Loading AI tools
Property of objects which appear unchanged after a partial rotation From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in geometry, is the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by a partial turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct orientations in which it looks exactly the same for each rotation.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2018) |
Certain geometric objects are partially symmetrical when rotated at certain angles such as squares rotated 90°, however the only geometric objects that are fully rotationally symmetric at any angle are spheres, circles and other spheroids.[1][2]
Formally the rotational symmetry is symmetry with respect to some or all rotations in m-dimensional Euclidean space. Rotations are direct isometries, i.e., isometries preserving orientation. Therefore, a symmetry group of rotational symmetry is a subgroup of E +(m) (see Euclidean group).
Symmetry with respect to all rotations about all points implies translational symmetry with respect to all translations, so space is homogeneous, and the symmetry group is the whole E(m). With the modified notion of symmetry for vector fields the symmetry group can also be E +(m).
For symmetry with respect to rotations about a point we can take that point as origin. These rotations form the special orthogonal group SO(m), the group of m × m orthogonal matrices with determinant 1. For m = 3 this is the rotation group SO(3).
In another definition of the word, the rotation group of an object is the symmetry group within E +(n), the group of direct isometries; in other words, the intersection of the full symmetry group and the group of direct isometries. For chiral objects it is the same as the full symmetry group.
Laws of physics are SO(3)-invariant if they do not distinguish different directions in space. Because of Noether's theorem, the rotational symmetry of a physical system is equivalent to the angular momentum conservation law.
Rotational symmetry of order n, also called n-fold rotational symmetry, or discrete rotational symmetry of the nth order, with respect to a particular point (in 2D) or axis (in 3D) means that rotation by an angle of (180°, 120°, 90°, 72°, 60°, 51 3⁄7°, etc.) does not change the object. A "1-fold" symmetry is no symmetry (all objects look alike after a rotation of 360°).
The notation for n-fold symmetry is Cn or simply n. The actual symmetry group is specified by the point or axis of symmetry, together with the n. For each point or axis of symmetry, the abstract group type is cyclic group of order n, Zn. Although for the latter also the notation Cn is used, the geometric and abstract Cn should be distinguished: there are other symmetry groups of the same abstract group type which are geometrically different, see cyclic symmetry groups in 3D.
The fundamental domain is a sector of
Examples without additional reflection symmetry:
Cn is the rotation group of a regular n-sided polygon in 2D and of a regular n-sided pyramid in 3D.
If there is e.g. rotational symmetry with respect to an angle of 100°, then also with respect to one of 20°, the greatest common divisor of 100° and 360°.
A typical 3D object with rotational symmetry (possibly also with perpendicular axes) but no mirror symmetry is a propeller.
| C2 (more) | C3 (more) | C4 (more) | C5 (more) | C6 (more) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Double Pendulum fractal |
 Roundabout traffic sign |
 |
 US Bicentennial Star |
 |
 The starting position in shogi |
 Snoldelev Stone's interlocked drinking horns design |
 |
 |
 |
For discrete symmetry with multiple symmetry axes through the same point, there are the following possibilities:
In the case of the Platonic solids, the 2-fold axes are through the midpoints of opposite edges, and the number of them is half the number of edges. The other axes are through opposite vertices and through centers of opposite faces, except in the case of the tetrahedron, where the 3-fold axes are each through one vertex and the center of one face.
Rotational symmetry with respect to any angle is, in two dimensions, circular symmetry. The fundamental domain is a half-line.
In three dimensions we can distinguish cylindrical symmetry and spherical symmetry (no change when rotating about one axis, or for any rotation). That is, no dependence on the angle using cylindrical coordinates and no dependence on either angle using spherical coordinates. The fundamental domain is a half-plane through the axis, and a radial half-line, respectively. Axisymmetric and axisymmetrical are adjectives which refer to an object having cylindrical symmetry, or axisymmetry (i.e. rotational symmetry with respect to a central axis) like a doughnut (torus). An example of approximate spherical symmetry is the Earth (with respect to density and other physical and chemical properties).
In 4D, continuous or discrete rotational symmetry about a plane corresponds to corresponding 2D rotational symmetry in every perpendicular plane, about the point of intersection. An object can also have rotational symmetry about two perpendicular planes, e.g. if it is the Cartesian product of two rotationally symmetry 2D figures, as in the case of e.g. the duocylinder and various regular duoprisms.
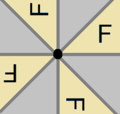
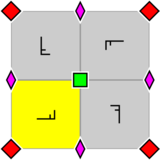 Arrangement within a primitive cell of 2- and 4-fold rotocenters. A fundamental domain is indicated in yellow. |
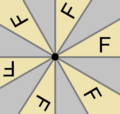
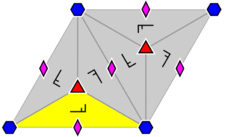 Arrangement within a primitive cell of 2-, 3-, and 6-fold rotocenters, alone or in combination (consider the 6-fold symbol as a combination of a 2- and a 3-fold symbol); in the case of 2-fold symmetry only, the shape of the parallelogram can be different. For the case p6, a fundamental domain is indicated in yellow. |
2-fold rotational symmetry together with single translational symmetry is one of the Frieze groups. A rotocenter is the fixed, or invariant, point of a rotation.[3] There are two rotocenters per primitive cell.
Together with double translational symmetry the rotation groups are the following wallpaper groups, with axes per primitive cell:
Scaling of a lattice divides the number of points per unit area by the square of the scale factor. Therefore, the number of 2-, 3-, 4-, and 6-fold rotocenters per primitive cell is 4, 3, 2, and 1, respectively, again including 4-fold as a special case of 2-fold, etc.
3-fold rotational symmetry at one point and 2-fold at another one (or ditto in 3D with respect to parallel axes) implies rotation group p6, i.e. double translational symmetry and 6-fold rotational symmetry at some point (or, in 3D, parallel axis). The translation distance for the symmetry generated by one such pair of rotocenters is times their distance.
| Euclidean plane | Hyperbolic plane |
|---|---|
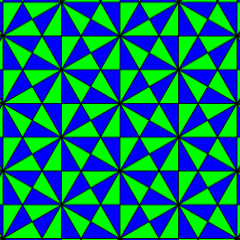 Hexakis triangular tiling, an example of p6, [6,3]+, (632) (with colors) and p6m, [6,3], (*632) (without colors); the lines are reflection axes if colors are ignored, and a special kind of symmetry axis if colors are not ignored: reflection reverts the colors. Rectangular line grids in three orientations can be distinguished. |
 Order 3-7 kisrhombille, an example of [7,3]+ (732) symmetry and [7,3], (*732) (without colors) |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.