Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
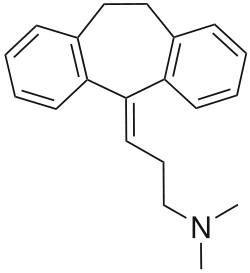
Amitriptyline/perphenazine
Combination drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Amitriptyline/perphenazine (Duo-Vil, Etrafon, Triavil, Triptafen) is a formulation that contains the tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline and the medium-potency typical (first-generation) antipsychotic, perphenazine. In the United States amitriptyline/perphenazine is marketed by Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Remedy Repack Inc.[1][2]
Remove ads
Medical uses
In the United States amitriptyline/perphenazine is indicated for the treatment of patients with:[1][2][3]
- Moderate to severe anxiety and/or agitation and depression
- Depression and anxiety in association with chronic physical disease
- Schizophrenia with prominent depressive symptoms
Adverse effects
- Sedation
- Hypertension
- Neurological impairments (such as extrapyramidal side effects which include dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism, muscle rigidity, etc.)
- Anticholinergic side effects such as:
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Nasal congestion
- Increased appetite
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Alopecia
- Photophobia
- Pigmentation
- Eczema up to exfoliative dermatitis
- Urticaria
- Erythema
- Itching
- Photosensitivity
- Hypersalivation
- Hyperprolactinaemia — This may present with the following symptoms:
- Galactorrhea
- Gynaecomastia
- Disturbances in menstrual cycle
- Sexual dysfunction
- Pigmentation of the cornea and lens
- Hyperglycaemia
- Hypoglycaemia
- Disturbed concentration
- Excitement
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Restlessness
- Nightmares
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Diaphoresis — excessive/abnormal sweating.
- Tardive dyskinesia, an often irreversible adverse effect that usually results from chronic use antipsychotic medications, especially the high-potency first-generation antipsychotics. It is characterised by slow (hence tardive), involuntary, repetitive, purposeless muscle movements.
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a potentially fatal complication of antipsychotic drug use. It is characterised by the following symptoms:
- Muscle rigidity
- Tremors
- Mental status change (e.g., hallucinations, agitation, stupor, confusion, etc.)
- Hyperthermia
- Autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, high blood pressure, diaphoresis, diarrhoea, etc.)
- Urinary retention
- Blood dyscrasias, e.g., agranulocytosis (a potentially fatal drop in white blood cell count), leukopaenia (a drop in white blood cell counts but not to as extreme an extent as agranulocytosis), neutropaenia (a drop in neutrophil count), thrombocytopaenia (a dangerous drop in platelet counts), eosinophilia (raised eosinophil count), purpura (the appearance of red or purple discolourations of the skin that do not blanch when pressure is applied)
- Hepatitis
- Jaundice
- Pigmentary retinopathy
- Anaphylactoid reactions
- Oedema
- Asthma
- Coma
- Seizures
- Confusional states
- Disorientation
- Incoordination
- Ataxia
- Tremors
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Numbness, tingling and paresthesias of the extremities
- Dysarthria
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- Tinnitus
- Alteration in EEG patterns
- Paralytic ileus
- Hyperpyrexia (elevated body temperature)
- Disturbance of accommodation
- Increased intraocular pressure
- Mydriasis
Remove ads
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Binding affinities (Ki [nM]; for human cloned receptors when available)[5][6][7]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads