key of B-flat minor. Sune Rose Wagner said it was because "Shostakovich's symphony no. 13 was in B flat minor".[5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads