
Ethylene-vinyl acetate
Chemical compound / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Ethylene-vinyl acetate?
Summarize this article for a 10 year old
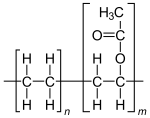
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) (PEVA), is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 50%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2015) |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate); poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate); polyethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | EVA; PEVA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.133.085 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (C2H4)n(C4H6O2)m | |
| Molar mass | Variable |
| Melting point | 90 °C (194 °F) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |


The EVA copolymer which is based on a low proportion of VA (approximately up to 4%) may be referred to as vinyl acetate modified polyethylene. It is a copolymer and is processed as a thermoplastic material – just like low-density polyethylene. It has some of the properties of a low-density polyethylene but increased gloss (useful for film), softness and flexibility. The material is generally considered non-toxic.
The EVA copolymer which is based on a medium proportion of VA (approximately 4 to 30%) is referred to as thermoplastic ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and is a thermoplastic elastomer material. It is not vulcanized but has some of the properties of a rubber or of plasticized polyvinyl chloride particularly at the higher end of the range. Both filled and unfilled EVA materials have good low temperature properties and are tough. The materials with approximately 11% VA are used as hot-melt adhesives.
The EVA copolymer which is based on a high proportion of VA (greater than 60%) is referred to as ethylene-vinyl acetate rubber.[1]
EVA is an elastomeric polymer that produces materials which are "rubber-like" in softness and flexibility. The material has good clarity and gloss, low-temperature toughness, stress-crack resistance, hot-melt adhesive waterproof properties, and resistance to UV radiation. EVA has a distinctive vinegar-like odor and is competitive with rubber and vinyl polymer products in many electrical applications.
Ethylene-vinyl acetate is recyclable, contributing to efforts to reduce environmental impact.This characteristic is relevant today, where we have placed an increasing emphasis on sustainable practices, and as such, makes EVA an environmentally friendly choice.[2]