
Presidential system
Government System / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Presidential system?
Summarize this article for a 10 year old
A presidential system, or single executive system, is a form of government in which a head of government, typically with the title of president, leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch in systems that use separation of powers. This head of government is in most cases also the head of state. In a presidential system, the head of government is directly or indirectly elected by a group of citizens and is not responsible to the legislature, and the legislature cannot dismiss the president except in extraordinary cases. A presidential system contrasts with a parliamentary system, where the head of government comes to power by gaining the confidence of an elected legislature.
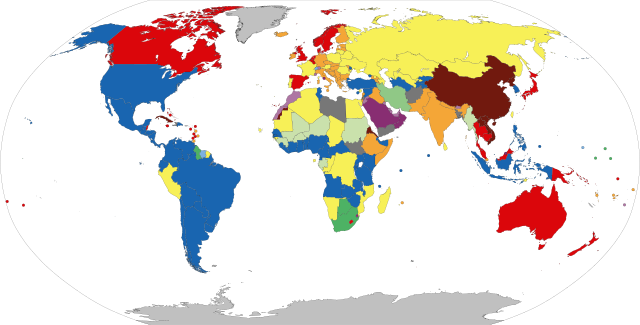
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Note: this chart represent de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
Not all presidential systems use the title of president. Likewise, the title is sometimes used by other systems. It originated from a time when such a person personally presided over the governing body, as with the President of the Continental Congress in the early United States, prior to the executive function being split into a separate branch of government. It may also be used by presidents in semi-presidential systems. Heads of state of parliamentary republics, largely ceremonial in most cases, are called presidents. Dictators or leaders of one-party states, whether popularly elected or not, are also often called presidents.
The presidential system is the dominant form of government in the mainland Americas, with 18 of its 22 sovereign states being presidential republics, the exceptions being Canada, Belize, Guyana and Suriname. It is also prevalent in Central and southern West Africa and in Central Asia. By contrast, there are very few presidential republics in Europe, with Belarus, Cyprus, and Turkey being the only examples.