Subset
set whose elements are all contained in another set From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In set theory, a set is called a subset of a set if all of the elements of are contained in . For example, any set is a subset of itself. Another example of a subset is a proper subset: a set is called a proper subset of a set if is subset of but is not equal to .
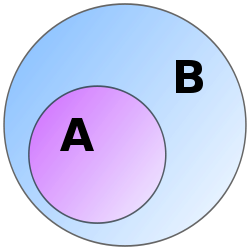
The symbol "" always means "is a subset of."[1][2][3] The symbol "" always means "is a proper subset of." There is also the symbol "", which some authors use to mean "is a subset of"[4] and other authors only use to mean "is a proper subset of."[1]
For example:
- is a subset of , so we could write .
- is a proper subset of , so we could write ,, or .
- The interval [0, 1] is a proper subset of the set of real numbers , so .
Remove ads
Related pages
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads













![{\displaystyle [0,1]\subset \mathbb {R} }](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/98ef6fb8c5d9b34f4ba677930a956bd62270f9a2)