Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Buccopharyngeal fascia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia of the pharynx.[1] It represents the posterior portion of the pretracheal fascia[2] (visceral fascia).[3] It covers the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, and buccinator muscle.[4]
Remove ads
Structure
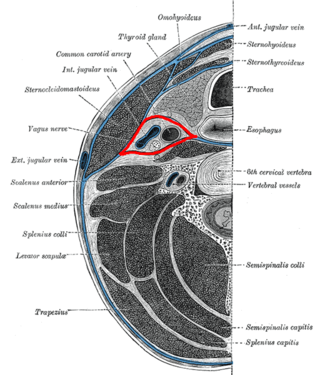
The buccopharyngeal fascia is a thin lamina given off from the pretracheal fascia.[citation needed] It is the portion of the pretracheal fascia situated posterior and lateral to the pharynx. It encloses the entire superior part of the alimentary canal.[3]
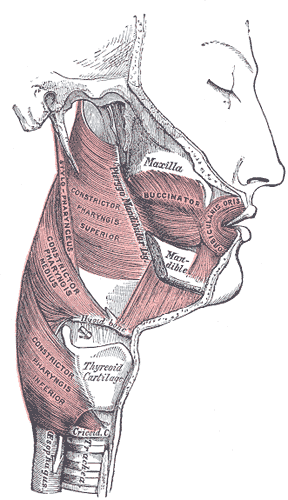
The buccopharyngeal fascia envelops the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles.[4][1] It extends anteriorly from the constrictor pharyngis superior[4] over the pterygomandibular raphe to cover the buccinator muscle[1] (though another source describes it as continuous with the fascia covering the buccinator muscle).[3]
Attachments
It is attached to the prevertebral fascia by loose connective tissue, with the retropharyngeal space found between them.[citation needed] It may also be attached to the alar fascia posteriorly at C3 and C6 levels.[5]
Relations
The thyroid gland wraps around the trachea and oesophagus anterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia, so that the lateral parts of the thyroid gland border it.[6]
The buccopharyngeal fascia runs parallel to the medial aspect of the carotid sheath.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Additional images
- Floor of mouth. Deep dissection.Anterior view.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads