Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Birmingham
City in the West Midlands, England From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Birmingham (/ˈbɜːrmɪŋəm/ ⓘ[4][5][6] BUR-ming-əm) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands region, in England. It is the largest local authority district in England by population[2] and the second-largest city in Britain[a][7] – commonly referred to as the second city of the United Kingdom[8][9][10][11][12] – with a population of 1.16 million people in the city proper in 2022.[2] Birmingham borders the Black Country to its west and, together with the city of Wolverhampton and towns including Dudley and Solihull, forms the West Midlands conurbation. The royal town of Sutton Coldfield is incorporated within the city limits to the northeast. The urban area has a population of 2.65 million.[13]
Located in the West Midlands region of England, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. It is just west of the traditional centre point of England at Meriden,[14] and is the most inland major city in the country,[15] lying north of the Cotswolds and east of the Shropshire Hills. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately 20 miles (32 km) west of the city centre. The city does however have numerous canals, collectively named the Birmingham Canal Navigations.[16]
Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midlands Enlightenment and during the Industrial Revolution, which saw advances in science, technology and economic development, producing a series of innovations that laid many of the foundations of modern industrial society.[17] By 1791, it was being hailed as "the first manufacturing town in the world".[18] Birmingham's distinctive economic profile, with thousands of small workshops practising a wide variety of specialised and highly skilled trades, encouraged exceptional levels of creativity and innovation; this provided an economic base for prosperity that was to last into the final quarter of the 20th century. The Watt steam engine was invented in Birmingham.[19]
The resulting high level of social mobility also fostered a culture of political radicalism which, under leaders from Thomas Attwood to Joseph Chamberlain, was to give it a political influence unparalleled in Britain outside London and a pivotal role in the development of British democracy.[20] From the summer of 1940 to the spring of 1943, Birmingham was bombed heavily by the German Luftwaffe in what is known as the Birmingham Blitz. The damage done to the city's infrastructure, in addition to a deliberate policy of demolition and new building by planners, led to extensive urban regeneration in subsequent decades.
Birmingham's economy is now dominated by the service sector.[21] The city is a major international commercial centre and an important transport, retail, events and conference hub. Its metropolitan economy is the second-largest in the United Kingdom with a GDP of £95.94bn (2014[update]).[22] Its five universities,[23] including the University of Birmingham, make it the largest centre of higher education in the country outside London.[24] Birmingham's major cultural institutions – the City of Birmingham Symphony Orchestra, Birmingham Royal Ballet, Birmingham Repertory Theatre, Library of Birmingham and Barber Institute of Fine Arts – enjoy international reputations,[25] and the city has vibrant and influential grassroots art, music, literary and culinary scenes.[26] Birmingham was the host city for the 2022 Commonwealth Games.[27][28] In 2021, Birmingham was the third most visited city in the UK by people from foreign nations.[29]
Remove ads
Toponymy
The name Birmingham comes from the Old English Beormingahām,[30] meaning the home or settlement of the Beormingas – a tribe or clan whose name means 'Beorma's people' and which may have formed an early unit of Anglo-Saxon administration.[31] Beorma, after whom the tribe was named, could have been its leader at the time of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, a shared ancestor, or a mythical tribal figurehead. Place names ending in -ingahām are characteristic of primary settlements established during the early phases of Anglo-Saxon colonisation of an area, suggesting that Birmingham was probably in existence by the early 7th century at the latest.[32] Surrounding settlements with names ending in -tūn ('farm'), -lēah ('woodland clearing'), -worð ('enclosure') and -field ('open ground') are likely to be secondary settlements created by the later expansion of the Anglo-Saxon population,[33] in some cases possibly on earlier British sites.[34]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Pre-history and medieval
There is evidence of early human activity in the Birmingham area dating back to around 8000 BC,[35] with Stone Age artefacts suggesting seasonal settlements, overnight hunting parties and woodland activities such as tree felling.[36] The many burnt mounds that can still be seen around the city indicate that modern humans first intensively settled and cultivated the area during the Bronze Age, when a substantial but short-lived influx of population occurred between 1700 BC and 1000 BC, possibly caused by conflict or immigration in the surrounding area.[37] During the 1st-century Roman conquest of Britain, the forested country of the Birmingham Plateau formed a barrier to the advancing Roman legions,[38] who built the large Metchley Fort in the area of modern-day Edgbaston in AD 48,[39] and made it the focus of a network of Roman roads.[40] Birmingham was then later established by the Beormingas around the 6th or 7th century as a small settlement in the then heavily forested Arden region in Mercia.
The development of Birmingham into a significant urban and commercial centre began in 1166, when the Lord of the Manor Peter de Bermingham obtained a charter to hold a market at his castle, and followed this with the creation of a planned market town and seigneurial borough within his demesne or manorial estate, around the site that became the Bull Ring.[41] This established Birmingham as the primary commercial centre for the Birmingham Plateau at a time when the area's economy was expanding rapidly, with population growth nationally leading to the clearance, cultivation and settlement of previously marginal land.[42] Within a century of the charter Birmingham had grown into a prosperous urban centre of merchants and craftsmen.[43] By 1327 it was the third-largest town in Warwickshire,[44] a position it would retain for the next 200 years.
Early modern
The principal governing institutions of medieval Birmingham – including the Guild of the Holy Cross and the lordship of the de Birmingham family – collapsed between 1536 and 1547,[45] leaving the town with an unusually high degree of social and economic freedom and initiating a period of transition and growth.[46]
The importance of the manufacture of iron goods to Birmingham's economy was recognised as early as 1538, and grew rapidly as the century progressed.[47] Equally significant was the town's emerging role as a centre for the iron merchants who organised finance, supplied raw materials and traded and marketed the industry's products.[48] By the 1600s Birmingham formed the commercial hub of a network of forges and furnaces stretching from South Wales to Cheshire[49] and its merchants were selling finished manufactured goods as far afield as the West Indies.[50] These trading links gave Birmingham's metalworkers access to much wider markets, allowing them to diversify away from lower-skilled trades producing basic goods for local sale, towards a broader range of specialist, higher-skilled and more lucrative activities.[51]

By the time of the English Civil War Birmingham's booming economy, its expanding population, and its resulting high levels of social mobility and cultural pluralism, had seen it develop new social structures very different from those of more established areas.[52] Relationships were built around pragmatic commercial linkages rather than the rigid paternalism and deference of feudal society, and loyalties to the traditional hierarchies of the established church and aristocracy were weak.[52] The town's reputation for political radicalism and its strongly Parliamentarian sympathies saw it attacked by Royalist forces in the Battle of Birmingham in 1643,[53] and it developed into a centre of Puritanism in the 1630s[52] and as a haven for Nonconformists from the 1660s.[54]
By 1700 Birmingham's population had increased fifteen-fold and the town was the fifth-largest in England and Wales.[55] The 18th century saw this tradition of free-thinking and collaboration blossom into the cultural phenomenon now known as the Midlands Enlightenment.[56] The town developed into a notable centre of literary, musical, artistic and theatrical activity;[57] and its leading citizens – particularly the members of the Lunar Society of Birmingham – became influential participants in the circulation of philosophical and scientific ideas among Europe's intellectual elite.[58] The close relationship between Enlightenment Birmingham's leading thinkers and its major manufacturers[59] – in men like Matthew Boulton and James Keir they were often in fact the same people[60] – made it particularly important for the exchange of knowledge between pure science and the practical world of manufacturing and technology.[61] This created a "chain reaction of innovation",[62] forming a pivotal link between the earlier Scientific Revolution and the Industrial Revolution that would follow.[63]
Industrial Revolution

Birmingham's explosive industrial expansion started earlier than that of the textile-manufacturing towns of the North of England,[64] and was driven by different factors. Instead of the economies of scale of a low-paid, unskilled workforce producing a single bulk product such as cotton or wool in large, mechanised units of production, Birmingham's industrial development was built on the adaptability and creativity of a highly paid workforce with a strong division of labour, practising a broad variety of skilled specialist trades and producing a constantly diversifying range of products, in a highly entrepreneurial economy of small, often self-owned workshops.[65] This led to exceptional levels of inventiveness: between 1760 and 1850 – the core years of the Industrial Revolution – Birmingham residents registered over three times as many patents as those of any other British town or city.[66]
The demand for capital to feed rapid economic expansion also saw Birmingham grow into a major financial centre with extensive international connections.[67] Lloyds Bank was founded in the town in 1765,[68] and Ketley's Building Society, the world's first building society, in 1775.[69] By 1800 the West Midlands had more banking offices per head than any other region in Britain, including London.[67]

Innovation in 18th-century Birmingham often took the form of incremental series of small-scale improvements to existing products or processes,[70] but also included major developments that lay at the heart of the emergence of industrial society.[17] In 1709 the Birmingham-trained Abraham Darby I moved to Coalbrookdale in Shropshire and built the first blast furnace to successfully smelt iron ore with coke, transforming the quality, volume and scale on which it was possible to produce cast iron.[71] In 1732 Lewis Paul and John Wyatt invented roller spinning, the "one novel idea of the first importance" in the development of the mechanised cotton industry.[72] In 1741 they opened the world's first cotton mill in Birmingham's Upper Priory.[73] In 1746 John Roebuck invented the lead chamber process, enabling the large-scale manufacture of sulphuric acid,[74] and in 1780 James Keir developed a process for the bulk manufacture of alkali,[75] together marking the birth of the modern chemical industry.[76] In 1765 Matthew Boulton opened the Soho Manufactory, pioneering the combination and mechanisation under one roof of previously separate manufacturing activities through a system known as "rational manufacture".[77] As the largest manufacturing unit in Europe, this came to symbolise the emergence of the factory system.[78]
Most significant, however, was the development in 1776 of the industrial steam engine by James Watt and Matthew Boulton.[79] Freeing for the first time the manufacturing capacity of human society from the limited availability of hand, water and animal power, this was arguably the pivotal moment of the entire Industrial Revolution and a key factor in the worldwide increases in productivity over the following century.[80]
Regency and Victorian

Birmingham rose to national political prominence in the campaign for political reform in the early 19th century, with Thomas Attwood and the Birmingham Political Union bringing the country to the brink of civil war during the Days of May that preceded the passing of the Reform Act 1832.[81] The union's meetings on Newhall Hill in 1831 and 1832 were the largest political assemblies Britain had ever seen.[82] Lord Durham, who drafted the act, wrote that "the country owed Reform to Birmingham, and its salvation from revolution".[83] This reputation for having "shaken the fabric of privilege to its base" in 1832 led John Bright to make Birmingham the platform for his successful campaign for the Reform Act 1867, which extended voting rights to the urban working class.[84]
The original charter of incorporation, dated 31 October 1838, was received in Birmingham on 1 November, then read in the town hall on 5 November with elections for the first Birmingham Town Council being held on 26 December. Sixteen aldermen and 48 councillors were elected and the borough was divided into 13 wards. William Scholefield became the first mayor and William Redfern was appointed as town clerk. Birmingham Town Police were established the following year.[citation needed]
Birmingham's tradition of innovation continued into the 19th century. Birmingham was the terminus for both of the world's first two long-distance railway lines: the 82-mile (132 km) Grand Junction Railway of 1837 and the 112-mile (180 km) London and Birmingham Railway of 1838.[85] Birmingham schoolteacher Rowland Hill invented the postage stamp and created the first modern universal postal system in 1839.[86] Alexander Parkes invented the first human-made plastic in the Jewellery Quarter in 1855.[87]
By the 1820s, the country's extensive canal system had been constructed, giving greater access to natural resources and fuel for industries. During the Victorian era, the population of Birmingham grew rapidly to well over half a million[88] and Birmingham became the second largest population centre in England. Birmingham was granted city status in 1889 by Queen Victoria.[89] Joseph Chamberlain, mayor of Birmingham and later an MP, and his son Neville Chamberlain, who was Lord Mayor of Birmingham and later the British Prime Minister, are two of the most well-known political figures who have lived in Birmingham. The city established its own university in 1900.[90]
20th century and contemporary


The city suffered heavy bomb damage during World War II's "Birmingham Blitz". The city was also the scene of two scientific discoveries that were to prove critical to the outcome of the war.[91] Otto Frisch and Rudolf Peierls first described how a practical nuclear weapon could be constructed in the Frisch–Peierls memorandum of 1940,[92] the same year that the cavity magnetron, the key component of radar and later of microwave ovens, was invented by John Randall and Henry Boot.[93] Details of these two discoveries, together with an outline of the first jet engine invented by Frank Whittle in nearby Rugby, were taken to the United States by the Tizard Mission in September 1940, in a single black box later described by an official American historian as "the most valuable cargo ever brought to our shores".[94]
The city was extensively redeveloped during the 1950s and 1960s.[95][96] This included the construction of large tower block estates, such as Castle Vale. The Bull Ring was reconstructed and New Street station was redeveloped. In the decades following World War II, the ethnic makeup of Birmingham changed significantly, as it received waves of immigration from the Commonwealth of Nations and beyond.[97] The city's population peaked in 1951 at 1,113,000 residents.[88]

21 people were killed and 182 were injured in a series of bomb attacks in 1974, thought to be carried out by the Provisional IRA. The bombings were the worst terror attacks in England up until the 2005 London bombings[98] and consisted of bombs being planted in two pubs in central Birmingham. Six men were convicted, who became known later as the Birmingham Six and sentenced to life imprisonment. They were acquitted after 16 years by the Court of Appeal.[99] The convictions are now considered one of the worst miscarriages of justice in the UK in recent times. The true perpetrators of the attacks are yet to be arrested.[100][101][102]

Birmingham remained by far Britain's most prosperous provincial city as late as the 1970s,[103] with household incomes exceeding even those of London and the South East,[104] but its economic diversity and capacity for regeneration declined in the decades that followed World War II as Central Government sought to restrict the city's growth and disperse industry and population to the stagnating areas of Wales and Northern England.[105] These measures hindered "the natural self-regeneration of businesses in Birmingham, leaving it top-heavy with the old and infirm",[106] and the city became increasingly dependent on the motor industry. The recession of the early 1980s saw Birmingham's economy collapse, with unprecedented levels of unemployment and outbreaks of social unrest in inner-city districts.[107]
Since the turn of the 21st century, many parts of Birmingham have been transformed, with the redevelopment of the Bullring Shopping Centre,[108] the construction of the new Library of Birmingham (the largest public library in Europe) and the completed regeneration of old industrial areas such as Brindleyplace, The Mailbox and the International Convention Centre, ongoing rebuilding of Eastside, Digbeth, and Centenary Square, as well as the rationalisation of the Inner Ring Road. In 1998 Birmingham hosted the 24th G8 summit. The city successfully hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games.[109][28]
On 5 September 2023, Birmingham city council issued a Section 114 notice to say that it could not meet its financial commitments after an equal pay lawsuit.[110] Effectively this meant the council was bankrupt. Major contributing factors include a £1.1 billion sum that has been paid out since 2010 for equal pay claims, an ongoing bill for £760 million, increasing by £14 million a month, and problems with a new IT system that was projected to cost £19 million, but is now closer to £100 million. There is a projected £87 million deficit for the financial year 2023/2024.[111]
Remove ads
Government
Summarize
Perspective


Birmingham City Council has 104 councillors representing 69 wards as of 2024.[112] Its headquarters are at the Council House in Victoria Square. As of 2023[update], the council has a Labour Party majority and is led by John Cotton.[113][114] Labour replaced the previous no overall control status at the May 2012 elections.[115] The honour and dignity of a Lord Mayoralty was conferred on Birmingham by Letters Patent on 3 June 1896.[116]
Birmingham's ten parliamentary constituencies are represented in the House of Commons as of 2024[update] by one Conservative, one independent and eight Labour MPs.[117]
Originally part of Warwickshire, Birmingham expanded in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, absorbing parts of Worcestershire to the south and Staffordshire to the north and west. The city absorbed Sutton Coldfield in 1974 and became a metropolitan borough in the new West Midlands county,[118] comprising Birmingham, Coventry, Dudley, Sandwell, Solihull, Walsall, and Wolverhampton. A top-level government body, the West Midlands Combined Authority, was formed in April 2016. The WMCA holds devolved powers in transport, development planning, economic growth, and large-scale investment. The authority is governed by a directly elected mayor, currently Labour's Richard Parker, similar to the Mayor of London.[119]
Geography
Summarize
Perspective
Birmingham is located in the centre of the West Midlands region of England on the Birmingham Plateau – an area of relatively high ground, ranging between 500 and 1,000 feet (150 and 300 metres) above sea level and crossed by Britain's main north–south watershed between the basins of the Rivers Severn and Trent. To the immediate south west of the city lie the Lickey Hills,[120] Clent Hills and Walton Hill, which reach 1,033 feet (315 m) and have extensive views over the city. Birmingham is drained only by minor rivers and brooks, primarily the River Tame and its tributaries the Cole and the Rea. Birmingham is located significantly inland, and its nearest body of sea is at Liverpool Bay. It lies at the same latitude as Lowestoft, Britain's easternmost settlement; it is therefore much more proximate to the western coast of Wales, at Cardigan Bay.[121][122]

The City of Birmingham forms a conurbation with the borough of Solihull to the south east, and with the city of Wolverhampton and the industrial towns of the Black Country to the north west, which form the West Midlands Built-up Area covering 59,972 ha (600 km2; 232 sq mi).[citation needed] Surrounding this is Birmingham's metropolitan area – the area to which it is closely economically tied through commuting – which includes the town of Tamworth and the city of Lichfield in Staffordshire to the north; the city of Coventry and the towns of Nuneaton, Bedworth, Whitnash, Kenilworth, Rugby, Atherstone, Coleshill, Warwick and Leamington Spa to the east in Warwickshire and the Worcestershire towns of Redditch and Bromsgrove to the south west.[123]
As the crow flies, Birmingham lies approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-west of London, 85 miles (137 km) north-east of the Welsh capital Cardiff, 45 miles (72 km) south-west of Nottingham, 70 miles (110 km) south of Manchester, and 75 miles (121 km) north-north-east of Bristol.
Much of the area now occupied by the city was originally a northern reach of the ancient Forest of Arden and the city remains relatively densely covered by oak in a large number of districts such as Moseley, Saltley, Yardley, Stirchley and Hockley. These places, with names ending in "-ley", deriving from Old English -lēah meaning "woodland clearing", are named after the former forest.[124]
Geology
Birmingham is dominated by the Birmingham Fault, which runs diagonally through the city from the Lickey Hills in the south west, passing through Edgbaston and the Bull Ring, to Erdington and Sutton Coldfield in the north east.[125] To the south and east of the fault the ground is largely softer Mercia Mudstone, interspersed with beds of Bunter pebbles and crossed by the valleys of the Rivers Tame, Rea and Cole and their tributaries.[126] To the north and west of the fault, between 150 and 600 feet (46 and 183 metres) higher than the surrounding area and underlying much of the city centre, lies a long ridge of harder Keuper Sandstone.[127][128] The bedrock underlying Birmingham was mostly laid down during the Permian and Triassic periods.[125]
The area has evidence of glacial deposits, with prominent erratic boulders becoming a tourist attraction in the early 1900s.[129][130][131]
Climate
Birmingham has a temperate maritime climate (Cfb according to the Köppen climate classification), like much of the British Isles, with average maximum temperatures in summer (July) being around 21.3 °C (70.3 °F); and in winter (January) around 6.7 °C (44.1 °F).[132] Between 1971 and 2000 the warmest day of the year on average was 28.8 °C (83.8 °F)[133] and the coldest night typically fell to −9.0 °C (15.8 °F).[134] Some 11.2 days each year rose to a temperature of 25.1 °C (77.2 °F) or above[135] and 51.6 nights reported an air frost.[136] The highest recorded temperature recorded at the Edgbaston Campus was 37.4 °C (99.3 °F),[137] whilst a temperature of 37.0 °C (98.6 °F) was recorded at Birmingham Airport on the city's eastern edge, both recorded on 19 July 2022.[138]
Like most other large cities, Birmingham has a considerable urban heat island effect.[139] During the coldest night recorded, 14 January 1982, the temperature fell to −20.8 °C (−5.4 °F) at Birmingham Airport, but just −14.3 °C (6.3 °F) at Edgbaston, near the city centre.[140] Birmingham is a snowy city relative to other large UK conurbations, due to its inland location and comparatively high elevation.[141] Between 1961 and 1990 Birmingham Airport averaged 13.0 days of snow lying annually,[142] compared to 5.33 at London Heathrow.[143] Snow showers often pass through the city via the Cheshire gap on north westerly airstreams, but can also come off the North Sea from north easterly airstreams.[141]
The city has been known to experience tornadoes: according to TORRO, Birmingham experienced 15 significant tornadoes between 1946 and 2005, with some being incredibly destructive. Most notably, a deadly F3 tornado on June 14, 1931, and another IF3 tornado which followed a similar path on July 28, 2005, becoming the United Kingdom's costliest tornado on record.[144][145] On 23 November 1981, during a record-breaking nationwide tornado outbreak, three tornadoes touched down within the Birmingham city limits – in Erdington, Selly Oak, and King's Heath–with three more tornadoes touching down within the boundaries of the wider West Midlands county.[146][144] Notable tornadoes also struck the city in 1946, 1968, and 1999.[144]
Environment

There are 571 parks within Birmingham[155] – more than any other European city[156] – totalling over 3,500 hectares (14 sq mi) of public open space.[155] The city has over six million trees,[156] and 250 miles (400 kilometres) of urban brooks and streams.[155] Sutton Park, which covers 2,400 acres (971 ha) in the north of the city,[157] is the largest urban park in Europe and a national nature reserve.[155] Birmingham Botanical Gardens, located close to the city centre, retains the regency landscape of its original design by J. C. Loudon in 1829,[158] while the Winterbourne Botanic Garden in Edgbaston reflects the more informal Arts and Crafts tastes of its Edwardian origins.[159]
Several green spaces within the borough are designated as green belt, as a portion of the wider West Midlands Green Belt. This is a strategic local government policy used to prevent urban sprawl and preserve greenfield land. Areas included are the aforementioned Sutton Park; land along the borough boundary by the Sutton Coldfield, Walmley and Minworth suburbs; Kingfisher, Sheldon, Woodgate Valley country parks; grounds by the Wake Green football club; Bartley and Frankley reservoirs; and Handsworth cemetery with surrounding golf courses.[160]
Birmingham has many areas of wildlife that lie in both informal settings such as the Project Kingfisher and Woodgate Valley Country Park and in a selection of parks such as Lickey Hills Country Park, Pype Hayes Park & Newhall Valley, Handsworth Park, Kings Heath Park, and Cannon Hill Park, the latter also housing the mini zoo, Birmingham Wildlife Conservation Park.[161]
Remove ads
Demographics
Summarize
Perspective

The 2021 census recorded 1,144,900 people living in Birmingham, an increase of around 6.7% from 2011 when 1,073,045 were recorded.[163] It is the 27th largest city in Europe by population within its city boundary.[164] Birmingham's continuous urban area extends beyond the city's boundaries: the Birmingham Larger Urban Zone, a Eurostat measure of the functional city-region approximated to local government districts, had a population of 2,357,100 in 2004.[165] In addition to Birmingham itself, the LUZ (West Midlands conurbation) includes the Metropolitan Boroughs of Dudley, Sandwell, Solihull and Walsall, along with the districts of Lichfield, Tamworth, North Warwickshire and Bromsgrove.[166] Beyond this is the wider metropolitan area with a population numbering 3,558,916 in 2019 according to Eurostat.[167] Around 305,688 or 26.7% of the population in 2021 were foreign-born, making it a city with one of the largest migrant populations in Europe.[168]

Ethnic groups
According to figures from the 2021 census, 48.7% of the population was White (42.9% White British, 1.5% White Irish, 4.0% Other White, 0.2% Roma, 0.1% Irish Traveller), 31% were Asian (17.0% Pakistani, 5.8% Indian, 4.2% Bangladeshi, 1.1% Chinese, 2.9% Other Asian), 10.9% were Black (5.8% African, 3.9% Caribbean, 1.2% Other Black), 4.8% of Mixed race (2.2% White and Black Caribbean, 0.4% White and Black African, 1.1% White and Asian, 1.1% Other Mixed), 1.7% Arab and 4.6% of Other ethnic heritage.[169] The 2021 census showed 26.7% of the population were born outside the UK, an increase of 4.5% percentage points from 2011.[168] Figures showed that the five largest foreign-born groups living in Birmingham were born in Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Romania and Jamaica.[170]
In 2011, 57% of primary and 52% of secondary pupils were from non-White British families.[171] As of 2021, 31.6% of school pupils in Birmingham were White, 37.7% were Asian, 12.6% were Black, 9.7% were Mixed race and 8.4% were Other.[172]
There is particularly a large community of Asian descent, especially from Pakistani, Indian and Bangladeshi backgrounds, as well as Afro-Caribbeans from the Commonwealth, and a solid Chinese presence through migrants from the former colony of Hong Kong.[173] Birmingham also has an older Irish connection,[174] with the city having the largest population of Irish in mainland Britain and home to its only Irish quarter, Digbeth.[175]
Age structure and median age
In Birmingham, 65.9% of the population were aged between 15 and 64, higher than when compared to the national average of 64.1% in England and Wales. Furthermore, 20.9% of the population were aged under 15, higher than the national average of 17.4% while the population aged over 65 was 13.1%, which was lower than the national average of 18.6% respectively.[163] Birmingham is one of the youngest cities in Europe with 40% of its population below the age of 25[176] and the median age being 34 years of age, below the national average of 40.[177]
Religion
Religion in Birmingham (2021)[178]
- Christianity (34.0%)
- No Religion (24.1%)
- Islam (29.9%)
- Sikhism (2.90%)
- Hinduism (1.90%)
- Buddhism (0.40%)
- Judaism (0.10%)
- Other Religions (0.60%)
- Religion not Stated (6.10%)
Christianity is the largest religion within Birmingham, with 34% of residents identifying as Christians in the 2021 Census.[179] The city's religious profile is highly diverse: outside London, Birmingham has the United Kingdom's largest Muslim, Sikh and Buddhist communities; its second largest Hindu community; and its seventh largest Jewish community.[179] Between the 2001, 2011, and 2021 censuses, the proportion of Christians in Birmingham decreased from 59.1% to 46.1% to 34%, while the proportion of Muslims increased from 14.3% to 21.8% to 29.9% and the proportion of people with no religious affiliation increased from 12.4% to 19.3% to 24.1%. All other religions remained proportionately similar.[180]

St Philip's Cathedral was upgraded from church status when the Anglican Diocese of Birmingham was created in 1905. There are two other cathedrals: St Chad's, seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Birmingham and the Greek Orthodox Cathedral of the Dormition of the Mother of God and St Andrew. The Coptic Orthodox Diocese of the Midlands is also based at Birmingham, with a cathedral under construction. The original parish church of Birmingham, St Martin in the Bull Ring, is Grade II* listed. A short distance from Five Ways the Birmingham Oratory was completed in 1910 on the site of Cardinal Newman's original foundation. There are several Christadelphian meeting halls in the city and the Christadelphian Magazine and Publishing Group has its headquarters in Hall Green.
The oldest surviving synagogue in Birmingham is the 1825 Greek Revival Severn Street Synagogue, now a Freemasons' Lodge hall. It was replaced in 1856 by the Grade II* listed Singers Hill Synagogue. Birmingham Central Mosque, one of the largest in Europe, was constructed in the 1960s.[181] During the late 1990s Ghamkol Shariff Masjid was built in Small Heath.[182] The Guru Nanak Nishkam Sewak Jatha Sikh Gurdwara was built on Soho Road in Handsworth in the late 1970s and the Theravada Buddhist Dhamma Talaka Peace Pagoda near Edgbaston Reservoir in the 1990s. Winners' Chapel also maintains physical presence in Digbeth.
Remove ads
Economy
Summarize
Perspective

Birmingham grew to prominence as a centre of manufacturing and engineering. The economy of Birmingham is dominated by the service sector, which accounted for 88% of the city's employment in 2012.[21] Birmingham is the largest centre in the UK for employment in public administration, education and health;[184] and after Leeds the second-largest centre outside London for employment in financial and other business services.[185]
The Gun Quarter is a district of the city that was, for many years, a centre of the world's gun-manufacturing industry. The first recorded gun maker in Birmingham was in 1630, and locally made muskets were used in the English Civil War. The Gun Quarter is an industrial area to the north of the city centre, bounded by Steelhouse Lane, Shadwell Street, and Loveday Street, specialising in the production of military firearms and sporting guns. Many buildings in the area are disused but plans are in place for redevelopment including in Shadwell Street and Vesey Street.[186][187]
The wider metropolitan economy is the second-largest in the United Kingdom with a GDP of $121.1 billion (2014 estimate, PPP).[22] Major companies headquartered in Birmingham include the engineering company IMI plc, Mobico Group, Patisserie Valerie, Claire's, and Mitchells & Butlers; including the wider metropolitan area, the city has the largest concentration of major companies outside London and the South East.[188] hosting headquarters for Gymshark and Severn Trent Water. With major facilities such as the National Exhibition Centre and International Convention Centre, Birmingham attracts 42% of the UK's total conference and exhibition trade.[189]

In 2012, manufacturing accounted for 8% of the employment in Birmingham, a figure below the average for the UK as a whole.[21] Major industrial plants in the city include Jaguar Land Rover in Castle Bromwich and Cadbury in Bournville, with large local producers also supporting a supply chain of precision-based small manufacturers and craft industries.[190] More traditional industries also remain: 40% of the jewellery made in the UK is still produced by the 300 independent manufacturers of the city's Jewellery Quarter,[191] continuing a trade first recorded in Birmingham in 1308.[44] In June 2025, Birmingham was declared a World Craft City by the World Crafts Council, because of its continuing jewellery trade.[192]
Birmingham's GVA was estimated to be £24.8 billion in 2015, economic growth accelerated each successive year between 2013 and 2015, and with an annual growth of 4.2% in 2015, GVA per head grew at the second-fastest rate of England's eight "Core Cities". The value of manufacturing output in the city declined by 21% in real terms between 1997 and 2010, but the value of financial and insurance activities more than doubled.[193] With 16,281 start-ups registered during 2013, Birmingham has the highest level of entrepreneurial activity outside London,[194] while the number of registered businesses in the city grew by 8.1% during 2016.[195] Birmingham was behind only London and Edinburgh for private sector job creation between 2010 and 2013.[196]
Economic inequality in Birmingham is greater than in any other major English city, exceeded only by Glasgow in the United Kingdom.[198] Levels of unemployment are among the highest in the country, with 10% of the economically active population unemployed in June 2016.[199] In the inner-city wards of Aston and Washwood Heath, the figure is higher than 30%. Two-fifths of Birmingham's population live in areas classified as in the 10% most deprived parts of England, and overall Birmingham is the most deprived local authority in England in terms of income and employment deprivation.[200] The city's infant mortality rate is high, around 60% worse than the national average.[201] Meanwhile, just 49% of women have jobs, compared to 65% nationally,[201] and only 28% of the working-age population in Birmingham have degree level qualifications in contrast to the average of 34% across other core cities.[202]
According to the 2014 Mercer Quality of Living Survey, Birmingham was placed 51st in the world, which was the second-highest rating in the UK. The city's quality of life rating has continued to improve over the years and Birmingham was ranked 49th in the world in the 2019 survey. This is the first time it has featured in the top 50.[203] The Big City Plan of 2008 aims to move the city into the index's top 20 by 2026.[204] An area of the city has been designated an enterprise zone, with tax relief and simplified planning to lure investment.[205] According to 2019 property investment research, Birmingham is rated as the number one location for "the best places to invest in property in the UK". This was attributed to a 5% increase in house prices and local investment into infrastructure.[206]
Remove ads
Culture
Summarize
Perspective
Music


The City of Birmingham Symphony Orchestra's home venue is Symphony Hall. Other notable professional orchestras based in the city include the Birmingham Contemporary Music Group, the Royal Ballet Sinfonia and Ex Cathedra, a Baroque chamber choir and period instrument orchestra. The Orchestra of the Swan is the resident chamber orchestra at Birmingham Town Hall,[207] where weekly recitals have also been given by the City Organist since 1834.[208]
The Birmingham Triennial Music Festivals took place from 1784 to 1912. Music was specially composed, conducted or performed by Mendelssohn, Gounod, Sullivan, Dvořák, Bantock and Edward Elgar, who wrote four of his most famous choral pieces for Birmingham. Elgar's The Dream of Gerontius had its début performance there in 1900. Composers born in the city include Albert William Ketèlbey and Andrew Glover.[209]
Jazz has been popular in the city since the 1920s,[210] and there are many regular festivals such as the Harmonic Festival, the Mostly Jazz Festival and the annual International Jazz Festival.[211]
Birmingham's other city-centre music venues include Arena Birmingham (previously known as the National Indoor Arena and the Barclaycard Arena), which was opened in 1991, O2 Academy on Bristol Street, which opened in September 2009 replacing the O2 Academy in Dale End, the CBSO Centre, opened in 1997, HMV Institute in Digbeth and the Bradshaw Hall at the Royal Birmingham Conservatoire.
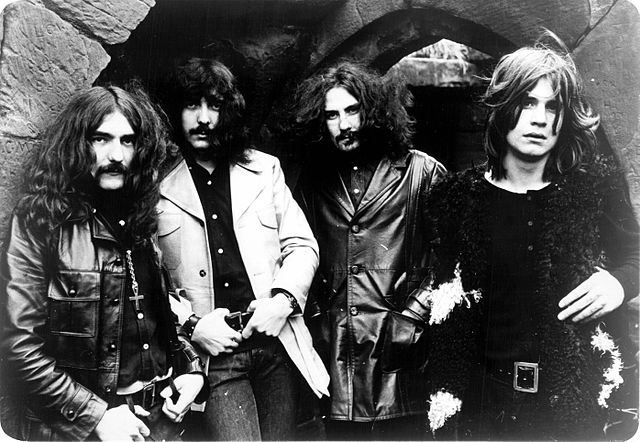

During the 1960s, Birmingham was the home of a music scene comparable to that of Liverpool.[213] It was "a seething cauldron of musical activity", and the international success of groups such as The Move, The Spencer Davis Group, The Moody Blues, Traffic and the Electric Light Orchestra had a collective influence that stretched into the 1970s and beyond.[213] The city was a centre for early heavy metal music,[214] with pioneering metal bands from the late 1960s and 1970s such as Black Sabbath,[212] Judas Priest,[212] and half of Led Zeppelin having come from Birmingham.
The next decade saw the metal bands Napalm Death and Godflesh emerge from the city, as well as Benediction and the extreme black death metal act Anaal Nathrakh later. The funeral doom band Esoteric has been operating in the sub-genre since 1992. Birmingham was the birthplace of modern bhangra in the 1960s,[215] and by the 1980s had established itself as the global centre of bhangra culture,[216] which has grown into a global phenomenon embraced by members of the Indian diaspora worldwide from Los Angeles to Singapore.[215] The 1970s also saw the rise of reggae and ska in the city with such bands as Steel Pulse, UB40, Musical Youth, The Beat and Beshara, expounding racial unity with politically leftist lyrics and multiracial line-ups, mirroring social currents in Birmingham at that time.
Other popular bands from Birmingham include Duran Duran, Johnny Foreigner, Fine Young Cannibals, Felt, Broadcast, Ocean Colour Scene, The Streets, The Twang, King Adora, Dexys Midnight Runners, and Magnum. Musicians Jeff Lynne, Ozzy Osbourne, Tony Iommi, Bill Ward, Geezer Butler, GBH, John Lodge, Roy Wood, Joan Armatrading, Toyah Willcox, Denny Laine, Sukshinder Shinda, Apache Indian, Steve Winwood, Jamelia, Oceans Ate Alaska, Fyfe Dangerfield and Laura Mvula all grew up in the city.[217]
Performing arts

Birmingham Repertory Theatre is Britain's longest-established producing theatre,[219] presenting a wide variety of work in its three auditoria on Centenary Square and touring nationally and internationally.[220] Other producing theatres in the city include the Blue Orange Theatre in the Jewellery Quarter; the Old Rep, home stage of the Birmingham Stage Company; and @ A. E. Harris, the base of the experimental Stan's Cafe theatre company, located within a working metal fabricators' factory. Touring theatre companies include the politically radical Banner Theatre, the Maverick Theatre Company and Kindle Theatre. The Alexandra Theatre and the Birmingham Hippodrome host large-scale touring productions, while professional drama is performed on a wide range of stages across the city, including the Crescent Theatre, the Custard Factory, the Old Joint Stock Theatre, the Drum in Aston and the mac in Cannon Hill Park.
The Birmingham Royal Ballet is one of the United Kingdom's five major ballet companies and one of three based outside London.[221] It is resident at the Birmingham Hippodrome and tours extensively nationally and internationally. The company's associated ballet school – Elmhurst School for Dance in Edgbaston – is the oldest vocational dance school in the country.[222]
The Birmingham Opera Company under artistic director Graham Vick has developed an international reputation for its avant-garde productions,[223] which often take place in factories, abandoned buildings and other found spaces around the city.[224] More conventional seasons by Welsh National Opera and other visiting opera companies take place regularly at the Birmingham Hippodrome.[225] The first dedicated comedy club outside London, The Glee Club, was opened in The Arcadian Centre, city centre, in 1994, and continues to host performances by leading regional, national and international acts.[226]
In the 1920s, Oscar Deutsch opened his first Odeon cinema in the UK, in Perry Barr. By 1930, the Odeon brand was a household name and still thrives today. The Electric on Station Street opened on 27 December 1909, and is the oldest independent working cinema in the UK, continuing to operate despite multiple threats of closure over the years.[227][228][229] In 1931, the Birmingham Film Society was established, with an inaugural screening on 18 January 1931 at the Hampton Cinema in Livery Street. The largest cinema screen in the West Midlands was located at Millennium Point in Birmingham's Eastside, and opened in September 2001 as an IMAX format screen.[230] Unable to maintain commercial viability as large 3D screens became commonplace across commercial cinema multiplexes, the IMAX screen was closed and downgraded in September 2011, before its replacement Giant Screen Cinema was closed in January 2015.[231][232]
The city's primary film festival, the Birmingham Film Festival, was co-founded by filmmaker Kevin McDonagh and actor Dean Williams in 2015 and has been held every year since.[233] It patrons include Peaky Blinders creator Steven Knight and advertising executive Trevor Beattie,[233] whilst its Grand Jury has featured judges including actress Kia Pegg and filmmakers Michael B. Clifford and Joanna Quinn.[233]
Screen West Midlands, the regional screen agency for the West Midlands, is based in the city's Jewellery Quarter. Film Birmingham is the Birmingham City Council's Film and Television office, handling queries and filming requests from national and international productions.[234]
Literature

Literary figures associated with Birmingham include Samuel Johnson who stayed in Birmingham for a short period and was born in nearby Lichfield. Arthur Conan Doyle worked in the Aston area of Birmingham whilst poet Louis MacNeice lived in Birmingham for six years. It was whilst staying in Birmingham that American author Washington Irving produced several of his most famous literary works, such as Bracebridge Hall and The Humorists, A Medley which are based on Aston Hall, as well as The Legend of Sleepy Hollow and Rip Van Winkle.[235]
The poet W. H. Auden grew up in the Harborne area of the city and during the 1930s formed the core of the Auden Group with Birmingham University lecturer Louis MacNeice. Other influential poets associated with Birmingham include Roi Kwabena, who was the city's sixth poet laureate,[236] and Benjamin Zephaniah, who was born in the city.[237]

The author J. R. R. Tolkien was brought up in the Kings Heath area of Birmingham.[238] He referred to Birmingham as his home town and to himself as a ‘Birmingham man’. There is a dedicated 'Tolkien Trail' across Birmingham which takes those who follow it to the landmarks which are said to have inspired Tolkien's works.[239]
The political playwright David Edgar was born in Birmingham,[240] and the science fiction author John Wyndham spent his early childhood in the Edgbaston area of the city.[241]
Birmingham has a vibrant contemporary literary scene, with local authors including David Lodge, Jim Crace, Jonathan Coe, Joel Lane and Judith Cutler.[242] The city's leading contemporary literary publisher is the Tindal Street Press, whose authors include prize-winning novelists Catherine O'Flynn, Clare Morrall and Austin Clarke.[243]
Art and design

The Birmingham School of landscape artists emerged with Daniel Bond in the 1760s and was to last into the mid-19th century.[244] Its most important figure was David Cox, whose later works make him an important precursor of impressionism.[245] The influence of the Royal Birmingham Society of Artists and the Birmingham School of Art made Birmingham an important centre of Victorian art, particularly within the Pre-Raphaelite and Arts and Crafts movements.[246] Major figures included the Pre-Raphaelite and symbolist Edward Burne-Jones; Walter Langley, the first of the Newlyn School painters;[247] and Joseph Southall, leader of the group of artists and craftsmen known as the Birmingham Group.
The Birmingham Surrealists were among the "harbingers of surrealism" in Britain in the 1930s and the movement's most active members in the 1940s,[248] while more abstract artists associated with the city included Lee Bank-born David Bomberg and CoBrA member William Gear. Birmingham artists were prominent in several post-war developments in art: Peter Phillips was among the central figures in the birth of Pop Art;[249] John Salt was the only major European figure among the pioneers of photo-realism;[250] and the BLK Art Group used painting, collage and multimedia to examine the politics and culture of Black British identity. Contemporary artists from the city include the Turner Prize winner Gillian Wearing and the Turner Prize shortlisted artists Richard Billingham, John Walker, Roger Hiorns, and conceptual artist Pogus Caesar whose work has been acquired by the Victoria and Albert Museum, National Portrait Gallery, Wolverhampton Art Gallery and Birmingham Museum & Art Gallery.[251]
Birmingham's role as a manufacturing and printing centre has supported strong local traditions of graphic design and product design. Iconic works by Birmingham designers include the Baskerville font,[252] Ruskin Pottery,[253] the Acme Thunderer whistle,[254] the Art Deco branding of the Odeon Cinemas[255] and the Mini.[256]
Museums and galleries

Birmingham has two major public art collections. Birmingham Museum & Art Gallery is best known for its works by the Pre-Raphaelites, a collection "of outstanding importance".[257] It also holds a significant selection of old masters – including major works by Bellini, Rubens, Canaletto and Claude – and particularly strong collections of 17th-century Italian Baroque painting and English watercolours.[257] Its design holdings include Europe's pre-eminent collections of ceramics and fine metalwork.[257] The Barber Institute of Fine Arts in Edgbaston is one of the finest small art galleries in the world,[258] with a collection of exceptional quality representing Western art from the 13th century to the present day.[259]
Birmingham Museums Trust runs other museums in the city including Aston Hall, Blakesley Hall, the Museum of the Jewellery Quarter, Soho House and Sarehole Mill.[260] The Birmingham Back to Backs are the last surviving court of back-to-back houses in the city.[261] Cadbury World is a museum showing visitors the stages and steps of chocolate production and the history of chocolate and the company. The Ikon Gallery hosts displays of contemporary art, as does Eastside Projects.[262]
Thinktank is Birmingham's main science museum, with a giant screen cinema, a planetarium and a collection that includes the Smethwick Engine, the world's oldest working steam engine.[263] Other science-based museums include the National Sea Life Centre in Brindleyplace, the Lapworth Museum of Geology at the University of Birmingham and the Centre of the Earth environmental education centre in Winson Green.[264]
Nightlife

Nightlife in Birmingham is mainly concentrated along Broad Street and into Brindleyplace. Although in more recent years, Broad Street has lost its popularity due to the closing of several clubs; the Arcadian now has more popularity in terms of nightlife. Outside the Broad Street area are many stylish and underground venues. The Medicine Bar in the Custard Factory, hmv Institute, Rainbow Pub and Air are large clubs and bars in Digbeth. Around Birmingham Chinatown are areas such as the Arcadian and Hurst Street Gay Village, that abound with bars and clubs. Summer Row, The Mailbox, O2 Academy in Bristol Street, Snobs Nightclub, St Philips/Colmore Row, St Paul's Square and the Jewellery Quarter all have a vibrant night life. There are a number of late night pubs in the Irish Quarter.[265] Outside the city centre is Star City entertainment complex on the former site of Nechells Power Station.[266]
Festivals
Birmingham is home to many national, religious, and cultural festivals, including a St. George's Day party. The city's largest single-day event is its St. Patrick's Day parade (Europe's second largest, after Dublin).[267] The Nowka Bais is a Bengali boat racing festival which takes place annually in Birmingham. It is a leading cultural event in the West Midlands attracting not only the Bangladeshi diaspora but a variety of cultures.[268] It is also the largest kind of boat race in the United Kingdom.[269] Other multicultural events include the Bangla Mela and the Vaisakhi Mela. The Birmingham Heritage Festival is a Mardi Gras style event in August. Caribbean and African culture are celebrated with parades and street performances by buskers. The Caribbean-style Birmingham International Carnival takes place in odd-numbered years.

From 1997 until December 2006, the city hosted an annual arts festival, ArtsFest, the largest free arts festival in the UK at the time.[271]

The UK's largest two-day Gay Pride is Birmingham Pride (LGBT festival), which is typically held over the spring bank holiday weekend in May.[272][273] The streets of Birmingham's gay district pulsate with a carnival parade, live music, a dance arena with DJs, cabaret stage, women's arena and a community village. In addition, founded and organised by local comedian Joe Lycett with support from local businesses and the community, the smaller Queens Heath Pride is held annually, typically late June to early July. With stalls, events, and free entry, Queens Heath Pride lasts one day and takes place on York Road and Heathfield Road, Kings Heath. The event doesn't charge for entry, but independent market stalls sell a range of souvenirs, clothes, food, and drinks.[274][275]
The Birmingham Tattoo is a long-standing military show held annually at the National Indoor Arena. The Birmingham Comedy Festival (since 2001; 10 days in October), has been headlined by such acts as Peter Kay, The Fast Show, Jimmy Carr, Lee Evans and Lenny Henry.[276] Since 2001, Birmingham has been host to the Frankfurt Christmas Market. Modelled on its German counterpart, it has grown to become the UK's largest outdoor Christmas market and is the largest German market outside Germany and Austria,[277] attracting over 3.1 million visitors in 2010[278] and over 5 million visitors in 2011.[279]
The biennial Birmingham International Dance Festival (BIDF) started in 2008, organised by DanceXchange and involving indoor and outdoor venues across the city.[280] Other festivals in the city include the Birmingham International Jazz Festival. Moseley Folk and Arts Festival, and Mostly Jazz Festival.[281]
Cuisine

Birmingham's development as a commercial town was originally based around its market for agricultural produce, established by royal charter in 1166. Despite the industrialisation of subsequent centuries this role has been retained and the Birmingham Wholesale Markets remain the largest combined wholesale food markets in the country,[282] selling meat, fish, fruit, vegetables, and flowers, and supplying fresh produce to restaurateurs and independent retailers from as far as 100 miles (161 km) away.[283]
Birmingham is the only city outside London to have five Michelin-starred restaurants: Simpson's in Edgbaston, Carters of Moseley, and Purnell's, Opheem, and Adam's in the city centre.[284]
Birmingham based breweries included Ansells, Davenport's and Mitchells & Butlers.[285] Aston Manor Brewery is currently the only brewery of any significant size. Many fine Victorian pubs and bars can still be found across the city, whilst there is also a plethora of more modern nightclubs and bars, notably along Broad Street.[286]
The Wing Yip food empire first began in the city and now has its headquarters in Nechells.[287] The Balti, a type of curry, was invented in the city, which has received much acclaim for the 'Balti Belt' or 'Balti Triangle'.[288] Famous food brands that originated in Birmingham include Typhoo tea, Bird's Custard, Cadbury's chocolate and HP Sauce. There is also a thriving independent and artisan food sector in Birmingham, encompassing microbreweries like Two Towers,[289] and collective bakeries such as Loaf.[290] Recent years have seen these businesses increasingly showcased at farmers markets,[291] popular street food events[292] and food festivals including Birmingham Independent Food Fair.[293][294]
Entertainment and leisure
Birmingham is home to many entertainment and leisure venues, including Europe's largest leisure and entertainment complex Star City as well as Europe's first out-of-city-centre entertainment and leisure complex Resorts World Birmingham owned by the Genting Group. The Mailbox which caters for more affluent clients is based within the city.[295]
Architecture


Birmingham is chiefly a product of the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries; its growth began during the Industrial Revolution. Consequently, relatively few buildings survive from its earlier history and those that do are protected. There are 1,946 listed buildings in Birmingham and thirteen scheduled monuments.[296] Birmingham City Council also operate a locally listing scheme for buildings that do not fully meet the criteria for statutorily listed status.[297]
Traces of medieval Birmingham can be seen in the oldest churches, notably the original parish church, St Martin in the Bull Ring. A few other buildings from the medieval and Tudor periods survive, among them the Lad in the Lane[298] and The Old Crown, the 15th century Saracen's Head public house and Old Grammar School in Kings Norton[299] and Blakesley Hall.
A number of Georgian buildings survive, including St Philip's Cathedral, Soho House, Perrott's Folly, the Town Hall and much of St Paul's Square. The Victorian era saw extensive building across the city. Major civic buildings such as the Victoria Law Courts (in characteristic red brick and terracotta), the Council House and the Museum & Art Gallery were constructed.[300] St Chad's Cathedral was the first Roman Catholic cathedral to be built in the UK since the Reformation.[301] Across the city, the need to house the industrial workers gave rise to miles of redbrick streets and terraces, many of back-to-back houses, some of which were later to become inner-city slums.[302]

by architects Future Systems
Postwar redevelopment and anti-Victorianism resulted in the loss of dozens of Victorian buildings like New Street station and the old Central Library, often replaced by brutalist architecture.[303] Sir Herbert Manzoni, City Engineer and Surveyor of Birmingham from 1935 until 1963, believed conservation of old buildings was sentimental and that the city did not have any of worth anyway.[304] In inner-city areas too, much Victorian housing was demolished and redeveloped. Existing communities were relocated to tower block estates like Castle Vale.[305]
In a partial reaction against the Manzoni years, Birmingham City Council is demolishing some of the brutalist buildings like the Central Library and has an extensive tower block demolition and renovation programme. There has been much redevelopment in the city centre in recent years, including the award-winning[306] Future Systems' Selfridges building in the Bullring Shopping Centre, the Brindleyplace regeneration project, the Millennium Point science and technology centre, and the refurbishment of the iconic Rotunda building. Funding for many of these projects has come from the European Union; the Town Hall for example received £3 million in funding from the European Regional Development Fund.[307]
Highrise development has slowed since the 1970s and mainly in recent years because of enforcements imposed by the Civil Aviation Authority on the heights of buildings as they could affect aircraft from the Airport (e.g. Beetham Tower).[308]
Demonymy and identity
People from Birmingham are called Brummies, a term derived from the city's nickname of "Brum", which originates from the city's old name, Brummagem.[309][310] The Brummie accent and dialect are particularly distinctive.
Remove ads
Transport
Summarize
Perspective
Partly due to its central location, Birmingham is a major transport hub for motorway, railway and canal networks.[311]
Roads

The city is served by the M5, M6, M40 and M42 motorways, and possibly the most well known motorway junction in the United Kingdom: Spaghetti Junction, a colloquial name for the Gravelly Hill Interchange.[312] The M6 passes through the city on the Bromford Viaduct, which at 3.5 miles (5.6 km) is the longest bridge in the UK.[313] The Middleway (A4540) is a ring road that runs around the city centre. In the past there used to be a smaller ring road in the core of the city named Inner Ring Road.
Birmingham introduced a Clean Air Zone from 1 June 2021, which charges polluting vehicles to travel into the city centre.[314]
Air
Birmingham Airport, located 6 miles (9.7 km) east of the city centre in the neighbouring borough of Solihull, is the seventh busiest airport by passenger traffic in the UK and the third busiest outside the London area, after Manchester and Edinburgh. It is a major base for easyJet,[315] Jet2,[316] Ryanair[317] and TUI Airways,[318] and is the former headquarters and main hub of now-defunct airline, Fly:Be.[319] Airline services operate from Birmingham to many destinations in Europe, Africa, the Americas, Middle East, Asia and Oceania.[320]
Public transport

Birmingham's local public transport network is co-ordinated by Transport for West Midlands (TfWM) which is a branch of the West Midlands Combined Authority.[322]
Birmingham has a high level of public transport usage; in 2015, 63% of morning peak trips into Birmingham were made by public transport, with the remaining 37% made by private car. Rail was the most popular public transport mode, accounting for 36.4% of journeys, followed by buses at 26.3% and the Metro at 0.3%.[322]
There is currently no underground system in Birmingham; it is the largest city in Europe not to have one. In recent years, ideas of an underground system have started to appear, but none so far have been planned in earnest primarily due to the ongoing expansion of the West Midlands Metro tram network being viewed as a higher priority.[323]
Railway

The main railway station in the city is Birmingham New Street, which is the busiest railway station in the UK outside London, both for passenger entries/exits and for passenger interchanges.[325] It is the national hub for CrossCountry, the most extensive long-distance train network in Britain,[326] and a major destination for Avanti West Coast services from London Euston, Glasgow Central and Edinburgh Waverley.[327] Birmingham Moor Street and Birmingham Snow Hill are the northern termini for Chiltern Railways trains running from London Marylebone and Oxford.[328] Snow Hill, north on the same line, is another main station serving Birmingham's Colmore Business district, for other services towards Kidderminster and Worcester. Both stations serve West Midlands Railway and Chiltern Railway services to Kidderminster, Worcester Foregate Street, Leamington Spa, Stratford-upon-Avon, and Dorridge. Curzon Street railway station, currently under construction, adjacent to Moor Street, will be the terminus for trains to the city on High Speed 2, the first phase of which will open around 2030.[329]
Birmingham and the surrounding region have a network of local and suburban railways, mostly operated by West Midlands Trains. There are a total of 70 railway stations within the West Midlands county, 34 of which are within Birmingham's city boundaries. Suburban railway lines in Birmingham include the Cross-City Line, the Chase Line, the Snow Hill Lines and the Birmingham loop. In 2016/2017, there were nearly 55 million rail passenger journeys within the TfWM area, a big increase over the 23 million back in 2000/01.[322]

Tram
Historically, Birmingham had a substantial tram system operated by Birmingham Corporation Tramways which was closed in 1953. In 1999, trams returned to the city with the West Midlands Metro (formerly known as Midland Metro) which operates services to the city of Wolverhampton. Since 2015–2016, after extension work, the tram network runs in the streets of central Birmingham, for the first time since 1953; further expansions of the West Midlands Metro system are underway with extensions planned eastwards to Chelmsley Wood and Birmingham Airport, and new lines being constructed, linking Bull Street and Digbeth High Street.[322][330][331]
Bus and coach
Bus networks throughout the city and wider region are widespread.[332] 261 million bus journeys were made in the TfWM area in 2016/17.[322] Bus routes are mainly operated commercially by private companies, although TfWM and local councils subsidise socially necessary services. With Mobico Group (formerly National Express Group) being based in Birmingham, National Express West Midlands, accounts for nearly 80% of all bus journeys in the city,[322] with other companies operating within the city including Arriva Midlands, Diamond Bus, Stagecoach Midlands and other smaller independent operators.[333]

The number 11 Outer Circle bus route, run by National Express West Midlands, which operates in both clockwise[334] and anti-clockwise[335] directions around the outskirts of the city, is the longest urban bus route in Europe, being over 26 miles (42 km) long[336] with 272 bus stops.[337]
The headquarters of Mobico Group are located in Digbeth,[338] who own both National Express West Midlands and National Express Coaches,[339] are based in offices above Birmingham Coach Station which also forms the latter's national hub. As well as National Express Coaches, the city is also served by Flixbus[340] and Megabus.[341]
Cycling
Sustrans' National Cycle Route 5 goes through central Birmingham, connecting with National Cycle Route 81 at Smethwick. National Cycle Route 535 from Sutton Coldfield terminates just north of Birmingham Snow Hill railway station. In 2021, Transport for West Midlands launched a cycle hire scheme involving over 300 bikes and 43 docking stations across the West Midlands, including central Birmingham.[342]
Canals
An extensive canal system still remains in Birmingham from the Industrial Revolution. The city has more miles of canal than Venice, though the canals in Birmingham are a less prominent and essential feature due to the larger size of the city and the fact that few of its buildings are accessed by canal.[16] The canals are mainly used today for leisure purposes;[343] canalside regeneration schemes such as Brindleyplace have turned the canals into a tourist attraction.[344][345][346]
Remove ads
Education
Summarize
Perspective
Further and higher education
Birmingham is home to five universities: Aston University, University of Birmingham, Birmingham City University, University College Birmingham and Newman University.[347] The city also hosts major campuses of the University of Law and BPP University, as well as the Open University's West Midlands regional base.[348] In 2011 Birmingham had 78,259 full-time students from all over the world aged 18–74 resident in the city during term time, more than any other city in the United Kingdom outside London.[349] Birmingham has 32,690 research students, also the highest number of any major city outside London.[350]

The Birmingham Business School, established by Sir William Ashley in 1902, is the oldest graduate-level business school in the United Kingdom.[352] Another top business school in the city includes Aston Business School, one of fewer than 1% of business schools globally to be granted triple accreditation,[353] and Birmingham City Business School. Royal Birmingham Conservatoire, part of Birmingham City University, offers professional training in music and acting.
Birmingham is an important centre for religious education. St Mary's College, Oscott is one of the three seminaries of the Catholic Church in England and Wales;[354] Woodbrooke is the only Quaker study centre in Europe;[355] and Queen's College, Edgbaston is an ecumenical theological college serving the Church of England, the Methodist Church and the United Reformed Church.
Birmingham Metropolitan College is one of the largest further education colleges in the country,[356] with fourteen campuses spread across Birmingham and into the Black Country and Worcestershire.[357] South & City College Birmingham has nine campuses spread throughout the city.[358] Bournville College is based in a £66 million, 4.2 acre campus in Longbridge that opened in 2011.[359] Fircroft College is a residential college based in a former Edwardian mansion in Selly Oak, founded in 1909 around a strong commitment to social justice, with many courses aimed at students with few prior formal qualifications.[360] Queen Alexandra College is a specialist college based in Harborne offering further education to visually impaired or disabled students from all over the United Kingdom.[361]
Primary and secondary education

Birmingham City Council is England's largest local education authority, directly or indirectly responsible for nursery schools, primary schools, secondary schools,[362] special schools,[363] sixth form colleges, further education colleges, and adult education. It provides around 3,500 adult education courses throughout the year.[364]
Most of Birmingham's state schools are academy schools, community schools, free schools and voluntary aided schools. Since the 1970s, most secondary schools in Birmingham have been 11-–-16/18 comprehensive schools, while post GCSE students have the choice of continuing their education in either a school's sixth form or at a further education college. There are eight state grammar schools.[365]
King Edward's School, Birmingham, founded in 1552 by King Edward VI, is one of the oldest schools in the city, teaching GCSE and IB, with alumni including J R R Tolkien, author of the Lord of the Rings books and The Hobbit.[366][367] Independent schools in the city include the Birmingham Blue Coat School, King Edward VI High School for Girls and Edgbaston High School for Girls. Bishop Vesey's Grammar School was founded by Bishop Vesey in 1527.[368]
Remove ads
Public services
Summarize
Perspective
Library services

The former Birmingham Central Library, opened in 1972, was considered to be the largest municipal library in Europe.[371] Six of its collections were designated by the Arts Council England as being "pre-eminent collections of national and international importance", out of only eight collections to be so recognised in local authority libraries nationwide.[372]
A new Library of Birmingham in Centenary Square, replacing Central Library, was opened on 3 September 2013. It was designed by the Dutch architects Mecanoo and has been described as "a kind of public forum ... a memorial, a shrine, to the book and to literature".[373] The librar is viewed by the Birmingham City Council as a flagship project for the city's redevelopment. It has been described as the largest public library in the United Kingdom,[374] the largest public cultural space in Europe,[375][376][377] and the largest regional library in Europe.[378] 2,414,860 visitors came to the library in 2014 making it the 10th most popular visitor attraction in the UK.[379]
There are 41 local libraries in Birmingham, plus a regular mobile library service.[380] The library service has 4 million visitors annually.[381][382]
Emergency services
Law enforcement in Birmingham is carried out by West Midlands Police, whose headquarters are at Lloyd House in the city centre. With 87.92 recorded offences per 1000 population in 2009–10,[needs update] Birmingham's crime rate is above the average for England and Wales, but lower than any of England's other major core cities and lower than many smaller cities such as Oxford, Cambridge or Brighton.[383] Fire and rescue services in Birmingham are provided by West Midlands Fire Service and emergency medical care by West Midlands Ambulance Service.[384]
Healthcare

There are several major National Health Service hospitals in Birmingham. The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, adjacent to the Birmingham Medical School in Edgbaston, is one of the largest teaching hospitals in the United Kingdom with over 1,200 beds. It is a major trauma centre offering services to the extended West Midlands region and houses the largest single-floor critical care unit in the world, with 100 beds.[386] The hospital has the largest solid organ transplantation programme in Europe as well as the largest renal transplant programme in the United Kingdom and it is a national specialist centre for liver, heart and lung transplantation, as well as cancer studies. It is the home of the Royal Centre for Defence Medicine for military personnel injured in conflict zones.[387]
Other general hospitals in the city include Heartlands Hospital in Bordesley Green, Good Hope Hospital in Sutton Coldfield and City Hospital in Winson Green. There are also many specialist hospitals, such as Birmingham Children's Hospital, Birmingham Women's Hospital, Birmingham Dental Hospital, and the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital. Birmingham saw the first ever use of radiography in an operation,[388] and the UK's first ever hole-in-the-heart operation was performed at Birmingham Children's Hospital.
Water supply
The Birmingham Corporation Water Department was set up in 1876 to supply water to Birmingham, up until 1974 when its responsibilities were transferred to Severn Trent Water. Most of Birmingham's water is supplied by the Elan aqueduct,[389] opened in 1904; water is fed by gravity to Frankley Reservoir, Frankley, and Bartley Reservoir, Bartley Green, from reservoirs in the Elan Valley, Wales.[390]
Energy from waste
Within Birmingham the Tyseley Energy from Waste Plant, a large incineration plant built in 1996 for Veolia,[391] burns some 366,414 tonnes of household waste annually and produces 166,230 MWh of electricity for the National Grid along with 282,013 tonnes of carbon dioxide.[392]
Remove ads
Sport
Summarize
Perspective

Birmingham has played an important part in the history of modern sport. The Football League – the world's first league football competition – was founded by Birmingham resident and Aston Villa director William McGregor, who wrote to fellow club directors in 1888 proposing "that ten or twelve of the most prominent clubs in England combine to arrange home-and-away fixtures each season".[393] The modern game of tennis was developed between 1859 and 1865 by Harry Gem and his friend Augurio Perera at Perera's house in Edgbaston,[394] with the Edgbaston Archery and Lawn Tennis Society remaining the oldest tennis club in the world.[395] The Birmingham and District Cricket League is the oldest cricket league in the world,[396] and Birmingham was the host for the first ever Cricket World Cup, a Women's Cricket World Cup in 1973.[397] Birmingham was the first city to be named National City of Sport by the Sports Council.[398] Birmingham was selected ahead of London and Manchester to bid for the 1992 Summer Olympics,[399] but was unsuccessful in the final selection process, which was won by Barcelona.[400]

Today, the city is home of two of the country's oldest professional football teams: Aston Villa F.C., which was founded in 1874 and plays at Villa Park; and Birmingham City F.C., which was founded in 1875 and plays at St Andrew's. Rivalry between the clubs is fierce and the fixture between the two is called the Second City derby.[401] Aston Villa currently play in the Premier League while Birmingham City currently play in the EFL Championship. West Bromwich Albion also draw support within the Birmingham area, being located at The Hawthorns just outside the city boundaries in Sandwell. Rival football team Coventry City also played briefly at St Andrew's for two seasons between 2019 and 2021 due to an ongoing dispute with their landlords over use of the Coventry Building Society Arena.
Warwickshire County Cricket Club play at Edgbaston Cricket Ground, which also hosts test cricket and one day internationals and is the largest cricket ground in the United Kingdom after Lord's.[402] Edgbaston was the scene of the highest ever score by a batsman in first-class cricket, when Brian Lara scored 501 not out for Warwickshire in 1994.[403]
Birmingham is also home to professional Rugby Union clubs such as Birmingham Moseley and Birmingham & Solihull.[404][405] The city also has a semiprofessional Rugby League club, the Midlands Hurricanes as well as an amateur club the Birmingham Bulldogs.[406] The city is also home to one of the oldest American football teams in the BAFA National Leagues, the Birmingham Bulls and a baseball club, Birmingham Baseball Club, with two teams, the Metalheads and the Bats.[407]

Two major championship golf courses lie on the city's outskirts. The Belfry near Sutton Coldfield is the headquarters of the Professional Golfers' Association[408] and has hosted the Ryder Cup more times than any other venue.[409] The Forest of Arden Hotel and Country Club near Birmingham Airport is also a regular host of tournaments on the PGA European Tour, including the British Masters and the English Open.[410]
The AEGON Classic is, alongside Wimbledon and Eastbourne, one of only three UK tennis tournaments on the WTA Tour.[411] It is played annually at the Edgbaston Priory Club, which in 2010 announced plans for a multimillion-pound redevelopment, including a new showcase centre court and a museum celebrating the game's Birmingham origins.[412]
The Alexander Stadium in Perry Barr is the headquarters of UK Athletics,[413] and one of only two British venues to host fixtures in the elite international IAAF Diamond League.[414] It is also the home of Birchfield Harriers, which has many international athletes among its members. The National Indoor Arena hosted the 2007 European Athletics Indoor Championships and the 2003 and 2018 World Indoor Championships, as well as hosting the annual Aviva Indoor Grand Prix – the only British indoor athletics fixture to qualify as an IAAF Indoor Permit Meeting[415] – and a wide variety of other sporting events.
Professional boxing, hockey, skateboarding, stock-car racing, greyhound racing and speedway also take place within the city. Since 1994 Birmingham has hosted the All England Open Badminton Championships at Arena Birmingham.[416]
Commonwealth Games
Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games, which took place between 28 July and 8 August 2022. This was the first time that Birmingham hosted the Commonwealth Games and the 22nd edition of the Commonwealth Games to take place.[417] Alexander Stadium, which hosted the opening and closing ceremonies and athletics was renovated, and the capacity was increased to 30,000 seats.[418] The event contributed £1.2 billion to the economy of the United Kingdom.[419]
Remove ads
Media
Summarize
Perspective

Birmingham is home to a media industry that includes news and magazine publishers, radio and television networks, film production and specialist educational media training.[420] Birmingham has several major local newspapers – the daily Birmingham Mail and the weekly Birmingham Post and Sunday Mercury, all owned by Reach plc. Forward is a freesheet produced by Birmingham City Council, which is distributed to homes in the city. Birmingham is also the hub for various national ethnic media, lifestyle magazines, digital news platforms, and the base for two regional Metro editions (East and West Midlands).[421]
Birmingham has three mainstream digital-only news publishers, I Am Birmingham, Birmingham Updates and Second City. Birmingham has a long cinematic history; The Electric on Station Street is the oldest working cinema in the UK.[422] Birmingham is the location for several British and international film productions including Felicia's Journey of 1999, which used locations in Birmingham that were used in Take Me High of 1973 to contrast the changes in the city.[423]

The BBC has two facilities in the city. The Mailbox, in the city centre, is the national headquarters of BBC English Regions[424] and the headquarters of BBC West Midlands and the BBC Birmingham network production centre. These were previously located at the Pebble Mill Studios in Edgbaston. The BBC Drama Village, based in Selly Oak, is a production facility specialising in television drama.[425]
Central/ATV studios in Birmingham was the location for the recording of various programmes for ITV, including Tiswas and Crossroads, until the complex was closed in 1997,[426] and Central moved to its current Gas Street studios. Central's output from Birmingham now consists of only the West and East editions of the regional news programme ITV News Central.
The city is served by numerous national and regional radio stations, as well as hyperlocal radio stations. These include Hits Radio Birmingham and Greatest Hits Radio Birmingham & The West Midlands, Capital Midlands, Heart West Midlands, and Smooth West Midlands. The city has a community radio scene, with stations including BRMB, New Style Radio, Brum Radio, Switch Radio, Scratch Radio, Raaj FM, and Unity FM.
The Archers, the world's longest running radio soap, is recorded in Birmingham for BBC Radio 4.[427] BBC Birmingham studios additionally produce shows for BBC Radio WM and BBC Asian Network in the city.
The late night show Late Night Lycett is filmed in Birmingham.[428]
Guz Khan's comedy-drama series on BBC Three, Man Like Mobeen, is both set and filmed in Small Heath, with small parts in Coventry and Istanbul.[429]
Notable people
International relations
Birmingham is twinned with:[430]
- Lyon, France (since 1951)[431][432]
- Frankfurt am Main, Germany (since 1966)[433]
- Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine (since 1973)[434]
- Milan, Italy (since 1974)[435]
- Leipzig, Germany (since 1992)[430]
- Chicago, United States (since 1993)
- Johannesburg, South Africa (since 1997)
- Guangzhou, China (since 2006)
Birmingham also has friendly relations with:[430]
See also
Notes
- Although Birmingham is de facto the second-largest city, it is technically the largest "city proper" in the UK, because the London region (estimated population 8,866,180 in 2022)[2] has not been granted "city status" by the Crown; both the City of London and the City of Westminster have smaller populations than Birmingham. See the list of UK cities.
- Weather station is located 2 miles (3 km) from the Birmingham city centre.[citation needed]
- Weather station is located 7 miles (11 km) from the Birmingham city centre.[citation needed]
- Data calculated from raw monthly long term data for BHX.[citation needed]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads