LaTeX
document markup language From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
LaTeX is a computer program used for making articles, books and math formulas look good. LaTeX is well-suited for expressing mathematical formulas on electronic devices in a more human readable format, by showing them in a way similar to how they would be written by hand.
LaTeX is used for making mathematical formulas for some articles on Wikipedia, in addition to being used within academic circles.
The writer types their article into a plain text document. A plain text document cannot have styled text, like bold or italic. When the writer wants to write styled text, they use special LaTeX commands that start with a backslash (\). For example, the command for bold text is \textbf{This text is bold}.
After the writer is finished writing the article, they tell LaTeX to read the document. After LaTeX is done, LaTeX makes a file that can be printed. The command \textbf{This text is bold} would print as This text is bold.
LaTeX was first made in the early 1980s by Leslie Lamport at SRI International, who published its first manual in 1986.[1] The current version is LaTeX2e (styled ![]() ), which has been active since 1994.[2]
), which has been active since 1994.[2]

Remove ads
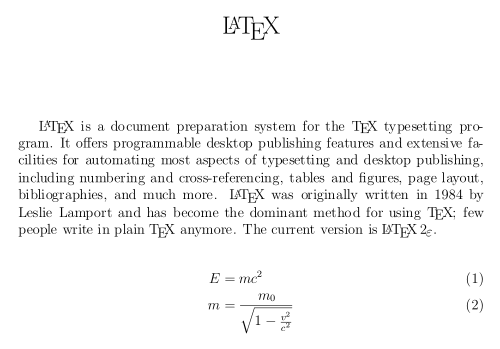
Example
The example below shows the LaTeX input and its corresponding output:
Remove ads
Academic contributions to LaTeX
In order to support mathematical typesetting, the American Mathematical Society (AMS) has made the AMS-LaTeX package.[3] AMS also founded MathJax, a Javascript extension to display mathematical formulas on web browsers, with the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.[4]
Related pages
- Acaric (Developer of Cloud LaTeX)
- Beamer (LaTeX-based presentation software)
- CTAN (One of the largest LaTeX-related website)
- KaTeX (LaTeX for web browsers)
- SATySFi (A computer program expected to be an alternative to LaTeX)
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads