Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Beta-2 adrenergic receptor
Mammalian protein found in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2 adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increases cAMP, and, via downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.[5]
Robert Lefkowitz and Brian Kobilka's study of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor as a model system earned them the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for studies of G-protein-coupled receptors".[6][7][8]
The official symbol for the human gene encoding the β2 adrenoreceptor is ADRB2.[9]
Remove ads
Gene
The ADRB2 gene is intronless. Different polymorphic forms, point mutations, and/or downregulation of this gene are associated with nocturnal asthma, obesity and type 2 diabetes.[10]
Structure
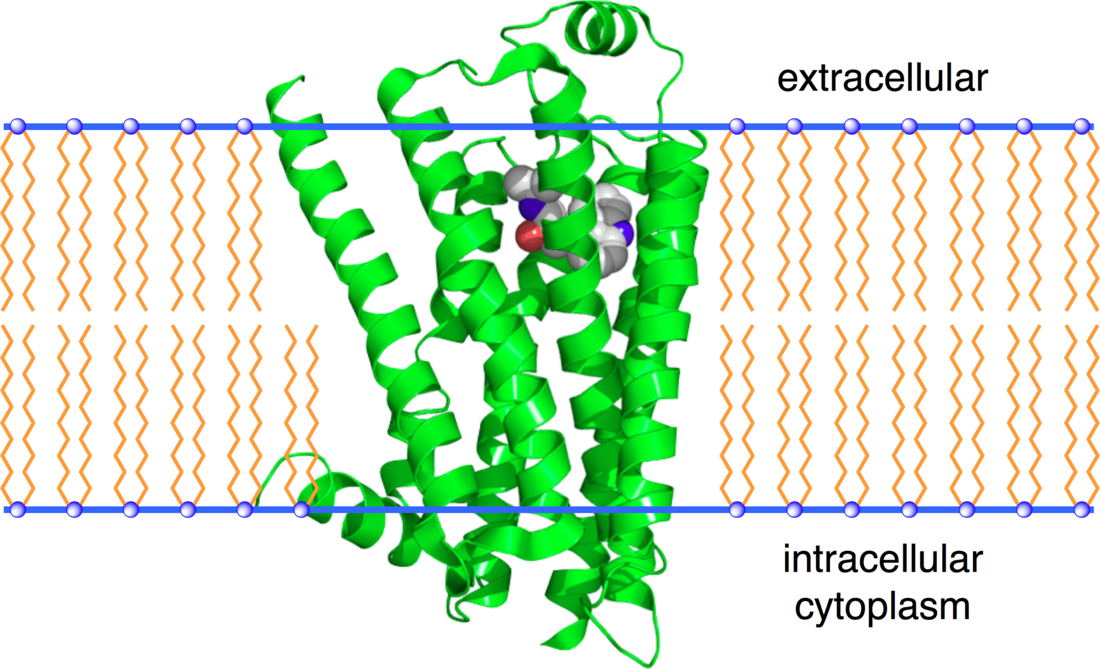
The 3D crystallographic structure (see figure and links to the right) of the β2-adrenergic receptor has been determined[11][12][13] by making a fusion protein with lysozyme to increase the hydrophilic surface area of the protein for crystal contacts. An alternative method, involving production of a fusion protein with an agonist, supported lipid-bilayer co-crystallization and generation of a 3.5 Å resolution structure.[14]
The crystal structure of the β2Adrenergic Receptor-Gs protein complex was solved in 2011. The largest conformational changes in the β2AR include a 14 Å outward movement at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment 6 (TM6) and an alpha helical extension of the cytoplasmic end of TM5.[15]
Remove ads
Mechanism
Summarize
Perspective
This receptor is directly associated with one of its ultimate effectors, the class C L-type calcium channel CaV1.2.[citation needed] This receptor-channel complex is coupled to the Gs G protein, which activates adenylyl cyclase, catalysing the formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) which then activates protein kinase A, and counterbalancing phosphatase PP2A. Protein kinase A then goes on to phosphorylate (and thus inactivate) myosin light-chain kinase, which causes smooth muscle relaxation, accounting for the vasodilatory effects of beta 2 stimulation. The assembly of the signaling complex provides a mechanism that ensures specific and rapid signaling. A two-state biophysical and molecular model has been proposed to account for the pH and REDOX sensitivity of this and other GPCRs.[16]
Beta-2 adrenergic receptors have also been found to couple with Gi, possibly providing a mechanism by which response to ligand is highly localized within cells. In contrast, Beta-1 adrenergic receptors are coupled only to Gs, and stimulation of these results in a more diffuse cellular response.[17] This appears to be mediated by cAMP induced PKA phosphorylation of the receptor.[18] Interestingly, Beta-2 adrenergic receptor was observed to localize exclusively to the T-tubular network of adult cardiomyocytes, as opposed to Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, which is observed also on the outer plasma membrane of the cell [19]
Function
Summarize
Perspective
| Legend |
Musculoskeletal system
Activation of the β2 adrenoreceptor with long-acting agents such as oral clenbuterol and intravenously-infused albuterol results in skeletomuscular hypertrophy and anabolism.[26][27] The comprehensive anabolic, lipolytic, and ergogenic effects of long-acting β2 agonists such as clenbuterol render them frequent targets as performance-enhancing drugs in athletes.[28] Consequently, such agents are monitored for and generally banned by WADA (World Anti-Doping Agency) with limited permissible usage under therapeutic exemptions; clenbuterol and other β2 adrenergic agents remain banned not as a beta-agonist, but rather an anabolic agent. These effects are largely attractive within agricultural contexts insofar that β2 adrenergic agents have seen notable extra-label usage in food-producing animals and livestock. While many countries including the United States have prohibited extra-label usage in food-producing livestock, the practice is still observed in many countries.[29][30]
Circulatory system
- Heart muscle contraction
- Increase cardiac output (minor degree compared to β1).
- Increases heart rate[20] in sinoatrial node (SA node) (chronotropic effect).
- Increases atrial cardiac muscle contractility. (inotropic effect).
- Increases contractility and automaticity[20] of ventricular cardiac muscle.
- Dilate hepatic artery.
- Dilate arterioles to skeletal muscle.
Eye
In the normal eye, beta-2 stimulation by salbutamol increases intraocular pressure via net:
- Increase in production of aqueous humour by the ciliary process,
- Subsequent increased pressure-dependent uveoscleral outflow of humour, despite reduced drainage of humour via the Canal of Schlemm.
In glaucoma, drainage is reduced (open-angle glaucoma) or blocked completely (closed-angle glaucoma). In such cases, beta-2 stimulation with its consequent increase in humour production is highly contra-indicated, and conversely, a topical beta-2 antagonist such as timolol may be employed.
Digestive system
- Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver.[20]
- Glycogenolysis and lactate release in skeletal muscle.[20]
- Contract sphincters of Gastrointestinal tract.
- Thickened secretions from salivary glands.[20]
- Insulin and glucagon secretion from pancreas.[25]
Other
- Inhibit histamine-release from mast cells.
- Increase protein content of secretions from lacrimal glands.
- Receptor also present in cerebellum.
- Bronchiole dilation (targeted while treating asthma attacks)
- Involved in brain - immune - communication [31]
Remove ads
Ligands
Summarize
Perspective
Agonists
Spasmolytics used in asthma and COPD
- Short-acting β2 agonists (SABA)
- bitolterol
- fenoterol
- hexoprenaline
- isoprenaline (INN) or isoproterenol (USAN)
- levosalbutamol (INN) or levalbuterol (USAN)
- orciprenaline (INN) or metaproterenol (USAN)
- pirbuterol
- procaterol
- salbutamol (INN) or albuterol (USAN)
- terbutaline
- Long-acting β2 agonists (LABA)
- arformoterol (some consider it to be an ultra-LABA)[32]
- bambuterol
- clenbuterol
- formoterol
- salmeterol
- Ultra-long-acting β2 agonists (ultra-LABA)
- carmoterol
- indacaterol
- milveterol (GSK 159797)
- olodaterol
- vilanterol (GSK 642444)
Tocolytic agents
- Short-acting β2 agonists (SABA)
- fenoterol
- hexoprenaline
- isoxsuprine
- ritodrine
- salbutamol (INN) or albuterol (USAN)
- terbutaline
β2 agonists used for other purposes
Antagonists
* denotes selective antagonist to the receptor.
Allosteric modulators
Remove ads
Interactions
Beta-2 adrenergic receptor has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads