Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Arcuate nucleus (medulla)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In the medulla oblongata, the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei.[1]
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Italian. (November 2025) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
They receive afferents from the corticospinal tract.[citation needed]
They in turn project efferents into the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle as:[1]
- the anterior internal arcuate fibers which pass along the midline before decussating near the rhomboid fossa (floor of fourth ventricle) then passing laterally as the medullary striae;
- the anterior external arcuate fibers.
Remove ads
Function
Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate.[2]
Additional images
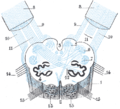
- Diagram showing the course of the arcuate fibers.
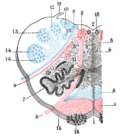
- The formatio reticularis of the medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive.
External links
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads