Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Zinc
Chemical element with atomic number 30 (Zn) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny blue whitish appearance when surface oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust, with an average concentration of 70 grams per ton.[8] Zinc also has five stable isotopes; the most abundant of which, Zn-64, comprises nearly half of zinc's total abundance. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.[b] The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest concentration of economically feasible lodes in descending order are located in China, Peru, and Australia, among others. Zinc is refined industrially by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity (electrowinning).
Zinc is an essential trace element for humans,[9][10][11] animals,[12] plants[13] and for microorganisms[14] and is necessary for both prenatal and postnatal development.[15] It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron, an important cofactor for many enzymes, and the only metal which appears in all enzyme classes.[13][11] Zinc is also an essential nutrient element for coral growth.[16]
Enzymes with a zinc atom in the reactive center are widespread in biochemistry, such as alcohol dehydrogenase in humans.[17] Deficiency of zinc intake affects about two billion people in the developing world and is associated with many diseases.[18] In children, deficiency causes growth retardation, delayed sexual maturation, infection susceptibility, and diarrhea.[15] However, consumption of excess zinc may cause ataxia, lethargy, and copper deficiency. In marine biomes, notably within polar regions, a deficit of zinc can compromise the vitality of primary algal communities, potentially destabilizing the intricate marine trophic structures and consequently impacting biodiversity.[19]
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc in various proportions, was used as early as the third millennium BCE in the Aegean area and the region which currently includes Iraq, the United Arab Emirates, Kalmykia, Turkmenistan and Georgia. In the second millennium BC it was used in the regions currently including West India, Uzbekistan, Iran, Syria, Iraq, and Israel.[20][21][22] Zinc metal was not produced on a large scale until the 12th century in India, though it was known to the ancient Romans and Greeks.[23] The mines of Rajasthan have given definite archeological evidence of zinc production harking back to the 6th century BCE.[24] The oldest man-made pure zinc comes from Zawar, Rajasthan, as early as the 9th century AD, when a distillation process was utilized to make virtually pure zinc.[25] Alchemists would burn zinc metal in air to form what they called "philosopher's wool" or "white snow" (zinc oxide, ZnO).
The element was probably named by the alchemist Paracelsus after the German word Zinke (prong, tooth). German chemist Andreas Sigismund Marggraf is credited with discovering pure metallic zinc in 1746. By 1800, work done by Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta had uncovered the electrochemical properties of zinc.
Plating of corrosion-resistant zinc on iron, achieved by a process named hot-dip galvanization, is the major application for zinc. Other applications include electrical batteries, small non-structural casts, and alloys such as brass. A variety of zinc compounds are commonly used, such as zinc carbonate, zinc gluconate (as dietary supplements), zinc chloride (in deodorants), zinc pyrithione (anti-dandruff shampoos), and zinc sulfide (in luminescent paints). In addition, dimethylzinc and diethylzinc are used for the chemical syntheses of organic compounds.
Remove ads
Characteristics
Summarize
Perspective
Physical properties

Zinc is a bluish-white, lustrous, diamagnetic metal,[26] though most common commercial grades of the metal have a dull finish.[27] It is somewhat less dense than iron and has a hexagonal crystal structure, with a distorted form of hexagonal close packing, in which each atom has six nearest neighbors (at 265.9 pm) in its own plane and six others at a greater distance of 290.6 pm.[28] The metal is hard and brittle at most temperatures but becomes malleable between 100 and 150 °C.[26][27] Above 210 °C, the metal becomes brittle again and can be pulverized by beating.[29] Zinc is a fair conductor of electricity.[26] For a metal, zinc has relatively low melting (419.53 °C) and boiling point (907 °C).[30] This melting point is the lowest of all the d-block metals aside from mercury and cadmium. For this reason among others, zinc, cadmium, and mercury are often not considered to be transition metals like the rest of the d-block metals.[30]
Many alloys contain zinc, the most famous example being brass. Other metals long known to form binary alloys with zinc are aluminium, antimony, bismuth, gold, iron, lead, mercury, silver, tin, magnesium, cobalt, nickel, tellurium, and sodium.[31] Although neither zinc nor zirconium is ferromagnetic, their alloy, ZrZn
2, exhibits ferromagnetism below 35 K.[26]
Occurrence
Zinc makes up about 70 ppm (0.007%) of Earth's crust in mass, making it the 24th-most abundant crustal element.[32] It also makes up 312 ppm of the Solar System, where it is the 22nd most abundant element.[33] Typical background concentrations of zinc do not exceed: 1 μg/m3 in atmosphere, 300 mg/kg in soil, 100 mg/kg in vegetation, 20 μg/L in freshwater, and 5 μg/L in seawater.[34] The element is normally found in association with other base metals such as copper and lead in the form of ores.[35] Zinc is a chalcophile, meaning the element is more likely to be found associated with sulfur and other heavy chalcogens, rather than with the light chalcogen oxygen or with non-chalcogen electronegative elements such as the halogens. Sulfides formed as the crust solidified under the highly reducing conditions of the young Earth's atmosphere.[36] Sphalerite, a crystalline form of zinc sulfide, is the most heavily mined zinc-containing ore as it contains 60–62% zinc by mass.[35]
Other source minerals for zinc include smithsonite (zinc carbonate), hemimorphite (zinc silicate), wurtzite (another zinc sulfide), and sometimes hydrozincite (basic zinc carbonate).[37] With the exception of wurtzite, all the other minerals were formed by weathering of the primordial zinc sulfides.[36]
Currently identified zinc resources across the globe total 1.9–2.8 billion tonnes.[38][39] Large deposits are in Australia, China, Canada, and the United States, with the largest potential reserves in Iran.[36][40][41] The most recent estimate of reserve base for zinc (meets specified minimum physical criteria related to current mining and production practices) was made in 2009 and was calculated to be roughly 480 Mt.[42] Zinc reserves, on the other hand, are geologically identified ore bodies whose suitability for recovery is economically practical (based on variables such as location, grade, quality, and quantity) at the time of determination. Since exploration and mine development is an ongoing process, the amount and number of zinc reserves is not a fixed number, and sustainability of zinc ore supplies cannot be judged by simply extrapolating the combined mine life of today's zinc mines. This concept is well supported by data from the United States Geological Survey (USGS), which illustrates that although refined zinc production increased 80% between 1990 and 2010, the reserve lifetime for zinc has remained unchanged, through the discovery of additional zinc deposits. About 346 million tonnes have been extracted throughout history up to 2002, and scholars have estimated that about 109–305 million tonnes are presently in use.[43][44][45]

Isotopes
Five stable isotopes of zinc occur in nature, with 64Zn being the most abundant isotope (49.17% natural abundance).[46][7] The other isotopes found in nature are 66
Zn (27.73%), 67
Zn (4.04%), 68
Zn (18.45%), and 70
Zn (0.61%).[7]
Several dozen radioisotopes have been characterized. 65
Zn, which has a half-life of 243.66 days, is the least active radioisotope, followed by 72
Zn with a half-life of 46.5 hours.[46] Zinc has 10 nuclear isomers, of which 69mZn has the longest half-life, at 13.75 hours.[7] The superscript m indicates a metastable isotope, whose nucleus is in an excited state and which will eventually return to its ground state, through the emission of excess energy in the form of one or more photons (gamma rays), with the nucleus decaying to the ground state by the end of the process.
The most common decay mode of a radioisotope of zinc with a mass number lower than 66 is electron capture. The resulting decay product will be an isotope of copper.[7]
The most common decay mode of a radioisotope of zinc with a mass number higher than 66 is beta decay (β−), producing an isotope of gallium.[7]
- n
30Zn → n
31Ga + e−
+ ν
e
Remove ads
Compounds and chemistry
Summarize
Perspective
Reactivity

Zinc has an electron configuration of [Ar]4s23d10 and is a member of the group 12 of the periodic table. It is a moderately reactive metal and strong reducing agent;[47] in the reactivity series it is comparable to manganese.[48] The surface of the pure metal tarnishes quickly, eventually forming a protective passivating layer of the basic zinc carbonate, Zn
5(OH)
6(CO3)
2, by reaction with atmospheric carbon dioxide.[49]
Zinc burns in air with a bright bluish-green flame, giving off fumes of zinc oxide.[50] Zinc reacts readily with acids, alkalis and other non-metals.[51] Extremely pure zinc reacts only slowly at room temperature with acids.[50] Strong acids, such as hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, can remove the passivating layer and the subsequent reaction with the acid releases hydrogen gas.[50]
Zinc chemistry resembles that of the late first-row transition metals, nickel and copper,[52] as well as certain main group elements. Almost all zinc compounds have the element in the +2 oxidation state.[53] When Zn2+ compounds form, the outer shell s electrons are lost, yielding a bare zinc ion with the electronic configuration [Ar]3d10.[54] The filled interior d shell generally does not participate in bonding, producing diamagnetic and mostly colorless compounds.[52] In aqueous solution an octahedral complex, [Zn(H
2O)6]2+
is the predominant species.[55]
The ionic radii of zinc and magnesium happen to be nearly identical. Consequently, some of the equivalent salts have the same crystal structure,[56] and in other circumstances where ionic radius is a determining factor, the chemistry of zinc has much in common with that of magnesium.[50] Compared to the transition metals, zinc tends to form bonds with a greater degree of covalency. Complexes with N- and S- donors are much more stable.[52] Complexes of zinc are mostly 4- or 6- coordinate, although 5-coordinate complexes are known.[50]
Other oxidation states require unusual physical conditions, and the only positive oxidation states demonstrated are +1 or +2.[53] The volatilization of zinc in combination with zinc chloride at temperatures above 285 °C indicates the formation of Zn
2Cl
2, a zinc compound with a +1 oxidation state.[50] Calculations indicate that a zinc compound with the oxidation state of +4 is unlikely to exist.[57] Zn(III) is predicted to exist in the presence of strongly electronegative trianions;[58][59] however, there exists some doubt around this possibility.[60]
Zinc(I) compounds
Zinc(I) compounds are very rare. The [Zn2]2+ ion is implicated by the formation of a yellow diamagnetic glass by dissolving metallic zinc in molten ZnCl2.[61] The [Zn2]2+ core would be analogous to the [Hg2]2+ cation present in mercury(I) compounds. The diamagnetic nature of the ion confirms its dimeric structure. The first zinc(I) compound containing the Zn–Zn bond, (η5-C5Me5)2Zn2 has been reported in 2004.[62]
Zinc(II) compounds

3CO
2)
2

Binary compounds of zinc are known for most of the metalloids and all the nonmetals except the noble gases. The oxide ZnO is a white powder that is nearly insoluble in neutral aqueous solutions, but is amphoteric, dissolving in both strong basic and acidic solutions.[50] The other chalcogenides (ZnS, ZnSe, and ZnTe) have varied applications in electronics and optics.[63] Pnictogenides (Zn
3N
2, Zn
3P
2, Zn
3As
2 and Zn
3Sb
2),[64][65] the peroxide (ZnO
2), the hydride (ZnH
2), and the carbide (ZnC
2) are also known.[66] Of the four halides, ZnF
2 has the most ionic character, while the others (ZnCl
2, ZnBr
2, and ZnI
2) have relatively low melting points and are considered to have more covalent character.[67]
In weak basic solutions containing Zn2+
ions, the hydroxide Zn(OH)
2 forms as a white precipitate. In stronger alkaline solutions, this hydroxide is dissolved to form zincates ([Zn(OH)4]2−
).[50] The nitrate Zn(NO3)
2, chlorate Zn(ClO3)
2, sulfate ZnSO
4, phosphate Zn
3(PO4)
2, molybdate ZnMoO
4, cyanide Zn(CN)
2, arsenite Zn(AsO2)
2, arsenate Zn(AsO4)
2·8H
2O and the chromate ZnCrO
4 (one of the few colored zinc compounds) are a few examples of other common inorganic compounds of zinc.[68][69]
Organozinc compounds are those that contain zinc–carbon covalent bonds. Diethylzinc ((C
2H5)
2Zn) is a reagent in synthetic chemistry. It was first reported in 1848 from the reaction of zinc and ethyl iodide, and was the first compound known to contain a metal–carbon sigma bond.[70]
Test for zinc
Cobalticyanide paper (Rinnmann's test for Zn) can be used as a chemical indicator for zinc. 4 g of K3Co(CN)6 and 1 g of KClO3 is dissolved on 100 ml of water. Paper is dipped in the solution and dried at 100 °C. One drop of the sample is dropped onto the dry paper and heated. A green disc indicates the presence of zinc.[71]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Ancient use
Various isolated examples of the use of impure zinc in ancient times have been discovered. Zinc ores were used to make the zinc–copper alloy brass thousands of years prior to the discovery of zinc as a separate element. Judean brass from the 14th to 10th centuries BC contains 23% zinc.[21]
Knowledge of how to produce brass spread to Ancient Greece by the 7th century BC, but few varieties were made.[22] Ornaments made of alloys containing 80–90% zinc, with lead, iron, antimony, and other metals making up the remainder, have been found that are 2,500 years old.[35] A possibly prehistoric statuette containing 87.5% zinc was found in a Dacian archaeological site.[72]
Strabo writing in the 1st century BC (but quoting a now lost work of the 4th century BC historian Theopompus) mentions "drops of false silver" which when mixed with copper make brass. This may refer to small quantities of zinc that is a by-product of smelting sulfide ores.[73] Zinc in such remnants in smelting ovens was usually discarded as it was thought to be worthless.[74]
The manufacture of brass was known to the Romans by about 30 BC.[75] They made brass by heating powdered calamine (zinc silicate or carbonate), charcoal and copper together in a crucible.[75] The resulting calamine brass was then either cast or hammered into shape for use in weaponry.[76] Some coins struck by Romans in the Christian era are made of what is probably calamine brass.[77]

The oldest known pills were made of the zinc carbonates hydrozincite and smithsonite. The pills were used for sore eyes and were found aboard the Roman ship Relitto del Pozzino, wrecked in 140 BC.[78][79]
The Berne zinc tablet is a votive plaque dating to Roman Gaul made of an alloy that is mostly zinc.[80]
The Charaka Samhita, thought to have been written between 300 and 500 AD,[81] mentions a metal which, when oxidized, produces pushpanjan, thought to be zinc oxide.[82] Zinc mines at Zawar, near Udaipur in India, have been active since the Mauryan period (c. 322 and 187 BCE). The smelting of metallic zinc here, however, appears to have begun around the 12th century AD.[83][84] One estimate is that this location produced an estimated million tonnes of metallic zinc and zinc oxide from the 12th to 16th centuries.[37] Another estimate gives a total production of 60,000 tonnes of metallic zinc over this period.[83] The Rasaratna Samuccaya, written in approximately the 13th century AD, mentions two types of zinc-containing ores: one used for metal extraction and another used for medicinal purposes.[84]
Early studies and naming
Zinc was distinctly recognized as a metal under the designation of Yasada or Jasada in the medical Lexicon ascribed to the Hindu king Madanapala (of Taka dynasty) and written about the year 1374.[85] Smelting and extraction of impure zinc by reducing calamine with wool and other organic substances was accomplished in the 13th century in India.[26][86] The Chinese did not learn of the technique until the 17th century.[86]

Alchemists burned zinc metal in air and collected the resulting zinc oxide (ZnO) on a condenser. Some alchemists called this zinc oxide lana philosophica, Latin for "philosopher's wool", because it collected in woolly tufts, whereas others thought it looked like white snow and named it nix album.[87]
The name of the metal was probably first documented by Paracelsus, a Swiss-born German alchemist, who referred to the metal as "zincum" or "zinken" in his book Liber Mineralium II, in the 16th century.[86][88] The word is probably derived from the German zinke, and supposedly meant "tooth-like, pointed or jagged" (metallic zinc crystals have a needle-like appearance).[89] Zink could also imply "tin-like" because of its relation to German zinn meaning tin.[90] Yet another possibility is that the word is derived from the Persian word سنگ seng meaning stone.[91] The metal was also called Indian tin, tutanego, calamine, and spinter.[35]
German metallurgist Andreas Libavius received a quantity of what he called "calay" (from the Malay or Hindi word for tin) originating from Malabar off a cargo ship captured from the Portuguese in the year 1596.[92] Libavius described the properties of the sample, which may have been zinc. Zinc was regularly imported to Europe from the Orient in the 17th and early 18th centuries,[86] but was at times very expensive.[c]
Isolation

Metallic zinc was isolated in India by 1300 AD.[93][94][95] Before it was isolated in Europe, it was imported from India in about 1600 CE.[96] Postlewayt's Universal Dictionary, a contemporary source giving technological information in Europe, did not mention zinc before 1751 but the element was studied before then.[84][97]
Flemish metallurgist and alchemist P. M. de Respour reported that he had extracted metallic zinc from zinc oxide in 1668.[37] By the start of the 18th century, Étienne François Geoffroy described how zinc oxide condenses as yellow crystals on bars of iron placed above zinc ore that is being smelted.[37] In Britain, John Lane is said to have carried out experiments to smelt zinc, probably at Landore, prior to his bankruptcy in 1726.[98]
In 1738 in Great Britain, William Champion patented a process to extract zinc from calamine in a vertical retort-style smelter.[99] His technique resembled that used at Zawar zinc mines in Rajasthan, but no evidence suggests he visited the Orient.[96] Champion's process was used through 1851.[86]
German chemist Andreas Marggraf normally gets credit for isolating pure metallic zinc in the West, even though Swedish chemist Anton von Swab had distilled zinc from calamine four years previously.[86] In his 1746 experiment, Marggraf heated a mixture of calamine and charcoal in a closed vessel without copper to obtain a metal.[100][74] This procedure became commercially practical by 1752.[101]
Later work

William Champion's brother, John, patented a process in 1758 for calcining zinc sulfide into an oxide usable in the retort process.[35] Prior to this, only calamine could be used to produce zinc. In 1798, Johann Christian Ruberg improved on the smelting process by building the first horizontal retort smelter.[102] Jean-Jacques Daniel Dony built a different kind of horizontal zinc smelter in Belgium that processed even more zinc.[86] Italian doctor Luigi Galvani discovered in 1780 that connecting the spinal cord of a freshly dissected frog to an iron rail attached by a brass hook caused the frog's leg to twitch.[103] He incorrectly thought he had discovered an ability of nerves and muscles to create electricity and called the effect "animal electricity".[104] The galvanic cell and the process of galvanization were both named after Luigi Galvani, and his discoveries paved the way for electrical batteries, galvanization, and cathodic protection.[104]
Galvani's friend, Alessandro Volta, continued researching the effect and invented the Voltaic pile in 1800.[103] Volta's pile consisted of a stack of simplified galvanic cells, each being one plate of copper and one of zinc connected by an electrolyte. By stacking these units in series, the Voltaic pile (or "battery") as a whole had a higher voltage, which could be used more easily than single cells. Electricity is produced because the Volta potential between the two metal plates makes electrons flow from the zinc to the copper and corrode the zinc.[103]
The non-magnetic character of zinc and its lack of color in solution delayed discovery of its importance to biochemistry and nutrition.[105] This changed in 1940 when carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that scrubs carbon dioxide from blood, was shown to have zinc in its active site.[105] The digestive enzyme carboxypeptidase became the second known zinc-containing enzyme in 1955.[105]
Remove ads
Production
Summarize
Perspective
Mining and processing




27°57′17″S 016°46′00″E

27°49′09″S 016°36′28″E
Zinc is the fourth most common metal in use, trailing only iron, aluminium, and copper with an annual production of about 13 million tonnes.[38] The world's largest zinc producer is Nyrstar, a merger of the Australian OZ Minerals and the Belgian Umicore.[108] About 70% of the world's zinc originates from mining, while the remaining 30% comes from recycling secondary zinc.[109]
Commercially pure zinc is known as Special High Grade, often abbreviated SHG, and is 99.995% pure.[110]
Worldwide, 95% of new zinc is mined from sulfidic ore deposits, in which sphalerite (ZnS) is nearly always mixed with the sulfides of copper, lead and iron.[111]: 6 Zinc mines are scattered throughout the world, with the main areas being China, Australia, and Peru. China produced 38% of the global zinc output in 2014.[38]
Zinc metal is produced using extractive metallurgy.[112]: 7 The ore is finely ground, then put through froth flotation to separate minerals from gangue (on the property of hydrophobicity), to get a zinc sulfide ore concentrate[112]: 16 consisting of about 50% zinc, 32% sulfur, 13% iron, and 5% SiO
2.[112]: 16
Roasting converts the zinc sulfide concentrate to zinc oxide:[111]
The sulfur dioxide is used for the production of sulfuric acid, which is necessary for the leaching process. If deposits of zinc carbonate, zinc silicate, or zinc-spinel (like the Skorpion Deposit in Namibia) are used for zinc production, the roasting can be omitted.[113]
For further processing two basic methods are used: pyrometallurgy or electrowinning. Pyrometallurgy reduces zinc oxide with carbon or carbon monoxide at 950 °C (1,740 °F) into the metal, which is distilled as zinc vapor to separate it from other metals, which are not volatile at those temperatures.[114] The zinc vapor is collected in a condenser.[111] The equations below describe this process:[111]
In electrowinning, zinc is leached from the ore concentrate by sulfuric acid and impurities are precipitated:[115]
Finally, the zinc is reduced by electrolysis.[111]
The sulfuric acid is regenerated and recycled to the leaching step.
When galvanised feedstock is fed to an electric arc furnace, the zinc is recovered from the dust by a number of processes, predominantly the Waelz process (90% as of 2014).[116]
Environmental impact
Refinement of sulfidic zinc ores produces large volumes of sulfur dioxide and cadmium vapor. Smelter slag and other residues contain significant quantities of metals. About 1.1 million tonnes of metallic zinc and 130 thousand tonnes of lead were mined and smelted in the Belgian towns of La Calamine and Plombières between 1806 and 1882.[117] The dumps of the past mining operations leach zinc and cadmium, and the sediments of the Geul River contain non-trivial amounts of metals.[117] About two thousand years ago, emissions of zinc from mining and smelting totaled 10 thousand tonnes a year. After increasing 10-fold from 1850, zinc emissions peaked at 3.4 million tonnes per year in the 1980s and declined to 2.7 million tonnes in the 1990s, although a 2005 study of the Arctic troposphere found that the concentrations there did not reflect the decline. Man-made and natural emissions occur at a ratio of 20 to 1.[13]
Zinc in rivers flowing through industrial and mining areas can be as high as 20 ppm.[118] Effective sewage treatment greatly reduces this; treatment along the Rhine, for example, has decreased zinc levels to 50 ppb.[118] Concentrations of zinc as low as 2 ppm adversely affects the amount of oxygen that fish can carry in their blood.[119]
Soils contaminated with zinc from mining, refining, or fertilizing with zinc-bearing sludge can contain several grams of zinc per kilogram of dry soil. Levels of zinc in excess of 500 ppm in soil interfere with the ability of plants to absorb other essential metals, such as iron and manganese. Zinc levels of 2000 ppm to 180,000 ppm (18%) have been recorded in some soil samples.[118]
Remove ads
Applications
Summarize
Perspective
Major applications of zinc include, with percentages given for the US[122]
- Galvanizing (55%)
- Brass and bronze (16%)
- Other alloys (21%)
- Miscellaneous (8%)
Anti-corrosion and batteries


Zinc is most commonly used as an anti-corrosion agent,[123] and galvanization (coating of iron or steel) is the most familiar form. In 2009 in the United States, 55% or 893,000 tons of the zinc metal was used for galvanization.[122]
Zinc is more reactive than iron or steel and thus will attract almost all local oxidation until it completely corrodes away.[124] A protective surface layer of oxide and carbonate (Zn
5(OH)
6(CO
3)
2) forms as the zinc corrodes.[125] This protection lasts even after the zinc layer is scratched but degrades through time as the zinc corrodes away.[125] The zinc is applied electrochemically or as molten zinc by hot-dip galvanizing or spraying. Galvanization is used on chain-link fencing, guard rails, suspension bridges, lightposts, metal roofs, heat exchangers, and car bodies.[126]
The relative reactivity of zinc and its ability to attract oxidation to itself makes it an efficient sacrificial anode in cathodic protection (CP). For example, cathodic protection of a buried pipeline can be achieved by connecting anodes made from zinc to the pipe.[125] Zinc acts as the anode (negative terminus) by slowly corroding away as it passes electric current to the steel pipeline.[125][d] Zinc is also used to cathodically protect metals that are exposed to sea water.[127] A zinc disc attached to a ship's iron rudder will slowly corrode while the rudder stays intact.[124] Similarly, a zinc plug attached to a propeller or the metal protective guard for the keel of the ship provides temporary protection.
With a standard electrode potential (SEP) of −0.76 volts, zinc is used as an anode material for primary cells. (More reactive lithium (SEP −3.04 V) is used for anodes in lithium batteries ). Powdered zinc is used in this way alkaline batteries and the case (which also serves as the anode) of zinc–carbon batteries is formed from sheet zinc.[128][129] There are also efforts to use zinc as anode material in secondary cells with a comparable cell chemistry, for example by advanced electrolytes.[130] Zinc is used as the anode or fuel of the zinc–air battery/fuel cell.[131][132][133] The zinc-cerium redox flow battery also relies on a zinc-based negative half-cell.[134]
Alloys
A widely used zinc alloy is brass, in which copper is alloyed with anywhere from 3% to 45% zinc, depending upon the type of brass.[125] Brass is generally more ductile and stronger than copper, and has superior corrosion resistance.[125] These properties make it useful in communication equipment, hardware, musical instruments, and water valves.[125]

Other widely used zinc alloys include nickel silver, typewriter metal, soft and aluminium solder, and commercial bronze.[26] Zinc is also used in contemporary pipe organs as a substitute for the traditional lead/tin alloy in pipes.[135] Alloys of 85–88% zinc, 4–10% copper, and 2–8% aluminium find limited use in certain types of machine bearings. Zinc has been the primary metal in American one cent coins (pennies) since 1982.[136] The zinc core is coated with a thin layer of copper to give the appearance of a copper coin. In 1994, 33,200 tonnes (36,600 short tons) of zinc were used to produce 13.6 billion pennies in the United States.[137]
Alloys of zinc with small amounts of copper, aluminium, and magnesium are useful in die casting as well as spin casting, especially in the automotive, electrical, and hardware industries.[26] These alloys are marketed under the name Zamak.[138] An example of this is zinc aluminium. The low melting point together with the low viscosity of the alloy makes possible the production of small and intricate shapes. The low working temperature leads to rapid cooling of the cast products and fast production for assembly.[26][139] Another alloy, marketed under the brand name Prestal, contains 78% zinc and 22% aluminium, and is reported to be nearly as strong as steel but as malleable as plastic.[26][140] This superplasticity of the alloy allows it to be molded using die casts made of ceramics and cement.[26]
Similar alloys with the addition of a small amount of lead can be cold-rolled into sheets. An alloy of 96% zinc and 4% aluminium is used to make stamping dies for low production run applications for which ferrous metal dies would be too expensive.[141] For building facades, roofing, and other applications for sheet metal formed by deep drawing, roll forming, or bending, zinc alloys with titanium and copper are used.[142] Unalloyed zinc is too brittle for these manufacturing processes.[142]
As a dense, inexpensive, easily worked material, zinc is used as a lead replacement. In the wake of lead concerns, zinc appears in weights for various applications ranging from fishing[143] to tire balances and flywheels.[144]
Cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) is a semiconductive alloy that can be divided into an array of small sensing devices.[145] These devices are similar to an integrated circuit and can detect the energy of incoming gamma ray photons.[145] When behind an absorbing mask, the CZT sensor array can determine the direction of the rays.[145]
Other industrial uses

Roughly one quarter of all zinc output in the United States in 2009 was consumed in zinc compounds;[122] a variety of which are used industrially. Zinc oxide is widely used as a white pigment in paints and as a catalyst in the manufacture of rubber to disperse heat. Zinc oxide is used to protect rubber polymers and plastics from ultraviolet radiation (UV).[126] The semiconductor properties of zinc oxide make it useful in varistors and photocopying products.[146] The zinc zinc-oxide cycle is a two step thermochemical process based on zinc and zinc oxide for hydrogen production.[147]
Zinc chloride is often added to lumber as a fire retardant[148] and sometimes as a wood preservative.[149] It is used in the manufacture of other chemicals.[148] Zinc methyl (Zn(CH3)
2) is used in a number of organic syntheses.[150] Zinc sulfide (ZnS) is used in luminescent pigments such as on the hands of clocks, X-ray and television screens, and luminous paints.[151] Crystals of ZnS are used in lasers that operate in the mid-infrared part of the spectrum.[152] Zinc sulfate is a chemical in dyes and pigments.[148] Zinc pyrithione is used in antifouling paints.[153]
Zinc powder is sometimes used as a propellant in model rockets.[154] When a compressed mixture of 70% zinc and 30% sulfur powder is ignited there is a violent chemical reaction.[154] This produces zinc sulfide, together with large amounts of hot gas, heat, and light.[154]
Zinc sheet metal is used as a durable covering for roofs, walls, and countertops, the last often seen in bistros and oyster bars, and is known for the rustic look imparted by its surface oxidation in use to a blue-gray patina and susceptibility to scratching.[155][156][157][158]
64
Zn, the most abundant isotope of zinc, is very susceptible to neutron activation, being transmuted into the highly radioactive 65
Zn, which has a half-life of 244 days and produces intense gamma radiation. Because of this, zinc oxide used in nuclear reactors as an anti-corrosion agent is depleted of 64
Zn before use, this is called depleted zinc oxide. For the same reason, zinc has been proposed as a salting material for nuclear weapons (cobalt is another, better-known salting material).[159] A jacket of isotopically enriched 64
Zn would be irradiated by the intense high-energy neutron flux from an exploding thermonuclear weapon, forming a large amount of 65
Zn significantly increasing the radioactivity of the weapon's fallout.[159] Such a weapon is not known to have ever been built, tested, or used.[159]
65
Zn is used as a tracer to study how alloys that contain zinc wear out, or the path and the role of zinc in organisms.[160]
Zinc dithiocarbamate complexes are used as agricultural fungicides; these include Zineb, Metiram, Propineb and Ziram.[161] Zinc naphthenate is used as wood preservative.[162] Zinc in the form of ZDDP, is used as an anti-wear additive for metal parts in engine oil.[163]
Organic chemistry
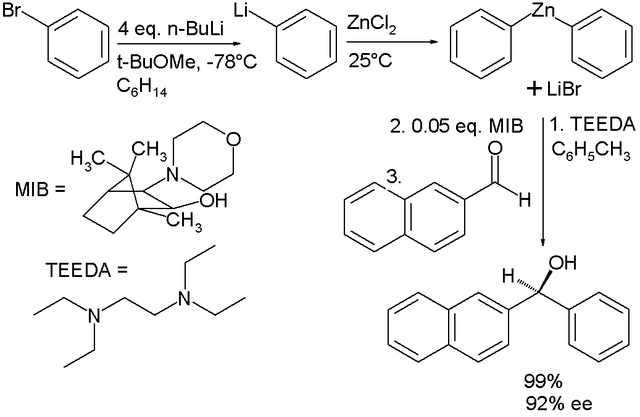
Organozinc chemistry is the science of compounds that contain carbon-zinc bonds, describing the physical properties, synthesis, and chemical reactions. Many organozinc compounds are commercially important.[165][166][167][168] Among important applications are:
- The Frankland-Duppa Reaction in which an oxalate ester (ROCOCOOR) reacts with an alkyl halide R'X, zinc and hydrochloric acid to form α-hydroxycarboxylic esters RR'COHCOOR[169][170]
- Organozincs have similar reactivity to Grignard reagents but are much less nucleophilic, and they are expensive and difficult to handle. Organozincs typically perform nucleophilic addition on electrophiles such as aldehydes, which are then reduced to alcohols. Commercially available diorganozinc compounds include dimethylzinc, diethylzinc and diphenylzinc. Like Grignard reagents, organozincs are commonly produced from organobromine precursors.
Zinc has found many uses in catalysis in organic synthesis including enantioselective synthesis, being a cheap and readily available alternative to precious metal complexes. Quantitative results (yield and enantiomeric excess) obtained with chiral zinc catalysts can be comparable to those achieved with palladium, ruthenium, iridium and others.[171]
Dietary supplement


In most single-tablet, over-the-counter, daily vitamin and mineral supplements, zinc is included in such forms as zinc oxide, zinc acetate, zinc gluconate, or zinc amino acid chelate.[172][173]
Generally, zinc supplement is recommended where there is high risk of zinc deficiency (such as low and middle income countries) as a preventive measure.[174] Although zinc sulfate is a commonly used zinc form, zinc citrate, gluconate and picolinate may be valid options as well. These forms are better absorbed than zinc oxide.[175]
Gastroenteritis
Zinc is an inexpensive and effective part of treatment of diarrhea among children in the developing world. Zinc becomes depleted in the body during diarrhea and replenishing zinc with a 10- to 14-day course of treatment can reduce the duration and severity of diarrheal episodes and may also prevent future episodes for as long as three months.[176] Gastroenteritis is strongly attenuated by ingestion of zinc, possibly by direct antimicrobial action of the ions in the gastrointestinal tract, or by the absorption of the zinc and re-release from immune cells (all granulocytes secrete zinc), or both.[177][178]
Common cold
Zinc supplements (frequently zinc acetate or zinc gluconate lozenges) are a group of dietary supplements that are commonly used in an attempt to treat the common cold.[179] Evidence suggests that zinc does not prevent colds but may reduce their duration, with minimal or no impact on symptom severity.[180][181] Adverse effects with zinc supplements by mouth include bad taste and nausea.[179] The intranasal use of zinc-containing nasal sprays has been associated with the loss of the sense of smell;[179] consequently, in June 2009, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) warned consumers to stop using intranasal zinc.[179]
The human rhinovirus – the most common viral pathogen in humans – is the predominant cause of the common cold.[182] The hypothesized mechanism of action by which zinc reduces the severity and/or duration of cold symptoms is the suppression of nasal inflammation and the direct inhibition of rhinoviral receptor binding and rhinoviral replication in the nasal mucosa.[179]Weight gain
Zinc deficiency may lead to loss of appetite.[183] The use of zinc in the treatment of anorexia has been advocated since 1979. At least 15 clinical trials have shown that zinc improved weight gain in anorexia. A 1994 trial showed that zinc doubled the rate of body mass increase in the treatment of anorexia nervosa. Deficiency of other nutrients such as tyrosine, tryptophan and thiamine could contribute to this phenomenon of "malnutrition-induced malnutrition".[184] A meta-analysis of 33 prospective intervention trials regarding zinc supplementation and its effects on the growth of children in many countries showed that zinc supplementation alone had a statistically significant effect on linear growth and body weight gain, indicating that other deficiencies that may have been present were not responsible for growth retardation.[185]
Other
People taking zinc supplements may slow down the progress to age-related macular degeneration.[186] Zinc supplement is an effective treatment for acrodermatitis enteropathica, a genetic disorder affecting zinc absorption that was previously fatal to affected infants.[75] Zinc deficiency has been associated with major depressive disorder (MDD), and zinc supplements may be an effective treatment.[187] Zinc may help individuals sleep more.[11]
Topical use
Topical preparations of zinc include those used on the skin, often in the form of zinc oxide. Zinc oxide is generally recognized by the FDA as safe and effective[188] and is considered a very photo-stable.[189] Zinc oxide is one of the most common active ingredients formulated into a sunscreen to mitigate sunburn.[75] Applied thinly to a baby's diaper area (perineum) with each diaper change, it can protect against diaper rash.[75]
Chelated zinc is used in toothpastes and mouthwashes to prevent bad breath; zinc citrate helps reduce the build-up of calculus (tartar).[190][191]
Zinc pyrithione is widely included in shampoos to prevent dandruff.[192]
Topical zinc has also been shown to effectively treat, as well as prolong remission in genital herpes.[193]
Remove ads
Biological role
Summarize
Perspective
Zinc is an essential trace element for humans.[9][10][11] and other animals,[12] for plants[13] and for microorganisms.[14] Zinc is required for the function of over 300 enzymes and 1000 transcription factors,[11] and is stored and transferred in metallothioneins.[194][195] It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron and it is the only metal which appears in all enzyme classes.[13][11]
In proteins, zinc ions are often coordinated to the amino acid side chains of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, cysteine and histidine. The theoretical and computational description of this zinc binding in proteins (as well as that of other transition metals) is difficult.[196]
Roughly 2–4 grams of zinc[197] are distributed throughout the human body. Most zinc is in the brain, muscle, bones, kidney, and liver, with the highest concentrations in the prostate and parts of the eye.[198] Semen is particularly rich in zinc, a key factor in prostate gland function and reproductive organ growth.[199]
Zinc homeostasis of the body is mainly controlled by the intestine. Here, ZIP4 and especially TRPM7 were linked to intestinal zinc uptake essential for postnatal survival.[200][201]
In humans, the biological roles of zinc are ubiquitous.[15][10] It interacts with "a wide range of organic ligands",[15] and has roles in the metabolism of RNA and DNA, signal transduction, and gene expression. It also regulates apoptosis. A review from 2015 indicated that about 10% of human proteins (~3000) bind zinc,[202] in addition to hundreds more that transport and traffic zinc; a similar in silico study in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana found 2367 zinc-related proteins.[13]
In the brain, zinc is stored in specific synaptic vesicles by glutamatergic neurons and can modulate neuronal excitability.[10][11][203] It plays a key role in synaptic plasticity and so in learning.[10][204] Zinc homeostasis also plays a critical role in the functional regulation of the central nervous system.[10][203][11] Dysregulation of zinc homeostasis in the central nervous system that results in excessive synaptic zinc concentrations is believed to induce neurotoxicity through mitochondrial oxidative stress (e.g., by disrupting certain enzymes involved in the electron transport chain, including complex I, complex III, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase), the dysregulation of calcium homeostasis, glutamatergic neuronal excitotoxicity, and interference with intraneuronal signal transduction.[10][205] L- and D-histidine facilitate brain zinc uptake.[206] SLC30A3 is the primary zinc transporter involved in cerebral zinc homeostasis.[10]
Enzymes


Zinc is an efficient Lewis acid, making it a useful catalytic agent in hydroxylation and other enzymatic reactions.[207] The metal also has a flexible coordination geometry, which allows proteins using it to rapidly shift conformations to perform biological reactions.[208] Two examples of zinc-containing enzymes are carbonic anhydrase and carboxypeptidase, which are vital to the processes of carbon dioxide (CO
2) regulation and digestion of proteins, respectively.[209]
In vertebrate blood, carbonic anhydrase converts CO
2 into bicarbonate and the same enzyme transforms the bicarbonate back into CO
2 for exhalation through the lungs.[210] Without this enzyme, this conversion would occur about one million times slower[211] at the normal blood pH of 7 or would require a pH of 10 or more.[212] The non-related β-carbonic anhydrase is required in plants for leaf formation, the synthesis of indole acetic acid (auxin) and alcoholic fermentation.[213]
Carboxypeptidase cleaves peptide linkages during digestion of proteins. A coordinate covalent bond is formed between the terminal peptide and a C=O group attached to zinc, which gives the carbon a positive charge. This helps to create a hydrophobic pocket on the enzyme near the zinc, which attracts the non-polar part of the protein being digested.[209]
Signalling
Zinc has been recognized as a messenger, able to activate signalling pathways. Many of these pathways provide the driving force in aberrant cancer growth. They can be targeted through ZIP transporters.[214]
Other proteins
Zinc serves a purely structural role in zinc fingers, twists and clusters.[215] Zinc fingers form parts of some transcription factors, which are proteins that recognize DNA base sequences during the replication and transcription of DNA. Each of the nine or ten Zn2+
ions in a zinc finger helps maintain the finger's structure by coordinately binding to four amino acids in the transcription factor.[211]
In blood plasma, zinc is bound to and transported by albumin (60%, low-affinity) and transferrin (10%).[197] Because transferrin also transports iron, excessive iron reduces zinc absorption, and vice versa. A similar antagonism exists with copper.[216] The concentration of zinc in blood plasma stays relatively constant regardless of zinc intake.[207] Cells in the salivary gland, prostate, immune system, and intestine use zinc signaling to communicate with other cells.[217]
Zinc may be held in metallothionein reserves within microorganisms or in the intestines or liver of animals.[218] Metallothionein in intestinal cells is capable of adjusting absorption of zinc by 15–40%.[219] However, inadequate or excessive zinc intake can be harmful; excess zinc particularly impairs copper absorption because metallothionein absorbs both metals.[220]
The human dopamine transporter contains a high affinity extracellular zinc binding site which, upon zinc binding, inhibits dopamine reuptake and amplifies amphetamine-induced dopamine efflux in vitro.[221][222][223] The human serotonin transporter and norepinephrine transporter do not contain zinc binding sites.[223] Some EF-hand calcium binding proteins such as S100 or NCS-1 are also able to bind zinc ions.[224]
Nutrition
Dietary recommendations
The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for zinc in 2001. The current EARs for zinc for women and men ages 14 and up is 6.8 and 9.4 mg/day, respectively. The RDAs are 8 and 11 mg/day. RDAs are higher than EARs so as to identify amounts that will cover people with higher than average requirements. RDA for pregnancy is 11 mg/day. RDA for lactation is 12 mg/day. For infants up to 12 months the RDA is 3 mg/day. For children ages 1–13 years the RDA increases with age from 3 to 8 mg/day. As for safety, the IOM sets Tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of zinc the adult UL is 40 mg/day including both food and supplements combined (lower for children). Collectively the EARs, RDAs, AIs and ULs are referred to as Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs).[207]
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL are defined the same as in the United States. For people ages 18 and older the PRI calculations are complex, as the EFSA has set higher and higher values as the phytate content of the diet increases. For women, PRIs increase from 7.5 to 12.7 mg/day as phytate intake increases from 300 to 1200 mg/day; for men the range is 9.4 to 16.3 mg/day. These PRIs are higher than the U.S. RDAs.[225] The EFSA reviewed the same safety question and set its UL at 25 mg/day, which is much lower than the U.S. value.[226]
For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For zinc labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 15 mg, but on May 27, 2016, it was revised to 11 mg.[227][228] A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
Dietary intake

Animal products such as meat, fish, shellfish, fowl, eggs, and dairy contain zinc. The concentration of zinc in plants varies with the level in the soil. With adequate zinc in the soil, the food plants that contain the most zinc are wheat (germ and bran) and various seeds, including sesame, poppy, alfalfa, celery, and mustard.[229] Zinc is also found in beans, nuts, almonds, whole grains, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and blackcurrant.[230]
Other sources include fortified food and dietary supplements in various forms. A 1998 review concluded that zinc oxide, one of the most common supplements in the United States, and zinc carbonate are nearly insoluble and poorly absorbed in the body.[231] This review cited studies that found lower plasma zinc concentrations in the subjects who consumed zinc oxide and zinc carbonate than in those who took zinc acetate and sulfate salts.[231] For fortification, however, a 2003 review recommended cereals (containing zinc oxide) as a cheap, stable source that is as easily absorbed as the more expensive forms.[232] A 2005 study found that various compounds of zinc, including oxide and sulfate, did not show statistically significant differences in absorption when added as fortificants to maize tortillas.[233]
Deficiency
Nearly two billion people in the developing world are deficient in zinc. Groups at risk include children in developing countries and elderly with chronic illnesses.[18] In children, it causes an increase in infection and diarrhea and contributes to the death of about 800,000 children worldwide per year.[15] The World Health Organization advocates zinc supplementation for severe malnutrition and diarrhea.[234] Zinc supplements help prevent disease and reduce mortality, especially among children with low birth weight or stunted growth.[234] However, zinc supplements should not be administered alone, because many in the developing world have several deficiencies, and zinc interacts with other micronutrients.[235] While zinc deficiency is usually due to insufficient dietary intake, it can be associated with malabsorption, acrodermatitis enteropathica, chronic liver disease, chronic renal disease, sickle cell disease, diabetes, malignancy, and other chronic illnesses.[18]
In the United States, a federal survey of food consumption determined that for women and men over the age of 19, average consumption was 9.7 and 14.2 mg/day, respectively. For women, 17% consumed less than the EAR, for men 11%. The percentages below EAR increased with age.[236] The most recent published update of the survey (NHANES 2013–2014) reported lower averages – 9.3 and 13.2 mg/day – again with intake decreasing with age.[237]
Symptoms of mild zinc deficiency are diverse.[207] Clinical outcomes include depressed growth, diarrhea, impotence and delayed sexual maturation, alopecia, eye and skin lesions, impaired appetite, altered cognition, impaired immune functions, defects in carbohydrate use, and reproductive teratogenesis.[207] Zinc deficiency depresses immunity,[238] but excessive zinc does also.[197]
Despite some concerns,[239] western vegetarians and vegans do not suffer any more from overt zinc deficiency than meat-eaters.[240] Major plant sources of zinc include cooked dried beans, sea vegetables, fortified cereals, soy foods, nuts, peas, and seeds.[239] However, phytates in many whole-grains and fibers may interfere with zinc absorption and marginal zinc intake has poorly understood effects. The zinc chelator phytate, found in seeds and cereal bran, can contribute to zinc malabsorption.[18] Some evidence suggests that more than the US RDA (8 mg/day for adult women; 11 mg/day for adult men) may be needed in those whose diet is high in phytates, such as some vegetarians.[239] The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines attempt to compensate for this by recommending higher zinc intake when dietary phytate intake is greater.[225] These considerations must be balanced against the paucity of adequate zinc biomarkers, and the most widely used indicator, plasma zinc, has poor sensitivity and specificity.[241]
Soil remediation
Species of Calluna, Erica and Vaccinium can grow in zinc-metalliferous soils, because translocation of toxic ions is prevented by the action of ericoid mycorrhizal fungi.[242]
Agriculture
Zinc deficiency appears to be the most common micronutrient deficiency in crop plants; it is particularly common in high-pH soils.[243] Zinc-deficient soil is cultivated in the cropland of about half of Turkey and India, a third of China, and most of Western Australia. Substantial responses to zinc fertilization have been reported in these areas.[13] Plants that grow in soils that are zinc-deficient are more susceptible to disease. Zinc is added to the soil primarily through the weathering of rocks, but humans have added zinc through fossil fuel combustion, mine waste, phosphate fertilizers, pesticide (zinc phosphide), limestone, manure, sewage sludge, and particles from galvanized surfaces. Excess zinc is toxic to plants, although zinc toxicity is far less widespread.[13]
Remove ads
Precautions
Summarize
Perspective
Toxicity
Although zinc is an essential requirement for good health, excess zinc can be harmful. Excessive absorption of zinc suppresses copper and iron absorption.[220] The free zinc ion in solution is highly toxic to plants, invertebrates, and even vertebrate fish.[244] The Free Ion Activity Model is well-established in the literature, and shows that just micromolar amounts of the free ion kills some organisms. A recent example showed 6 micromolar killing 93% of all Daphnia in water.[245]
The free zinc ion is a powerful Lewis acid up to the point of being corrosive. Stomach acid contains hydrochloric acid, in which metallic zinc dissolves readily to give corrosive zinc chloride. Swallowing a post-1982 American one cent piece (97.5% zinc) can cause damage to the stomach lining through the high solubility of the zinc ion in the acidic stomach.[246]
Evidence shows that people taking 100–300 mg of zinc daily may suffer induced copper deficiency. A 2007 trial observed that elderly men taking 80 mg daily were hospitalized for urinary complications more often than those taking a placebo.[247] Levels of 100–300 mg may interfere with the use of copper and iron or adversely affect cholesterol.[220] Zinc in excess of 500 ppm in soil interferes with the plant absorption of other essential metals, such as iron and manganese.[118] A condition called the zinc shakes or "zinc chills" can be induced by inhalation of zinc fumes while brazing or welding galvanized materials.[151] Zinc is a common ingredient of denture cream which may contain between 17 and 38 mg of zinc per gram. Disability and even deaths from excessive use of these products have been claimed.[248]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) states that zinc damages nerve receptors in the nose, causing anosmia. Reports of anosmia were also observed in the 1930s when zinc preparations were used in a failed attempt to prevent polio infections.[249] On June 16, 2009, the FDA ordered removal of zinc-based intranasal cold products from store shelves. The FDA said the loss of smell can be life-threatening because people with impaired smell cannot detect leaking gas or smoke, and cannot tell if food has spoiled before they eat it.[250]
Recent research suggests that the topical antimicrobial zinc pyrithione is a potent heat shock response inducer that may impair genomic integrity with induction of PARP-dependent energy crisis in cultured human keratinocytes and melanocytes.[251]
Poisoning
In 1982, the US Mint began minting pennies coated in copper but containing primarily zinc. Zinc pennies pose a risk of zinc toxicosis, which can be fatal. One reported case of chronic ingestion of 425 pennies (over 1 kg of zinc) resulted in death due to gastrointestinal bacterial and fungal sepsis. Another patient who ingested 12 grams of zinc showed only lethargy and ataxia (gross lack of coordination of muscle movements).[252] Several other cases have been reported of humans suffering zinc intoxication by the ingestion of zinc coins.[253][254]
Pennies and other small coins are sometimes ingested by dogs, requiring veterinary removal of the foreign objects. The zinc content of some coins can cause zinc toxicity, commonly fatal in dogs through severe hemolytic anemia and liver or kidney damage; vomiting and diarrhea are possible symptoms.[255] Zinc is highly toxic in parrots and poisoning can often be fatal.[256] The consumption of fruit juices stored in galvanized cans has resulted in mass parrot poisonings with zinc.[75]
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- The thermal expansion of zinc is anisotropic. The coefficients for each crystal axis are (at 20 °C): αa = 13.06×10−6/K, αc = 64.12×10−6/K, and αaverage = αvolume/3 = 30.08×10−6/K.
- The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table.
- An East India Company ship carrying a cargo of nearly pure zinc metal from the Orient sank off the coast Sweden in 1745.(Emsley 2001, p. 502)
- Electric current will naturally flow between zinc and steel but in some circumstances inert anodes are used with an external DC source.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



![{\displaystyle {2\,\mathrm {ZnS} {}+{}3\,\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}\mathrel {\xrightarrow {\mathrm {t} {\vphantom {A}}^{o}} } {}2\,\mathrm {ZnO} {}+{}2\,\mathrm {SO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/686cb2d7d73dea23bc0e3431bfab4016d5fd71ed)

![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {ZnO} {}+{}\mathrm {CO} {}\mathrel {\xrightarrow {950{\vphantom {A}}^{o}\mathrm {C} } } {}\mathrm {Zn} {}+{}\mathrm {CO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ab85d04dfa0b8e0280b72062a5ecbe660fd247b1)
![{\displaystyle {\mathrm {ZnO} {}+{}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}\mathrm {ZnSO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} }}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8dece6d8838ec01b21c572dbe4e3404d47f6aa05)
![{\displaystyle {2\,\mathrm {ZnSO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {O} {}\mathrel {\longrightarrow } {}2\,\mathrm {Zn} {}+{}\mathrm {O} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}{}+{}2\,\mathrm {H} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{2}}\mathrm {SO} {\vphantom {A}}_{\smash[{t}]{4}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/347f94534be68e78b991b2639b79b8b2f91b90a7)
