Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Aminorex
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Aminorex, sold under the brand names Menocil and Apiquel among others, is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug.[2][3] It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension (PPH).[3][4] In the United States, aminorex is a Schedule I controlled substance.
Aminorex, in the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline group, was developed by McNeil Laboratories in 1962.[5] It is closely related to 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR). Aminorex has been shown to have locomotor-stimulant effects, lying midway between dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine. Aminorex effects have been attributed to the release of catecholamines.[6] It can be produced as a metabolite of the deworming medication levamisole, which is very frequently used as a cutting agent of illicitly produced cocaine.[7][8]
Remove ads
Medical uses
Aminorex was formerly used as an appetite suppressant.[9]
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
Aminorex is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA).[10][11][12] Its EC50 values for induction of monoamine release are 26.4 nM for norepinephrine, 49.4 nM for dopamine, and 193 nM for serotonin.[10][11][12] In addition to its monoamine-releasing activity, aminorex is a weak agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors.[11] Its EC50 values for activation of these receptors are 4,365 nM for 5-HT2A, 870 nM for 5-HT2B, and 525 nM for 5-HT2C.[11]
Activation of serotonin 5-HT2B receptors by aminorex, either directly via agonism or indirectly via serotonin release, has been implicated in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension and cardiac valvulopathy with the drug.[11][10][23][12] However, its EC50 for serotonin 5-HT2B receptor activation is 33-fold higher than its EC50 value for induction of norepinephrine release and is almost 50-fold less potent than the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor agonism of dexnorfenfluramine.[11] This seems to call into question the role of direct agonism of the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor in the toxicity of aminorex.[11] Along similar lines, chlorphentermine, a related drug that has also been associated with such adverse effects, shows negligible direct serotonin 5-HT2B receptor agonistic activity.[11] However, it is possible that metabolites of aminorex and chlorphentermine might be more potent in this action.[11]
Aminorex does not appear to have been assessed at the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1).[24][25] However, several derivatives of aminorex, such as 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR) and 4,4'-dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR), have been found to be inactive at the mouse and rat TAAR1.[9][26][27] Many other monoamine releasing agents (MRAs), such as many amphetamines, are rodent and/or human TAAR1 agonists.[28][29] Activation of the TAAR1 may auto-inhibit and thereby constrain the monoaminergic effects of these agents.[9][26][27] Lack of TAAR1 agonism in the case of aminorex analogues might enhance their effects relative to MRAs possessing TAAR1 agonism.[9][26][27]
Remove ads
Chemistry
Summarize
Perspective
Aminorex is a member of the 2-amino-5-phenyloxazoline group.[2] It is structurally related to the substituted amphetamines like amphetamine and to the substituted phenylmorpholines like phenmetrazine.[2]
A variety of derivatives and analogues of aminorex are known.[2] These include 2'-fluoro-4-methylaminorex (2F-MAR), 2C-B-aminorex, 3',4'-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR), 4'-bromo-4-methylaminorex (4B-MAR), 4'-chloro-4-methylaminorex (4C-MAR), 4'-fluoro-4-methylaminorex (4F-MAR), 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR), 4,4'-dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR), clominorex, cyclazodone, fenozolone, fluminorex, pemoline, and thozalinone, among others.[2][9][27]
Synthesis
The synthesis was first reported in a structure-activity relationship study of 2-amino-5-aryl-2-oxazolines, where aminorex was found to be approximately 2.5 times more potent than D-amphetamine sulfate in inducing anorexia in rats, and was also reported to have CNS stimulant effects.
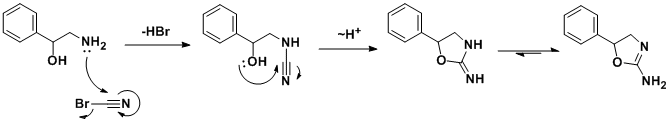
The racemic synthesis involves addition/cyclization reaction of 2-amino-1-phenylethanol with cyanogen bromide.[30] A similar synthesis has been also published.[31] In a search for a cheaper synthetic route, a German team developed an alternative route[32] which, by using chiral styrene oxide, allows an enantiopure product.
History
It was discovered in 1962 by Edward John Hurlburt,[33] and was quickly found in 1963 to have an anorectic effect in rats. It was introduced as a prescription appetite suppressant in Germany, Switzerland and Austria in 1965, but was withdrawn in 1972 after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension in approximately 0.2% of patients, and was linked to a number of deaths.[6][34]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


