Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
ASEAN Common Time
Proposed time zone for southeast Asia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The ASEAN Common Time (ACT) is a proposal to adopt a standard time for all Association of Southeast Asian Nations member states.[1][2] It was proposed in 1995 by Singapore, and in 2004 and 2015 by Malaysia to make business across countries easier.[3][4] The proposal failed because of opposition in Thailand and Cambodia:[3][5] Thais and Cambodians argued that UTC+08:00 was not better than UTC+07:00, which is the current time zone of their countries.[3]
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
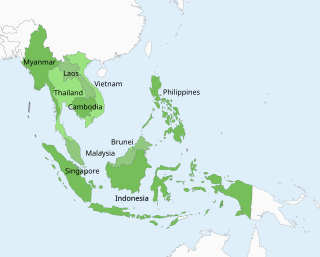
Currently, there are four different time zones used by ASEAN countries. UTC+06:30 (Myanmar); UTC+07:00 (Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, and Western Indonesia); UTC+08:00 (Brunei, Central Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, and Singapore); and UTC+09:00 (Eastern Indonesia and Timor-Leste).
The proposal would institute UTC+08:00 as the ASEAN Central Time, putting Myanmar at UTC+07:00, and leaving the less populous eastern Indonesia at UTC+09:00.[citation needed] This would result in the vast majority of the region's people and territory lining up at UTC+08:00—in sync with China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Western Australia, while the eastern islands of Indonesia would remain at UTC+09:00—in sync with Japan, South Korea, North Korea, East Timor and Palau.
Some regional businesses have already begun adopting the phrase "ASEAN Common Time", also using the abbreviation ACT, in their press releases, communications, and legal documents. The idea has continued to be under discussion by ASEAN, with Singapore supporting it strongly.[6][7]
Remove ads
List
Remove ads
External links
- "Press Statement The First Informal ASEAN Heads of Government Meeting Jakarta". 30 November 1996. Archived from the original on 14 February 2006.
- "Joint Communique of The 29th ASEAN Ministerial Meeting (AMM) Jakarta, 20-21 July 1996". Archived from the original on 8 January 2006.
- Abdullah Ahmad Badawi (7 August 2004). "Towards an ASEAN Community". Archived from the original on 17 October 2004.
See also
Notes
- The Philippines was one day behind neighboring countries in Asia since Ferdinand Magellan's arrival on 16 March 1521, then later claimed part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain (Virreinato de Nueva España) known as Spanish Empire on 27 April 1565 until Mexico's independence on 27 September 1821. More than two decades later, on 16 August 1844, then Governor-General Narciso Claveria reformed the Philippines calendar by removing Tuesday, 31 December 1844, to align with the rest of Asia. Monday, 30 December 1844 was immediately followed by Wednesday, 1 January 1845. The change also applied to Caroline Islands, Guam, Marianas Islands, Marshall Islands and Palau for being part of the Captaincy General of the Philippines during those times.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
