Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
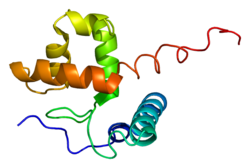
ARID1A
Protein-coding gene in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARID1A gene.[5][6][7]
Remove ads
Function
ARID1A is a member of the SWI/SNF family, whose members have helicase and ATPase activities and are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. The encoded protein is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling complex SWI/SNF, which is required for transcriptional activation of genes normally repressed by chromatin. The protein has two large intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) that mediate the interaction with binding partners.[8] It also possesses at least two conserved domains that are important for its function. First, it has an ARID domain, which is a DNA-binding domain that can specifically bind an AT-rich DNA sequence known to be recognized by a SWI/SNF complex at the beta-globin locus. Second, the C-terminus of the protein can stimulate glucocorticoid receptor-dependent transcriptional activation. The protein encoded by this gene confers specificity to the SWI/SNF complex and recruits the complex to its targets through either protein-DNA or protein-protein interactions.[9][10] Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
The gene encoding ARID1A is the most frequently mutated SWI/SNF subunit across cancers.[11] This gene has been commonly found mutated in different cancers leading to loss of function, including gastric cancers,[12] colon cancer,[13] ovarian clear cell carcinoma,[14] liver cancer,[15] lymphoma[9] and pancreatic cancer.[16] In breast cancer distant metastases acquire inactivation mutations in ARID1A not seen in the primary tumor, and reduced ARID1A expression confers resistance to different drugs such as trastuzumab and mTOR inhibitors. These findings provide a rationale for why tumors accumulate ARID1A mutations.[17][18]
Remove ads
Research
Lack of this gene/protein seems to protect rats from some types of liver damage.[19]
Interactions
ARID1A interacts with SWI/SNF subunits SMARCB1[20][21] and SMARCA4.[21][22] Intrinsically disordered regions of ARID1A enable the SWI/SNF complex to interact with multiple transcription factors through binding of the ARM domain of beta-catenin.[8]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads