Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Atlantic Seaboard Fall Line
Escarpment in the Eastern United States From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
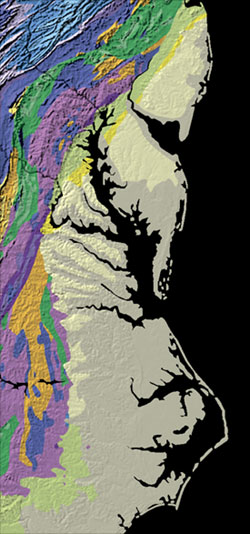
The Atlantic Seaboard Fall Line, or Fall Zone, is a 900-mile (1,400 km) escarpment where the Piedmont and Atlantic coastal plain meet in the eastern United States.[3] Much of the Atlantic Seaboard fall line passes through areas where no evidence of faulting is present.
The fall line marks the geologic boundary of hard metamorphosed terrain—the product of the Taconic orogeny—and the sandy, relatively flat alluvial plain of the upper continental shelf, formed of unconsolidated Cretaceous and Cenozoic sediments. Examples of Fall Zone features include the Potomac River's Little Falls and the rapids in Richmond, Virginia, where the James River falls across a series of rapids down to its own tidal estuary.
Before navigation improvements, such as locks, the fall line was generally the head of navigation on rivers due to their rapids or waterfalls, and the necessary portage around them. Numerous cities initially formed along the fall line because of the easy river transportation to seaports, as well as the availability of water power to operate mills and factories, thus bringing together river traffic and industrial labor. U.S. Route 1 and Interstate 95 link many of the fall-line cities.
In 1808, Treasury Secretary Albert Gallatin noted the significance of the fall line as an obstacle to improved national communication and commerce between the Atlantic seaboard and the western river systems:[4]
The most prominent, though not perhaps the most insuperable obstacle in the navigation of the Atlantic rivers, consists in their lower falls, which are ascribed to a presumed continuous granite ridge, rising about one hundred and thirty feet above tide water. That ridge from New York to James River inclusively arrests the ascent of the tide; the falls of every river within that space being precisely at the head of the tide; pursuing thence southwardly a direction nearly parallel to the mountains, it recedes from the sea, leaving in each southern river an extent of good navigation between the tide and the falls. Other falls of less magnitude are found at the gaps of the Blue Ridge, through which the rivers have forced their passage...
Gallatin's observation was sound, though simplified and limited by the knowledge of his time. The limits of the Fall Line are subject to some dispute. In the north, the fall line is usually understood to have its northern limit at New Brunswick, New Jersey, a geologic continuation in fact crosses the Hackensack and Passaic rivers at the cities of those names, to which navigation was possible. In the south, some such as Gallatin above, and the USGS source in the infobox, imply its end to be in the Carolinas or Georgia, and to include only rivers running to the Atlantic; but it is more accurate, as the Georgia source in the infobox does, to trace it farther west through Georgia and Alabama, as that is the geologic continuation.[5]
Remove ads
Cities and towns
Summarize
Perspective
Only the principal city of an area is listed below. However, two cities may belong on one river, if the one downstream is at the effective head of navigation and the one upstream at the site of useful water power.
Cities that lie along the Piedmont–Coastal Plain fall line include the following (from north to south):
- New Brunswick, New Jersey on the Raritan River.
- Trenton, New Jersey, on the Delaware River.[3]
- Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on the Schuylkill River.[6]
- Wilmington, Delaware, on the Brandywine River.
- Havre de Grace, Maryland, on the Susquehanna River/head of Chesapeake Bay.
- Baltimore, Maryland, on Herring Run, Jones Falls, and Gwynns Falls.[7]
- Washington, D.C., on the Potomac River.[8]
- Fredericksburg, Virginia on the Rappahannock River.[8]
- Richmond, Virginia, on the James River.[9]
- Goldsboro, North Carolina and Smithfield, North Carolina, on the Neuse River.[10]
- Fayetteville, North Carolina, on the Cape Fear River.[citation needed]
- Columbia, South Carolina, on the Congaree River.[2][9]
- Augusta, Georgia, on the Savannah River.[2]
- Macon, Georgia, on the Ocmulgee River.[2]
- Columbus, Georgia, on the Chattahoochee River.[2]
- Tuscaloosa, Alabama, on the Black Warrior River.[2]
- Wetumpka, Alabama, on the Coosa River. The river and fall line run along the outside slope of the Wetumpka meteor impact crater, through an uplifted area. The crater is 82 MYA and the fall line is over 200 MYA.[11][12]
Remove ads
Geographic coordinates
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads