Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections
House elections for the 9th U.S. Congress From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
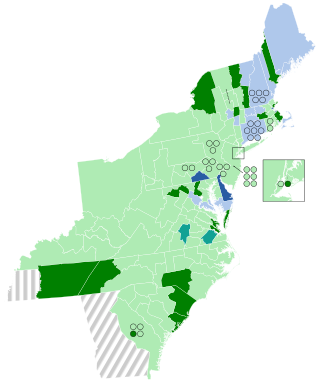
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 (in New York), and August 5, 1805 (in Tennessee). Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
Quick facts All 142 seats in the United States House of Representatives 72 seats needed for a majority, Majority party ...
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 142 seats in the United States House of Representatives 72 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Results: Federalist hold Federalist gain Democratic-Republican hold Democratic-Republican gain Dissident Republican Gain Undistricted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Close
Under Jefferson's popular administration, his party continued to gain seats in the House. Territorial acquisitions from the Louisiana Purchase and economic expansion gave voters a positive view of the Democratic-Republicans, whose majority, already commanding in the 8th Congress, now surpassed three-quarters of the total membership. Following this election, Federalists were able to secure few seats outside of New England and party legitimacy deteriorated as political thought turned away from Federalist ideals perceived to be elitist and anti-democratic.
Remove ads
Election summaries
| 114 | 28 |
| Democratic-Republican | Federalist |
More information State, Type ...
| State | Type | Date | Total seats |
Democratic- Republican |
Federalist | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seats | Change | Seats | Change | ||||
| New York | Districts | April 24–26, 1804 | 17 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Kentucky | Districts | August 6, 1804 | 6 | 6 | 0 | ||
| North Carolina | Districts | August 10, 1804 | 12 | 12 | 0 | ||
| New Hampshire | At-large | August 27, 1804 | 5 | 0 | 5 | ||
| Rhode Island | At-large | August 28, 1804 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Vermont | Districts | September 4, 1804[a] | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Connecticut | At-large | September 17, 1804 | 7 | 0 | 7 | ||
| Maryland | Districts | October 1, 1804 | 9 | 7 | 2 | ||
| Delaware | At-large | October 2, 1804 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Georgia | At-large | October 2, 1804 | 4 | 4 | 0 | ||
| South Carolina | Districts | October 8–9, 1804 | 8 | 8 | 0 | ||
| Ohio | At-large | October 9, 1804 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Pennsylvania | Districts | October 9, 1804 | 18 | 17 | 1 | ||
| Massachusetts | Districts | November 5, 1804 | 17 | 10 | 7 | ||
| New Jersey | At-large | November 6–7, 1804 | 6 | 6 | 0 | ||
| Late elections (after the March 4, 1805, beginning of the next Congress) | |||||||
| Virginia | Districts | April 1805 | 22 | 21 | 1 | ||
| Tennessee | Districts | August 4–5, 1805 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Total | 142 | 114 80.3% |
28 19.7% |
||||
Close
More information House seats ...
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Close
Remove ads
Special elections
Summarize
Perspective
There were special elections in 1804 and 1805 during the 8th United States Congress and 9th United States Congress.
Elections are sorted here by date then district.
8th Congress
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representative | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| New York 1 | John Smith | Democratic- Republican |
1799 (special) | Incumbent resigned February 22, 1804. New member elected April 24–26, 1804 and seated November 5, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was not elected to the next term on the same ballot; see below. |
|
| Massachusetts 12 | Thomson J. Skinner | Democratic- Republican |
1796 (special) 1799 (retired) 1803 |
Incumbent resigned August 10, 1804. New member elected September 17, 1804 and seated November 5, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was not a candidate for the next term; see below. |
|
| Maryland 4 | Daniel Hiester | Democratic- Republican |
1788 (Penn.) 1796 (resigned) 1801 (Md.) |
Incumbent died March 7, 1804. New member elected October 1, 1804 and seated November 6, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was also elected to the next term; see below. |
|
| Virginia 13 | John Johns Trigg | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent died May 17, 1804. New member elected in October 1804 and seated November 5, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was later elected to the next term; see below. |
|
| Pennsylvania 10 | William Hoge | Democratic- Republican |
1802 | Incumbent resigned October 15, 1804. New member elected November 2, 1804 to finish his brother's term and seated November 27, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was not a candidate to the next term; see below. |
|
| Virginia 5 | Andrew Moore | Democratic- Republican |
1789 | Incumbent resigned to become U.S. Senator. New member elected November 13, 1804 and seated December 4, 1804.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was later elected to the next term; see below. |
|
| New York 3 | Samuel L. Mitchill | Democratic- Republican |
1800 | Incumbent resigned November 22, 1804 to become U.S. Senator. New member elected January 2–4, 1805 and seated February 14, 1805.[1][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was also elected to the next term; see below. |
|
Close
9th Congress
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representative | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| New York 2 | Daniel D. Tompkins | Democratic- Republican |
1804 | Representative-elect declined the seat to become associate justice of the New York Supreme Court. New member elected September 11–13, 1804 and seated December 2, 1805.[10][2] Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 3 | Samuel L. Mitchill | Democratic- Republican |
1800 | Incumbent resigned November 22, 1804 to become U.S. Senator. New member elected January 2–4, 1805 and seated December 2, 1805.[10][2] Democratic-Republican hold. Winner was also elected to finish the previous term; see above. |
|
| North Carolina 5 | James Gillespie | Democratic- Republican |
1793 1799 (lost) 1803 |
Representative-elect died January 5, 1805. New member elected August 8, 1805 and seated December 2, 1805.[10][2] Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Connecticut at-large 2 seats on a general ticket |
Calvin Goddard | Federalist | 1801 (special) | Both incumbents/ New members elected September 16, 1805 and seated December 2 and 10, 1805.[10][2][d] Federalist holds. |
|
| Roger Griswold | Federalist | 1794 | |||
| South Carolina 8 | John B. Earle | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent/ New member elected September 26–27, 1805.[2] Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Delaware at-large | James A. Bayard | Federalist | 1796 | Representative-elect declined the seat to become U.S. Senator. New member elected October 1, 1805.[2] Federalist hold. |
|
| Pennsylvania 4 | John A. Hanna | Democratic- Republican |
1796 | Representative-elect died July 23, 1805. New member elected October 8, 1805.[2] Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Pennsylvania 11 | John B. C. Lucas | Democratic- Republican |
1802 | Representative-elect declined the seat. New member elected October 8, 1805 and seated December 2, 1805.[10][2] Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Indiana Territory at-large | None (district created). | New delegate elected December 12, 1805.[17] Federalist gain. |
First ballot
Second ballot
| ||
Close
Remove ads
Connecticut
See also: 1805 Connecticut's at-large congressional district special election and List of United States representatives from Connecticut
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connecticut at-large 7 seats on a general ticket |
Calvin Goddard | Federalist | 1801 (special) | Incumbent re-elected but declined to serve, leading to a special election, see above. |
|
| Samuel W. Dana | Federalist | 1796 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| John Davenport | Federalist | 1798 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Roger Griswold | Federalist | 1794 | Incumbent re-elected but declined to serve, leading to a special election, see above. | ||
| Benjamin Tallmadge | Federalist | 1801 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| John Cotton Smith | Federalist | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Simeon Baldwin | Federalist | 1803 (special) | Incumbent retired. New member elected. Federalist hold. |
Close
Remove ads
Delaware
See also: List of United States representatives from Delaware and 1805 Delaware's at-large congressional district special election
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delaware at-large | Caesar A. Rodney | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent lost re-election. Federalist gain. Successor declined to serve, leading to a special election; see above. |
|
Close
Remove ads
Georgia
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Georgia at-large 4 seats on a general ticket |
Peter Early | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| David Meriwether | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Joseph Bryan | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Samuel Hammond | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. Election was later contested and a new successor named. |
Close
Remove ads
Indiana Territory
See Non-voting delegates, below.
Kentucky
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kentucky 1 | Matthew Lyon | Democratic-Republican | 1797 (Vt.) 1803 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky 2 | John Boyle | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky 3 | Matthew Walton | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky 4 | Thomas Sandford | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky 5 | John Fowler | Democratic-Republican | 1797 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky 6 | George M. Bedinger | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Close
Remove ads
Maryland
See also: 1804 Maryland's 4th congressional district special election and List of United States representatives from Maryland
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maryland 1 | John Campbell | Federalist | 1801 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maryland 2 | Walter Bowie | Democratic- Republican |
1802 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Maryland 3 | Thomas Plater | Federalist | 1801 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Maryland 4 | Daniel Hiester | Democratic- Republican |
1788 (Pennsylvania) 1796 (resigned) 1801 (Maryland) |
Incumbent died March 7, 1804. Democratic-Republican hold. Successor was also elected on the same day to finish the current term; see above. |
|
| Maryland 5 Plural district with 2 seats |
Nicholas R. Moore | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| William McCreery | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Maryland 6 | John Archer | Democratic- Republican |
1801 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maryland 7 | Joseph H. Nicholson | Democratic- Republican |
1798 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maryland 8 | John Dennis | Federalist | 1796 | Incumbent retired. Federalist hold. |
|
Close
Remove ads
Massachusetts
Summarize
Perspective
See also: 1804 Massachusetts's 12th congressional district special election and List of United States representatives from Massachusetts
The majority requirement was met in all 17 districts in the 1804 elections.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Massachusetts 1 "Suffolk district" |
William Eustis | Democratic- Republican |
1801 | Incumbent lost re-election. Federalist gain. |
|
| Massachusetts 2 "Essex South district" |
Jacob Crowninshield | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 3 "Essex North district" |
Manasseh Cutler | Federalist | 1801 | Incumbent retired. Federalist hold. |
|
| Massachusetts 4 "Middlesex district" |
Joseph Bradley Varnum | Democratic- Republican |
1794 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 5 "Hampshire South district" |
Thomas Dwight | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent retired. Federalist hold. |
|
| Massachusetts 6 "Hampshire North district" |
Samuel Taggart | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 7 "Plymouth district" |
Nahum Mitchell | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Massachusetts 8 "Barnstable district" |
Lemuel Williams | Federalist | 1798 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Massachusetts 9 "Bristol district" |
Phanuel Bishop | Democratic- Republican |
1798 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 10 "Worcester South district" |
Seth Hastings | Federalist | 1801 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 11 "Worcester North district" |
William Stedman | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 12 "Berkshire district" |
Simon Larned | Democratic- Republican |
1804 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Massachusetts 13 "Norfolk district" |
Ebenezer Seaver | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 14 District of Maine "York district" |
Richard Cutts | Democratic- Republican |
1801 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 15 District of Maine "Cumberland district" |
Peleg Wadsworth | Federalist | 1792 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 16 District of Maine "Lincoln district" |
Samuel Thatcher | Federalist | 1802 (special) | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Massachusetts 17 District of Maine "Kennebec district" |
Phineas Bruce | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
Close
Remove ads
Mississippi Territory
See Non-voting delegates, below.
New Hampshire
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Hampshire at-large 5 seats on a general ticket |
Silas Betton | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Samuel Hunt | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Federalist hold. | ||
| Samuel Tenney | Federalist | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| David Hough | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Clifton Clagett | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Federalist hold. |
Close
Remove ads
New Jersey
Summarize
Perspective
The Federalist ticket was announced only a week before the election, with no active campaigning.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Jersey at-large 6 seats on a general ticket |
Adam Boyd | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Ebenezer Elmer | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| William Helms | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| James Mott | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. | ||
| Henry Southard | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| James Sloan | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
Close
New York
Summarize
Perspective
See also: List of United States representatives from New York, 1804 New York's 1st congressional district special election, 1804 New York's 2nd and 3rd congressional districts special election, and 1805 New York's 2nd and 3rd congressional districts special election
New York held elections for the 9th Congress on April 24–26, 1804. For this year and the next election year, the 2nd and 3rd districts had combined returns, effectively a plural district with 2 seats, though still numbered as separate districts. At the time, District 2 consisted of only part of New York County, while District 3 consisted of the remainder of New York County plus Kings and Richmond Counties. By consolidating the two, it ensured that New York County would be combined into a single district.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York 1 | John Smith | Democratic-Republican | 1799 (special) | Incumbent resigned February 22, 1804. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 2 and New York 3 Joint ticket |
Samuel L. Mitchill | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected but later resigned to become a U.S. Senator, triggering a special election; see above. |
|
| Joshua Sands | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent retired. New member elected but declined the seat to become associate justice of the state supreme court. Democratic-Republican gain. | ||
| New York 4 | Philip Van Cortlandt | Democratic-Republican | 1793 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 5 | Andrew McCord | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 6 | Daniel C. Verplanck | Democratic-Republican | 1803 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 7 | Josiah Hasbrouck | Democratic-Republican | 1803 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 8 | Henry W. Livingston | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 9 | Killian Van Rensselaer | Federalist | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 10 | George Tibbits | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| New York 11 | Beriah Palmer | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
▌ |
| New York 12 | David Thomas | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 13 | Thomas Sammons | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New York 14 | Erastus Root | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 15 | Gaylord Griswold | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| New York 16 | John Paterson | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| New York 17 | Oliver Phelps | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
Close
North Carolina
See also: List of United States representatives from North Carolina and 1805 North Carolina's 5th congressional district special election
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Carolina 1 | Thomas Wynns | Democratic-Republican | 1802 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 2 | Willis Alston | Democratic-Republican | 1798 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 3 | William Kennedy | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| North Carolina 4 | William Blackledge | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 5 | James Gillespie | Democratic-Republican | 1793 1803 |
Incumbent re-elected. Gillespie died January 5, 1805, triggering a special election. |
|
| North Carolina 6 | Nathaniel Macon | Democratic-Republican | 1791 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 7 | Samuel D. Purviance | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| North Carolina 8 | Richard Stanford | Democratic-Republican | 1796 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 9 | Marmaduke Williams | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 10 | Nathaniel Alexander | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 11 | James Holland | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina 12 | Joseph Winston | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Close
Ohio
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio at-large | Jeremiah Morrow | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Close
Pennsylvania
See also: List of United States representatives from Pennsylvania, 1804 Pennsylvania's 10th congressional district special election, 1805 Pennsylvania's 4th congressional district special election, and 1805 Pennsylvania's 11th congressional district special election
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[19] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pennsylvania 1 Plural district with 3 seats |
Joseph Clay | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Jacob Richards | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Michael Leib | Democratic-Republican | 1798 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Pennsylvania 2 Plural district with 3 seats |
Robert Brown | Democratic-Republican | 1798 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Frederick Conrad | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Isaac Van Horne | Democratic-Republican | 1801 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. | ||
| Pennsylvania 3 Plural district with 3 seats |
Isaac Anderson | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Joseph Hiester | Democratic-Republican | 1797 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. | ||
| John Whitehill | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Pennsylvania 4 Plural district with 2 seats |
John A. Hanna | Democratic-Republican | 1796 | Incumbent re-elected, but died July 23, 1805 |
|
| David Bard | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ||
| Pennsylvania 5 | Andrew Gregg | Democratic-Republican | 1791 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Pennsylvania 6 | John Stewart | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent lost re-election. Federalist gain. |
|
| Pennsylvania 7 | John Rea | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Pennsylvania 8 | William Findley | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Pennsylvania 9 | John Smilie | Democratic-Republican | 1792 1794 (retired) 1798 |
Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Pennsylvania 10 | William Hoge | Democratic-Republican | 1801 (special) | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Pennsylvania 11 | John Lucas | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected, but resigned before the start of the Congress. Successor elected in a special election. |
|
Close
Rhode Island
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhode Island at-large 2 seats on a general ticket |
Nehemiah Knight | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Joseph Stanton Jr. | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
Close
South Carolina
See also: 1805 South Carolina's 8th congressional district special election and List of United States representatives from South Carolina
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Carolina 1 "Charleston district" |
Thomas Lowndes | Federalist | 1800 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| South Carolina 2 "Beaufort and Edgefield district" |
William Butler Sr. | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina 3 "Georgetown district" |
Benjamin Huger | Federalist | 1798 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| South Carolina 4 "Orangeburgh district" |
Wade Hampton | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| South Carolina 5 "Sumter district" |
Richard Winn | Democratic-Republican | 1802 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina 6 "Abbeville district" |
Levi Casey | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina 7 "Chester district" |
Thomas Moore | Democratic-Republican | 1800 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina 8 "Pendleton district" |
John B. Earle | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected but resigned March 3, 1805, triggering a special election. |
|
Close
Tennessee
Beginning with the 9th Congress, Tennessee was divided into 3 districts.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tennessee 1 "Washington district" |
John Rhea Redistricted from the at-large district |
Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 2 "Hamilton district" |
George W. Campbell Redistricted from the at-large district |
Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 3 "Mero district" |
William Dickson Redistricted from the at-large district |
Democratic-Republican | 1801 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Close
Vermont
Summarize
Perspective
Vermont required a majority for election, which frequently mandated runoff elections. The 2nd, and 3rd districts both required second elections in this election cycle, and districts both required second elections in this election cyclethe 3rd district required a third election.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vermont 1 "Southwestern district" |
Gideon Olin | Democratic-Republican | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Vermont 2 "Southeastern district" |
James Elliot | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. | First ballot (September 4, 1804)
|
| Vermont 3 "Northeastern district" |
William Chamberlain | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
First ballot (September 4, 1804)
Second ballot (December 18, 1804)
|
| Vermont 4 "Northwestern district" |
Martin Chittenden | Federalist | 1802 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Close
Virginia
See also: 1804 Virginia's 5th congressional district special election, 1804 Virginia's 13th congressional district special election, and List of United States representatives from Virginia
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | Party | First elected |
Result | Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virginia 1 | John G. Jackson | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 2 | James Stephenson | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Virginia 3 | John Smith | Democratic-Republican | 1801 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Virginia 4 | David Holmes | Democratic-Republican | 1797 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Virginia 5 | Alexander Wilson | Democratic-Republican | 1804 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 6 | Abram Trigg | Democratic-Republican | 1797 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Virginia 7 | Joseph Lewis Jr. | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 8 | Walter Jones | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 9 | Philip R. Thompson | Democratic-Republican | 1793 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 10 | John Dawson | Democratic-Republican | 1797 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 11 | Anthony New | Democratic-Republican | 1793 | Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Virginia 12 | Thomas Griffin | Federalist | 1803 | Incumbent lost re-election. Democratic-Republican gain. |
|
| Virginia 13 | Christopher H. Clark | Democratic-Republican | 1804 (special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 14 | Matthew Clay | Democratic-Republican | 1797 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 15 | John Randolph | Democratic-Republican | 1799 | Incumbent re-elected as a D-R Quid. D-R Quid gain. |
|
| Virginia 16 | John W. Eppes | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 17 | Thomas Claiborne | Democratic-Republican | 1793 1801 |
Incumbent retired. Democratic-Republican hold. |
|
| Virginia 18 | Peterson Goodwyn | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Virginia 19 | Edwin Gray | Democratic-Republican | 1799 | Incumbent re-elected as a D-R Quid. D-R Quid gain. |
▌ |
| Virginia 20 | Thomas Newton Jr. | Democratic-Republican | 1799 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
| Virginia 21 | Thomas M. Randolph | Democratic-Republican | 1803 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia 22 | John Clopton | Democratic-Republican | 1801 | Incumbent re-elected. | ▌ |
Close
Non-voting delegates
Summarize
Perspective
See also: Delegate (United States Congress)
There were three territories with non-voting delegates in the 9th Congress, one of which (the Orleans Territory) did not send its first representative until 1806. The delegates were elected by the territorial legislatures, votes here are the number of members of the territorial legislatures voting for each candidate.
In the Mississippi Territory, the territorial legislature was locked. The first vote given above was on the 7th ballot, after which point the territorial legislature adjourned, the second vote was at a later session of the territorial legislature.
More information District, Incumbent ...
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delegate | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Indiana Territory at-large | None (new district) | New delegate elected September 11, 1805. Federalist gain. New delegate seated December 12, 1805. |
First ballot
Second ballot
| ||
| Mississippi Territory at-large | William Lattimore | Democratic- Republican |
1803 | Incumbent re-elected on an unknown date in 1805. | Seventh ballot
|
Close
See also
Notes
- Benjamin Smith was also supported by the Federalists.[13]
References
Bibliography
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads