热门问题
时间线
聊天
视角
2010年航天活动列表
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
Remove ads
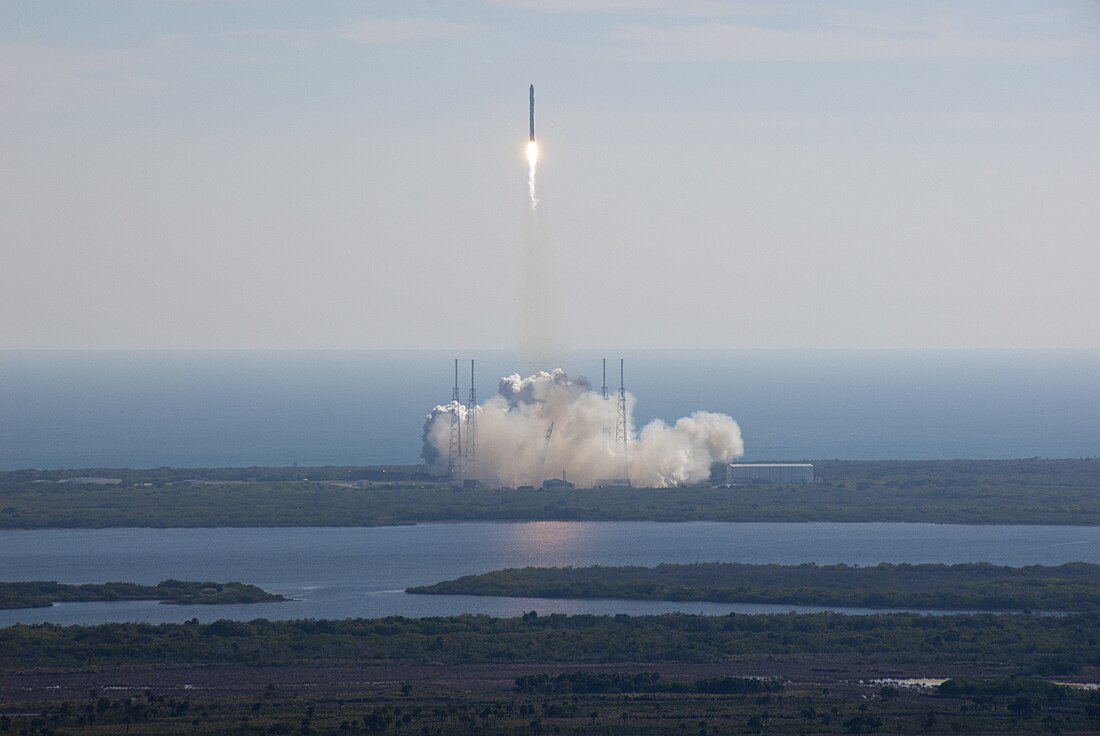
2010年,全球航天活动中出现了许多重大事件。包括用于商业轨道运输服务(英语:Commercial Orbital Transportation Services)的SpaceX龙飞船的首次飞行,该飞船旨在为国际空间站运输补给,以及猎鹰9号和米诺陶4号运载火箭的首飞。2010年6月,韩国进行了第二次罗老运载火箭的发射,该火箭在2009年首飞失败;然而,第二次尝试也失败了。宇宙3号M型运载火箭退役,于4月进行了其最后一次飞行;在9月进行了最后一次飞行后,闪电-M运载火箭(英语:Molniya-M)也宣布退役。[1]
Remove ads
概述
2010年的全球首次亚轨道发射于1月10日23:00(UTC)进行,当时一枚黑雁IX探空火箭(英语:Black Brant (rocket))作为波音YAL-1机载激光系统的目标发射。1月11日,中国进行了该国首次反弹道导弹试验,涉及两枚导弹。全球首次轨道发射于1月16日16:12(UTC)进行,当时长征三号丙运载火箭从西昌卫星发射中心发射了北斗-G1导航卫星。
2010年共进行了74次轨道发射,其中70次成功,4次失败。最后一次轨道发射是在12月29日,当时阿丽亚娜5号ECA构型从库鲁附近的圭亚那航天中心发射了Hispasat-1E和Koreasat 6号航天器。
深空探测
5月,日本使用H-IIA运载火箭发射发射了该国首个金星探测器“破晓”号。其目的是寻找金星上的闪电和火山。[2]尽管发射成功,但该航天器未能在12月进入环绕金星的轨道[3],最终它在5年后的2015年12月才成功进入金星轨道。第一艘可操作的太阳帆“IKAROS”号与“破晓”号搭乘同一枚火箭升空。
日本的第一个小行星探测器“隼鸟”号于6月13日返回地球,此前它曾降落在小行星25143“丝川”上收集样本。[4]这也是世界上第一个成功从小行星采样返回的航天任务。[5]
10月1日10:59:57(UTC),中国成功发射嫦娥二号探测器,这是嫦娥工程的第二次任务。此次任务使用长征三号丙运载火箭从西昌卫星发射中心发射。嫦娥二号的任务与之前的嫦娥一号类似,但重点是绘制潜在着陆点,为嫦娥三号无人月球着陆器做好准备。[6]
载人航天
2010年按计划进行了7次载人飞行任务,包括3次航天飞机和4次联盟号飞船任务,用于国际空间站乘组人员轮换。STS-130使用奋进号,是本年度首次载人飞行,奋进号于2月8日发射,搭载宁静号节点舱和穹顶舱前往国际空间站。4月5日,发现号执行STS-131任务,搭载“莱昂纳多”多功能后勤模块(英语:Multi-Purpose_Logistics_Module)(MPLM)为空间站提供补给。
4月2日,联盟TMA-18飞船将远征23(英语:Expedition 23)乘组人员送往国际空间站;该飞船计划在空间站对接约6个月,以便乘组人员在紧急情况下撤离。此前不久,联盟TMA-16飞船脱离对接,将前一批国际空间站乘组人员送回地球。5月14日,美国航天飞机 亚特兰蒂斯号发射升空,执行其倒数第二次飞行——STS-132任务,将晨曦号实验舱(英语:Rassvet (ISS module))送往国际空间站。6月15日,联盟TMA-19飞船搭载远征24(英语:Expedition 24)乘组发射升空。10月8日,联盟TMA-01M飞船发射升空,这是现代化改造的联盟TMA飞船的首次飞行,搭载远征25(英语:Expedition 25)乘组人员前往国际空间站。最后,在年底,远征26(英语:Expedition 26)于12月15日搭乘联盟TMA-20飞船发射升空。
发射失败
2010年共发生了4起轨道发射失败事故。其中两起影响地球同步卫星运载火箭(GSLV),一起影响罗老运载火箭,另一起影响质子运载火箭。第一次失败发生在4月15日,当时是GSLV Mk.II型首次发射。火箭的第三级发生故障,导致火箭和GSAT-4卫星无法进入轨道并坠入大海。第二次失败发生在罗老运载火箭的第二次试飞期间,当时火箭搭载着STSAT-2B航天器。火箭在起飞137秒后爆炸。[7]
第三次故障发生在12月5日,当时搭载首个Blok DM-03上面级的质子-M运载火箭未能将三颗格洛纳斯-M卫星送入轨道。发射前,Blok DM的燃料加注错误,导致火箭太重而无法到达停泊轨道。[8]第四次故障发生在2010年12月25日,当时GSLV Mk.I型在GSAT-5P发射过程中爆炸。由于第一级的液体燃料助推器失控,火箭被发射场安全控制系统下令摧毁。[9]
轨道发射
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
| ← 一月 • 二月 • 三月 • 四月 • 五月 • 六月 • 七月 • 八月 • 九月 • 十月 • 十一月 • 十二月 → |
更多信息 发射时间 (UTC), 运载火箭 ...
| 发射时间 (UTC) | 运载火箭 | 火箭编号 | 发射场 | 发射服务提供商(英语:List of launch service providers) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效载荷 (⚀ = 立方星) |
载荷用户 | 轨道 | 功能 | 再入时间 (UTC) | 结果 | |||
| 附注 | ||||||||
January | ||||||||
| 16 January 16:12 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 28 January 00:18 |
||||||||
| VKS | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
February | ||||||||
| 3 February 03:45 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 1 July 14:40 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 36P | ||||||||
| 8 February 09:14 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 22 February 03:22 |
Successful | ||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Crewed flight with six astronauts. | ||||||||
| 11 February 15:23 |
||||||||
| NASA | Geosynchronous | Heliophysics | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 12 February 00:39 |
||||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
March | ||||||||
| 1 March 21:19 |
||||||||
(Glonass-M 731) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 732) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 735) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| 4 March 23:57 |
||||||||
| NOAA / NASA | Geosynchronous | Meteorology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Satellite redesignated EWS-G2 after being transferred to the U.S. Space Force in September 2023.[11] | ||||||||
| 5 March 04:55 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | ELINT | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| First Long March 4 series launch from Jiuquan. | ||||||||
| 20 March 18:27 |
||||||||
| Echostar | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
April | ||||||||
| 2 April 04:04 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 23 | 25 September 05:23 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. | ||||||||
| 5 April 10:21 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 20 April 13:08:35 |
Successful | ||||
| ASI / NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | Successful | |||||
| Crewed flight with seven astronauts. | ||||||||
| 8 April 13:57 |
||||||||
| ESA | Low Earth | Climatology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 15 April 10:57 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Intended: Geosynchronous | Communications Navigation |
15 April | Launch failure | ||||
| Maiden flight of GSLV Mk. II, third stage failure. | ||||||||
| 16 April 15:00[来源请求] |
||||||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Reconnaissance | 21 July | Successful | ||||
| 22 April 23:52[14] |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 3 December 09:16 |
Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Atlas V 501 and Boeing X-37B. | ||||||||
| 24 April 11:19 |
||||||||
| SES World Skies | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 27 April 01:05 |
||||||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Navigation Communications |
在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Final flight of Kosmos-3M. | ||||||||
| 28 April 17:15 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 15 November 09:35:39 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 37P | ||||||||
May | ||||||||
| 14 May 18:20 |
||||||||
| NASA | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 26 May 12:48:11 |
Successful | ||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS assembly | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Crewed flight with six astronauts. Rassvet was launched along with the MLM outfittings that included a spare elbow joint for the European Robotic Arm (ERA) (which was launched with Nauka) and an ERA-portable workpost used during EVAs, as well as a heat radiator, internal hardware and an experiment airlock for launching CubeSats to be positioned on the modified passive forward port near the nadir end of the Nauka module.[15] | ||||||||
| 20 May 21:58:22[18] |
||||||||
| JAXA | Intended: Cytherocentric Actual: Heliocentric, corrected to Cytherocentric |
Venus orbiter | 在轨 | Operational after partial spacecraft failure | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Solar sail | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| ⚀ |
Waseda | Low Earth | Earth observation | 15 August[19] | Spacecraft failure[16][20] | |||
| ⚀ |
Kagoshima | Low Earth | Earth observation | 28 June[22] – 14[23] July | Partial spacecraft failure | |||
| ⚀ |
Soka | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 26 June[24] | Successful | |||
| UNISEC | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Spacecraft failure[16][26] | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| JAXA | Heliocentric | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Successful | ||||
| Waseda-SAT2 never contacted ground, Hayato affected by communications problems, contact lost with Shin'en on 21 May, unclear if data has been received since.[16] DCAM spacecraft deployed from IKAROS and used to observe deployment of the solar sail.[17] Akatsuki malfunctioned during Cytherocentric orbit insertion, and failed to enter orbit. It managed to orbit around Venus five years later. | ||||||||
| 21 May 22:01 |
||||||||
| SES Astra | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Bundeswehr | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 28 May 03:00 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
June | ||||||||
| 2 June 01:59 |
||||||||
| USEF | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 2 June 15:53:04 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 3 June 22:00:08 |
||||||||
| ARABSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 4 June 18:45[31] |
||||||||
| SpaceX | Low Earth | Boilerplate | 27 June 00:50[36] |
Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Falcon 9.[29][30] | ||||||||
| 10 June 08:01[37] |
||||||||
| KARI | Intended: Low Earth | Technology demonstration | +137 seconds | Launch failure | ||||
| Exploded during first stage burn.[7] | ||||||||
| 15 June 01:39[39] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 15 June 14:42 |
||||||||
| SSC | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| SSC | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNES | Low Earth (SSO)[42] | Helioseismology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Hartron-Arkos | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| BPA-1 intentionally remained attached to upper stage. | ||||||||
| 15 June 21:35 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 24 | 26 November 04:46:53 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts | ||||||||
| 21 June 02:14 |
||||||||
| DLR | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 22 June 19:00 |
||||||||
| IAI / Israeli Defense Forces | Low Earth (retrograde) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational[45] | ||||
| Known as Ofek-8 before launch.[43] | ||||||||
| 26 June 21:41 |
||||||||
| ARABSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| KARI | Geosynchronous[47] | Communications Meteorology Oceanography |
在轨 | Successful[48] | ||||
| 30 June 15:35 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 6 September 12:53:20 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 38P | ||||||||
July | ||||||||
| 10 July 18:40 |
||||||||
| Echostar | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 12 July[49] 03:53 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ASAL | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
StudSat | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| NDRE | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
SUPSI | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| AISSat and TIsat cubeSats to be launched as NLS-6, coordinated by UTIAS | ||||||||
| 31 July 21:30 |
||||||||
| CNSA | IGSO | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
August | ||||||||
| 4 August 20:59 |
||||||||
| Nilesat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| RASCOM-QAF | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 9 August 22:49[50] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 14 August 11:07 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Intended: Geosynchronous Actual: GTO |
Communications | 在轨 | Partial spacecraft failure[51] Operational | ||||
| Maiden flight of Atlas V 531; liquid apogee engine failed to operate during orbital insertion process.[51] | ||||||||
| 24 August 07:10 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
September | ||||||||
| 2 September 00:53:43 |
||||||||
(Glonass-M 736) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 737) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
(Glonass-M 738) |
VKS | Medium Earth | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| 4 September 16:14 |
||||||||
| Sinosat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 8 September 03:30 |
||||||||
| Gonets Satellite System[52] | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| VKS | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 10 September 10:22 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 20 February 2011 16:12 |
Successful | ||||
| ISS flight 39P | ||||||||
| 11 September[53] 11:17 |
||||||||
| JAXA | Tundra | Navigation | 在轨 | Successful[55] | ||||
| 21 September 04:03:30 |
||||||||
| NRO | Low Earth (retrograde) | 在轨 | Operational | |||||
| NRO Launch 41 | ||||||||
| 22 September 02:42[56] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 26 September 04:41 |
||||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration Space surveillance |
在轨 | Operational | ||||
| First orbital launch of Minotaur IV. | ||||||||
| 30 September[57] 17:01[1] |
||||||||
| VKS | Molniya | Missile defense | 15 October 2022[58] | Successful | ||||
| Final flight of Molniya-M.[1] | ||||||||
October | ||||||||
| 1 October 10:59:57[59] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Selenocentric[60] | Lunar orbiter | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 6 October 00:49 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 7 October 23:10:57 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 25 | 16 March 2011 07:54 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts, maiden flight of modernised Soyuz-TMA spacecraft. | ||||||||
| 14 October 18:53[61] |
||||||||
| XM Satellite Radio | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 19 October 17:10:59 |
||||||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Globalstar | Low Earth | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 27 October 15:11:53 |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | ISS logistics | 24 January 2011 | Successful[62] | ||||
| ISS flight 40P. | ||||||||
| 28 October[64] 21:51 |
||||||||
| Eutelsat | Intended: Geosynchronous Actual: GTO |
Communications | 在轨 | Spacecraft failure[65] | ||||
| BSAT | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational[67] | ||||
| Eutelsat W3B written-off as a total loss immediately after launch due to an oxidizer leak in the satellite's main propulsion system.[63] | ||||||||
| 31 October 16:26 |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
November | ||||||||
| 2 November 00:59[68] |
||||||||
| VKS | Molniya | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 4 November 18:37[69] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Low Earth (SSO) | Meteorology | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 6 November 02:20 |
||||||||
| ASI | Low Earth (SSO) | Earth observation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Final flight of Delta II 7420.[70] | ||||||||
| 14 November 17:29 |
||||||||
| SkyTerra | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational[71] | ||||
| 20 November 01:25 |
||||||||
| STP | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| ⚀ |
NASA AMES | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| ⚀ |
University of Michigan | Low Earth | Auroral | 在轨 | Operational | |||
| NASA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Partial spacecraft failure | ||||
| ⚀ |
NASA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 17 September 2011[72] | Successful | |||
| Texas | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| UT Austin | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| USAFA | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Maiden flight of Minotaur IV/HAPS. NanoSail-D2 should have been deployed from FASTSAT seven days after launch, immediate deployment failed but ejection was confirmed almost two months later on 19 January 2011 | ||||||||
| 21 November 22:58[73] |
||||||||
| NRO | Geosynchronous | Reconnaissance | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| NROL-32 mission. | ||||||||
| 24 November 16:09[74] |
||||||||
| CNSA | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 26 November 18:39 |
||||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Avanti[76] | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 40th consecutive Ariane 5 launch success. | ||||||||
December | ||||||||
| 5 December 10:25 |
||||||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | 5 December | Launch failure | ||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | ||||||
| VKS | Intended: Medium Earth | Navigation | ||||||
| Maiden flight of Blok DM-03. Incorrect fuelling of upper stage led to mass being too great to achieve parking orbit, reentered over the Pacific Ocean.[8] | ||||||||
| 8 December 15:43 |
||||||||
| SpaceX / NASA | Low Earth | Flight test | 8 December 19:02 |
Successful | ||||
| ⚀ |
U.S. Army | Low Earth | Communications | 12 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
Northrop Grumman / USC | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 22 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
NRO | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 6 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
NRO | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 16 January 2011 | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 30 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 31 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 30 December | Successful | |||
| ⚀ |
LANL | Low Earth | Technology demonstration | 31 December | Successful | |||
| COTS Demo 1; maiden flight of the SpaceX Dragon; Mayflower included Caerus payload operated by USC. | ||||||||
| 15 December 19:09[77] |
||||||||
| Roscosmos | Low Earth (ISS) | Expedition 26 | 24 May 2011 02:27 |
Successful | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. | ||||||||
| 17 December 20:04 |
||||||||
| CNSA | IGSO | Navigation | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 25 December 10:34 |
||||||||
| ISRO | Intended: Geosynchronous | Communications | 25 December | Launch failure | ||||
| Disintegrated during first stage flight. | ||||||||
| 26 December 22:51 |
||||||||
| Eutelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| 29 December 21:27 |
||||||||
| Hispasat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
| Koreasat | Geosynchronous | Communications | 在轨 | Operational | ||||
关闭
| ← 一月 • 二月 • 三月 • 四月 • 五月 • 六月 • 七月 • 八月 • 九月 • 十月 • 十一月 • 十二月 → |
Remove ads
亚轨道发射
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
更多信息 发射时间 (UTC), 运载火箭 ...
| 发射时间 (UTC) | 运载火箭 | 火箭编号 | 发射场 | 发射服务提供商(英语:List of launch service providers) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效载荷 (⚀ = 立方星) |
载荷用户 | 轨道 | 功能 | 再入时间 (UTC) | 结果 | ||
| 附注 | |||||||
| 10 January 23:00:00[80] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 10 January | Successful | |||
| 11 January 11:55[81] |
|||||||
| PLA | Suborbital | ABM target | 11 January | Successful | |||
| Target | |||||||
| 11 January 12:00 |
|||||||
| PLA | Suborbital | ABM test | 11 January | Successful[82] | |||
| Interceptor | |||||||
| 14 January 06:50[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 14 January 07:35[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 14 January[84] 07:45 |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 14 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 548 km(341 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 06:50[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 07:35[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January 10:30[84] |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 116 km(72 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 15 January[84] 07:45 |
|||||||
| ISRO | Suborbital | Solar/Aeronomy | 15 January | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 523 km(325 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 January 08:25[81] |
|||||||
| DGA | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 January | Successful | |||
| First launch of M51 from a submarine[85] | |||||||
| 31 January 11:40[86] |
FTG-06 | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 30 January | Successful[86] | |||
| Maiden flight of Trident I in LV-2 configuration, interceptor failed[86] | |||||||
| 31 January | FTG-06 | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM test | 30 January | Spacecraft failure[86] | |||
| Radar tracking problem caused by unexpected "chuffing", compounded by thruster problem on interceptor, resulted in failure to intercept Trident[86] | |||||||
| 3 February | |||||||
| ISA | Suborbital | Biological | 3 February | Successful[87] | |||
| 4 February 08:03:07 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 4 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 7 February 05:20 |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 7 February | Successful[88] | |||
| Travelled 3,500 km(2,175 mi) downrange | |||||||
| 9 February 09:01:00 |
|||||||
| Alaska | Suborbital | Auroral | 9 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 12 February 04:44[89] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 12 February | Successful[89] | |||
| Destroyed by Boeing YAL-1 aircraft | |||||||
| 12 February 05:31:20 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 12 February | Successful[80] | |||
| 15 February 09:49:11 |
|||||||
| Dartmouth | Suborbital | Auroral | 15 February | Successful[80] | |||
| Apogee: 803 km(499 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 17 February | |||||||
| US Army | Suborbital | Target | 17 February | Successful | |||
| Target for MIM-104 Patriot PAC-3 MSE test, successful intercept | |||||||
| 4 March 04:50 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 4 March | Successful | |||
| 15 March | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Target | 15 March | Launch failure | |||
| Target for ABM test, deviated from planned course, interceptor not launched[90] | |||||||
| 22 March | |||||||
| DSTO/U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 22 March | Successful | |||
| Hypersonic research experiment | |||||||
| 26 March 13:43 |
|||||||
| SSC / ESA | Suborbital | Microgravity | 26 March 13:55 |
Successful[91] | |||
| Apogee: 700 km(435 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 March 00:14[83] |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 March | Successful | |||
| 27 March 00:18[83] |
|||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 27 March | Successful | |||
| 27 March 14:09:56[93] |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Test flight | 27 March | Successful | |||
| CalPoly | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 March | Successful | |||
| Kentucky Space | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 March | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Terrier-Improved Malemute, apogee: 270 km(168 mi)[83] | |||||||
| 27 March 19:37[83] |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 March | Successful | |||
| 22 April 23:00[14] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 22 April | Spacecraft failure[95] | |||
| Maiden flight of Minotaur IV, loss of contact with HTV nine minutes after launch.[95] | |||||||
| 3 May 09:47:00 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 3 May | Successful | |||
| 3 May 18:32:00 |
|||||||
| CU Boulder | Suborbital | Geospace/Solar | 3 May | Successful | |||
| Used to calibrate the Solar Dynamics Observatory[96] | |||||||
| 4 May 12:41:02[99] |
|||||||
| CSG | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 4 May | Successful | |||
| NMSU | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | Successful | ||||
| UNM | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | Successful | ||||
| Celestis | Suborbital | Space burial | Successful | ||||
| Reached an apogee of 113 km(70 mi), successfully recovered.[98] | |||||||
| 6 May 03:50[100][101] |
Sounding Rocket VII | ||||||
| NSPO/NCU | Suborbital | Ionospheric research | 6 May | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 289 km(180 mi)[100] | |||||||
| 8 May | |||||||
| ASFC | Suborbital | Missile test | 8 May | Successful | |||
| 8 May | |||||||
| ASFC | Suborbital | Missile test | 8 May | Successful | |||
| 17 May 11:29 |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 17 May | Successful | |||
| Travelled 2,500 km(1,553 mi) downrange | |||||||
| 21 May 09:00:00 |
|||||||
| CU Boulder | Suborbital | Astronomy | 21 May | Spacecraft failure[80] | |||
| 6 June 22:25[83] |
|||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Test flight | 6 June | Successful | |||
| Two stage test vehicle, non-intercept test | |||||||
| 8 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 8 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 42 | |||||||
| 8 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 8 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 42 | |||||||
| 9 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 9 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 43 | |||||||
| 9 June | |||||||
| US Navy | Suborbital | Test flight | 9 June | Successful | |||
| Follow-on Commander's Evaluation Test 43 | |||||||
| 16 June 10:01 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Missile test | 16 June | Successful | |||
| Travelled 6,743 km(4,190 mi) to Kwajalein Atoll | |||||||
| 24 June 11:17:00 |
|||||||
| Colorado | Suborbital | Student research | 24 June | Successful | |||
| 30 June 10:40:01[83] |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Missile test | 30 June | Successful | |||
| 10 July 11:32[102] |
|||||||
| DGA/Marine nationale | Suborbital | Test flight | 10 July | Successful | |||
| 11 July | |||||||
| Caltech[103] | Suborbital | Astronomy | 11 July | Successful | |||
| 27 July | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Target | 27 July | Successful | |||
| Target for ABM test, intercepted successfully by AAD | |||||||
| 30 July 18:18 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Solar | 30 July | Successful | |||
| 4 August 09:15 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Test flight Technology |
4 August | Successful | |||
| Tests of Nihka rocket motor, with secondary technology experiments | |||||||
| 6 August[104] | |||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 6 August | Successful | |||
| 6 August[104] | |||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 6 August | Successful | |||
| 23 August 17:57 |
|||||||
| SwRI | Suborbital | Solar | 23 August | Successful | |||
| 30 August 20:00[106] |
|||||||
| JAXA/TMU/Kagawa /Shizuoka |
Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 30 August | Partial spacecraft failure[105] | |||
| High-voltage control experiments not conducted as planned[105] | |||||||
| 17 September 10:03 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Test flight | 17 September | Successful | |||
| 21 September 13:07:30[107] |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 21 September 13:23[107] |
Successful[107] | |||
| 6 October | |||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Aegis radar target | 6 October | Successful | |||
| Aegis radar target, detected by STSS-Satellites | |||||||
| 6 October | |||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | Aegis radar target | 6 October | Successful | |||
| Aegis radar target, detected by STSS-Satellites | |||||||
| 7 October[来源请求] 03:10 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 7 October | Successful | |||
| 21 October[108] 17:00 |
|||||||
| U.S. Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 21 October | Successful | |||
| 27 October 10:15[109] |
|||||||
| DLR | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 27 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 153 km(95 mi) | |||||||
| 28 October[来源请求] 09:59 |
|||||||
| RVSN | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 28 October 10:30[来源请求] |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 28 October 10:30[来源请求] |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 28 October | Successful | |||
| 29 October[来源请求] 01:10 |
|||||||
| VMF | Suborbital | Missile test | 29 October | Successful | |||
| 29 October 03:06 |
JFTM-4 | ||||||
| JMSDF/MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 29 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 161 km(100 mi), intercepted by SM-3 | |||||||
| 29 October 03:09 |
JFTM-4 | ||||||
| JMSDF | Suborbital | ABM test | 29 October | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 161 km(100 mi), intercepted target | |||||||
| 25 November 04:40 |
|||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 25 November | Successful | |||
| 4 December 04:21[110] |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 4 December | Successful | |||
| 5 December 19:11 |
|||||||
| RVSN | Suborbital | Missile test | 5 December | Successful | |||
| 6 December 16:45 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Technology demonstration | 6 December | Successful | |||
| 6 December 17:19 |
|||||||
| INPE | Suborbital | Microgravity | 6 December | Successful | |||
| Test for Operation Maracati 2[111] | |||||||
| 10 December | |||||||
| Indian Army | Suborbital | Missile test | 10 December | Launch failure | |||
| Upgraded Agni II version, fell into the sea shortly after launch | |||||||
| 12 December 06:38[112] |
|||||||
| New Hampshire | Suborbital | Geospace | 12 December | Launch failure[113] | |||
| 12 December 12:35 |
|||||||
| INPE | Suborbital | Microgravity | 12 December 12:51 |
Successful | |||
| Operation Maracati 2, MICROG 1A payload[114] | |||||||
| 13 December 03:24 |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 13 December | Successful | |||
| 15 December | FTG-06a | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM target | 15 December | Successful | |||
| 15 December | FTG-06a | ||||||
| MDA | Suborbital | ABM test | 15 December | Spacecraft failure | |||
| Interceptor failed, the cause is under investigation | |||||||
| 19 December 02:36 |
|||||||
| Andøya/DLR | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 19 December | Successful | |||
| 21 December | |||||||
| Army of Pakistan | Suborbital | Missile test | 21 December | Successful | |||
| Apogee: 100 km(62 mi) | |||||||
| 22 December | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 22 December | Successful | |||
| 22 December | |||||||
| DRDO | Suborbital | Missile test | 22 December | Successful | |||
关闭
Remove ads
深空机动
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
更多信息 日期 (UTC), 航天器 ...
| 日期 (UTC) | 航天器 | 事件 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 January | Cassini | 65th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,073 km(667 mi) |
| 28 January | Cassini | 66th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 7,490 km(4,654 mi) |
| 31 January | Artemis P1 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 11,992 km(7,451 mi) at 08:13 UTC[115] |
| 1 February | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 69,222 km(43,013 mi) at 14:44 UTC[115] |
| 13 February | Artemis P1 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 2,958 km(1,838 mi) at 10:06 UTC[115] |
| 13 February | Cassini | Flyby of Mimas | Closest approach: 9,520 km(5,915 mi) |
| 16 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 991 km(616 mi) |
| 22 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 574 km(357 mi) |
| 25 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 398 km(247 mi) |
| 28 February | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 226 km(140 mi) |
| 1 March | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 68,036 km(42,276 mi) at 04:11 UTC[115] |
| 2 March | Cassini | 2nd flyby of Rhea | Closest approach: 100 km(62 mi) |
| 3 March | Cassini | Flyby of Helene | Closest approach: 1,803 km(1,120 mi) |
| 3 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 67 km(42 mi) |
| 7 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 107 km(66 mi) |
| 10 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 286 km(178 mi) |
| 13 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 476 km(296 mi) |
| 16 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 662 km(411 mi) |
| 19 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 848 km(527 mi) |
| 23 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 1,341 km(833 mi) |
| 26 March | Mars Express | Flyby of Phobos | Closest approach: 1,304 km(810 mi) |
| 28 March | Artemis P2 | Lunar flyby | Closest approach: 9,366 km(5,820 mi) at 07:34 UTC[115] |
| 5 April | Cassini | 67th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 7,462 km(4,637 mi) |
| 7 April | Cassini | 2nd flyby of Dione | Closest approach: 504 km(313 mi) |
| 28 April | Cassini | 9th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 103 km(64 mi) |
| 18 May | Cassini | 10th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 201 km(125 mi) |
| 20 May | Cassini | 68th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,400 km(870 mi) |
| 5 June | Cassini | 69th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 2,044 km(1,270 mi) |
| 13 June | Hayabusa | First sample return mission from asteroid | Sample canister successful recovered to Earth |
| 21 June | Cassini | 70th flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 955 km(593 mi) |
| 7 July | Cassini | 71st flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 1,005 km(624 mi) |
| 10 July | Rosetta | Flyby of 21 Lutetia | Closest approach: 3,100 km(1,926 mi)[116] |
| 13 August | Cassini | 11th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 2,554 km(1,587 mi) |
| 25 August | Artemis P1 | LL2 orbit insertion | |
| 24 September | Cassini | 72nd flyby of Titan | Closest approach: 8,175 km(5,080 mi) |
| 6 October | Chang'e 2 | Lunar orbit insertion | |
| 16 October | Cassini | Flyby of Pallene | Closest approach: 36,000 km(22,369 mi) |
| 22 October | Artemis P2 | LL1 orbit insertion | |
| 4 November | Deep Impact | Flyby of Hartley 2 | Closest approach: 700 km(435 mi)[117] |
| 11 November | Cassini | 73rd flyby of Titan | |
| 30 November | Cassini | 12th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 47.9 km(30 mi) |
| 7 December | Akatsuki | 1st flyby of Venus | Cytherocentric orbit insertion failure Closest approach: 550 km(342 mi) |
| 8 December | IKAROS | Flyby of Venus | Closest approach: 80,800 km(50,207 mi) |
| 21 December | Cassini | 13th flyby of Enceladus | Closest approach: 50 km(31 mi) |
| December | Shin'en | Flyby of Venus | not confirmed. |
关闭
Remove ads
舱外活动
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
更多信息 开始时间, 持续时间 ...
| 开始时间 | 持续时间 | 结束时间 | 航天器 | 乘组 | 工作内容 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 January 10:05 |
5 hours 44 minutes |
15:49 | Expedition 22 ISS Pirs |
Prepared the Poisk module for future dockings.[118][119] | ||
| 12 February 02:17 |
6 hours 32 minutes |
08:49 | STS-130 ISS Quest |
Removed a protective cover on a port on the Unity node where Tranquility was berthed halfway through the spacewalk. The pair then transferred a spare parts platform for the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator from the shuttle to the station. Once that task is completed Behnken and Patrick made several connections on the newly installed Tranquility node to begin its activation.[120][121] | ||
| 14 February 02:20 |
5 hours 54 minutes |
08:14 | STS-130 ISS Quest |
Installed ammonia plumbing and connectors between Unity, Destiny and Tranquility and covered them with thermal insulation. Prepared the nadir port on Tranquility for the relocation of the Cupola, and installed handrails on the exterior of Tranquility.[122][123] | ||
| 17 February 02:15 |
5 hours 48 minutes |
08:03 | STS-130 ISS Quest |
Installed additional ammonia plumbing between Unity and Tranquility, removed insulation and launch locks from the Cupola, installed additional handrails on the exterior of Tranquility and performed get-ahead tasks to support the installation of a Power Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) on the exterior of Zarya with cable installation on Unity and the S0 truss.[124][125] | ||
| 9 April 05:31 |
6 hours 27 minutes |
11:58 | STS-131 ISS Quest |
Relocated new an ammonia tank from the Shuttle's payload bay to a temporary stowage location and disconnected the fluid lines to the old ammonia tank on the S1 truss. Retrieved a Japanese seed experiment from the exterior of the Kibo laboratory for return to earth and replaced a failed gyroscope on the S0 truss. Performed get-ahead tasks including the opening of a window flap on the zenith CBM of Harmony, and removed launch restraint bolts from a Flex Hose Rotary Coupler (FHRC) on the P1 truss.[126][127] | ||
| 11 April 05:30 |
7 hours 26 minutes |
12:56 | STS-131 ISS Quest |
The old ammonia tank was removed from the S1 truss and was replaced with the new tank. The electrical connections to the tank were made, but the fluid lines were deferred to the mission's third EVA due to time constraints since the installation was prolonged by a problem with the bolts that hold the tank to the truss. The old tank was relocated to a temporary stowage location on the station and a foot restraint was relocated in preparation for a future shuttle mission's spacewalk.[128][129] | ||
| 13 April 06:14 |
6 hours 24 minutes |
12:36 | STS-131 ISS Quest |
The fluid lines were connected to the new ammonia tank and the old tank was moved to the shuttle's payload bay for return to Earth. Micro-meteoroid debris shields from the Quest airlock which were no longer necessary were brought inside the airlock for return to Earth inside the Leonardo MPLM. The Z1 truss was prepared for the installation of a spare antenna on the next shuttle mission, and a foot restraint was relocated in preparation for a future spacewalk. The retrieval of an external carrier plate on Columbus was deferred to another shuttle mission due to time constraints after problems were encountered with attaching the old ammonia tank to a carrier in the payload bay, and several other tasks were deferred to later EVAs due to the replanning from the problems with the mission's second EVA.[130][131] | ||
| 17 May 11:54 |
7 hours 25 minutes |
19:19 | STS-132 ISS Quest |
Installed a spare space-to-ground Ku-band antenna on the Z1 truss; installed new tool platform on Dextre, and broke torque on bolts holding replacement batteries to the ICC-VLD cargo carrier.[132][133] | ||
| 19 May 10:38 |
7 hours 9 minutes |
17:47 | STS-132 ISS Quest |
Repaired Atlantis' Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS); P6 battery replacement (4 of 6 units); and removed gimbal locks from the Ku-band antenna installed on the first EVA of the mission.[134][135] | ||
| 21 May 10:27 |
6 hours 46 minutes |
17:13 | STS-132 ISS Quest |
P6 battery replacement (final 2 of 6 units); installed ammonia "jumpers" at the P4/P5 interface; retrieved a spare PDGF from Atlantis' payload bay and stowed it inside the Quest airlock. The spacewalkers also replenished supplies of EVA tools in toolboxes on the exterior of the station.[136][137] | ||
| 27 July 04:11 |
6 hours 42 minutes |
10:53 | Expedition 24 ISS Pirs |
Replaced an ATV video camera on Zvezda, routed command and data handling lines from Zvezda and Zarya to the new Rassvet module as well as made KURS connections between Rassvet and Zarya to allow future automated dockings to the new module. Then the two cosmonauts jettisoned the old ATV video camera.[138][139] | ||
| 7 August 11:19 |
8 hours 3 minutes |
19:22 | Expedition 24 ISS Quest |
Attempted to replace failed S1 ammonia pump module. The spacewalkers did not complete all of the planned tasks due to a quick disconnect that got stuck and would not release. The pair had to complete a "bake-out" in order to ensure there was no ammonia on their suits before re-entering the Space Station.[140][141] | ||
| 11 August 12:27 |
7 hours 26 minutes |
19:53 | Expedition 24 ISS Quest |
Completed removal of failed pump module from the S1 truss and began installation preparations on the replacement pump.[142][143] | ||
| 16 August 10:20 |
7 hours 20 minutes |
17:40 | Expedition 24 ISS Quest |
Installed new pump module on the S1 truss.[144][145] | ||
| 15 November 14:55 |
6 hours 27 minutes |
21:22 | Expedition 25 ISS Pirs |
Install a multipurpose workstation on Zvezda, retrieve camera, retrieve kontur, install new materials experiment, collect samples below insulation.[146][147] |
关闭
Remove ads
轨道发射统计
就本章节的主旨而言,每次航天飞行所属的国家以火箭的原产国为准,而不是发射服务提供商或发射场所在国。例如,第聂伯运载火箭虽然从俄罗斯发射,但被计入乌克兰。
- 中国: 15
- 欧洲: 6
- 印度: 3
- 以色列: 1
- 日本: 2
- 韩国: 1
- 俄罗斯: 28
- 乌克兰: 3
- 美国: 15
Remove ads
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
5
10
15
20
Ariane
Atlas
Delta
Falcon
GSLV
H-II
Long March
Minotaur
R-7
R-36
Shuttle
UR
Others
- Ariane 5
- Atlas V
- Delta II
- Delta IV
- Delta IV Heavy
- Falcon 9
- GSLV
- H-IIA
- Long March 2
- Long March 3
- Long March 4
- Minotaur IV
- Molniya-M
- Soyuz-U
- Soyuz-FG
- Soyuz-2
- Dnepr
- Space Shuttle
- Proton-M
- Rokot
- Others
By family
更多信息 Family, Country ...
| Family | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angara | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Ariane | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| GLSV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| H-II | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-7 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-36 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Universal Rocket | 14 | 13 | 1 | 0 |
关闭
By type
更多信息 Rocket, Country ...
| Rocket | Country | Family | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 | Ariane | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V | Atlas | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta II | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta IV | Delta | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dnepr | R-36 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon 9 | Falcon | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| GSLV | GSLV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| H-IIA | H-II | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos | R-12/R-14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 2 | Long March | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3 | Long March | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4 | Long March | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur IV | Minotaur | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Molniya | R-7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Naro | Angara | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton | Universal Rocket | 12 | 11 | 1 | 0 | ||
| PSLV | PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit | Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz | R-7 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-2 | R-7 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| UR-100 | Universal Rocket | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
关闭
By configuration
更多信息 Rocket, Country ...
| Rocket | Country | Type | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 ECA | Ariane 5 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V 401 | Atlas V | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas V 501 | Atlas V | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Atlas V 531 | Atlas V | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Delta II 7420 | Delta II | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight[70] | |
| Delta IV-M+(4,2) | Delta IV | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta IV Heavy | Delta IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dnepr | Dnepr | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Falcon 9 v1.0 | Falcon 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| GSLV Mk I(c) | GSLV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Only flight | |
| GSLV Mk II | GSLV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| H-IIA 202 | H-IIA | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos-3M | Kosmos | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Long March 2D | Long March 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3A | Long March 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3B | Long March 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 3C | Long March 3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4B | Long March 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Long March 4C | Long March 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Minotaur IV | Minotaur IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Minotaur IV / HAPS | Minotaur IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Molniya-M / 2BL | Molniya | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight[1] | |
| Naro-1 | Naro | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / DM-2 | Proton | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / DM-03 | Proton | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton-M / Briz-M | Proton | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | ||
| PSLV-CA | PSLV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Rokot / Briz-KM | UR-100 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Shavit-2 | Shavit | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-2.1a / Fregat-M | Soyuz-2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-U | Soyuz | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-FG | Soyuz | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Space Shuttle | Space Shuttle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
关闭
Remove ads
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
5
10
15
20
25
30
China
France
India
Israel
Japan
Kazakhstan
South Korea
Russia
United States
- Jiuquan
- Taiyuan
- Xichang
- Kourou
- Satish Dhawan
- Palmachim
- Tanegashima
- Baikonur
- Naro
- Dombarovsky
- Plesetsk
- Cape Canaveral
- Kennedy
- Kodiak
- MARS
- Vandenberg
更多信息 Site, Country ...
| Site | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baikonur | 24 | 23 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Cape Canaveral | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Dombarovsky | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Jiuquan | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kennedy | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kodiak | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kourou | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Naro | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Palmachim | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Plesetsk | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Satish Dhawan | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Taiyuan | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Tanegashima | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Vandenberg | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Xichang | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 74 | 70 | 4 | 0 | ||
关闭
已隐藏部分未翻译内容,欢迎参与翻译。
10
20
30
40
- Transatmospheric
- Low Earth
- Low Earth (ISS)
- Low Earth (SSO)
- Low Earth (retrograde)
- Medium Earth
- Geosychronous
(transfer) - Inclined GSO
- High Earth
- Heliocentric
更多信息 Orbital regime, Launches ...
| Orbital regime | Launches | Successes | Failures | Accidentally achieved |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transatmospheric | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Low Earth | 37 | 36 | 1 | 0 | 12 to ISS |
| Medium Earth / Molniya | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | |
| Geosynchronous / GTO | 29 | 27 | 2 | 0 | |
| High Earth / Lunar transfer | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Heliocentric / Planetary transfer | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 74 | 70 | 4 | 0 |
关闭
参考
- 中国国家航天局
- 中国探月网
- Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Gunter's Space Page - Chronology of Space Launches
- 日本宇宙航空研究开发机构
- Jonathan's Space Report(SatCat.txt与Launchlog.txt两项)
- Mission Set Database (NASA GFC)
- NASA
- NASA SpaceFlight.com
- Orbital Report News Agency's Launch Logs
- Space Calander (NASA JPL)
- Southwest Space Archive
- SPACE.com Launch Forecast
- SpaceFlightNow
- Steven Pietrobon's Space Archive
- U.S. Space Objects Registry
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads

