Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Norgestrienone
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Norgestrienone, sold under the brand names Ogyline, Planor, and Miniplanor, is a progestin medication which has been used in birth control pills, sometimes in combination with ethinylestradiol.[1][2][3][4][5] It was developed by Roussel Uclaf and has been registered for use only in France.[4][5][6] Under the brand name Planor, it has been marketed in France as 2 mg norgestrienone and 50 μg ethinylestradiol tablets.[7] It is taken by mouth.[5]
Norgestrienone is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[8] It has some androgenic activity.[9][10][11][12]
Norgestrienone was first described in the literature in 1965.[10] It is sometimes referred to as a "second-generation" progestin.[13] Norgestrienone is no longer available.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Medical uses
Norgestrienone was used in hormonal contraception to prevent pregnancy.[2][7] It has typically been used as an oral contraceptive at a dosage of 2 mg/day in combination with ethinylestradiol and 350 μ/day when used alone.[5]
Side effects
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
Norgestrienone has been found to possess similar affinity for the progesterone receptor and androgen receptor,[8] and in accordance, has some androgenic activity.[9][10][11][12] The androgenic activity of norgestrienone is greater than that of other 19-nortestosterone derivatives due to the presence of the C9(11) double bond, which enhances said activity.[12] The ratio of progestogenic to androgenic activity appears to be much lower for norgestrienone that it is for other 19-nortestosterone progestins such as norethisterone and levonorgestrel.[14][15][16][17] Gestrinone, the 18-methyl analogue of norgestrienone, has even greater androgenic activity than norgestrienone, as this modification increases androgenic activity similarly.[12]
Pharmacokinetics
The metabolism of norgestrienone in humans has been studied.[18]
Remove ads
Chemistry
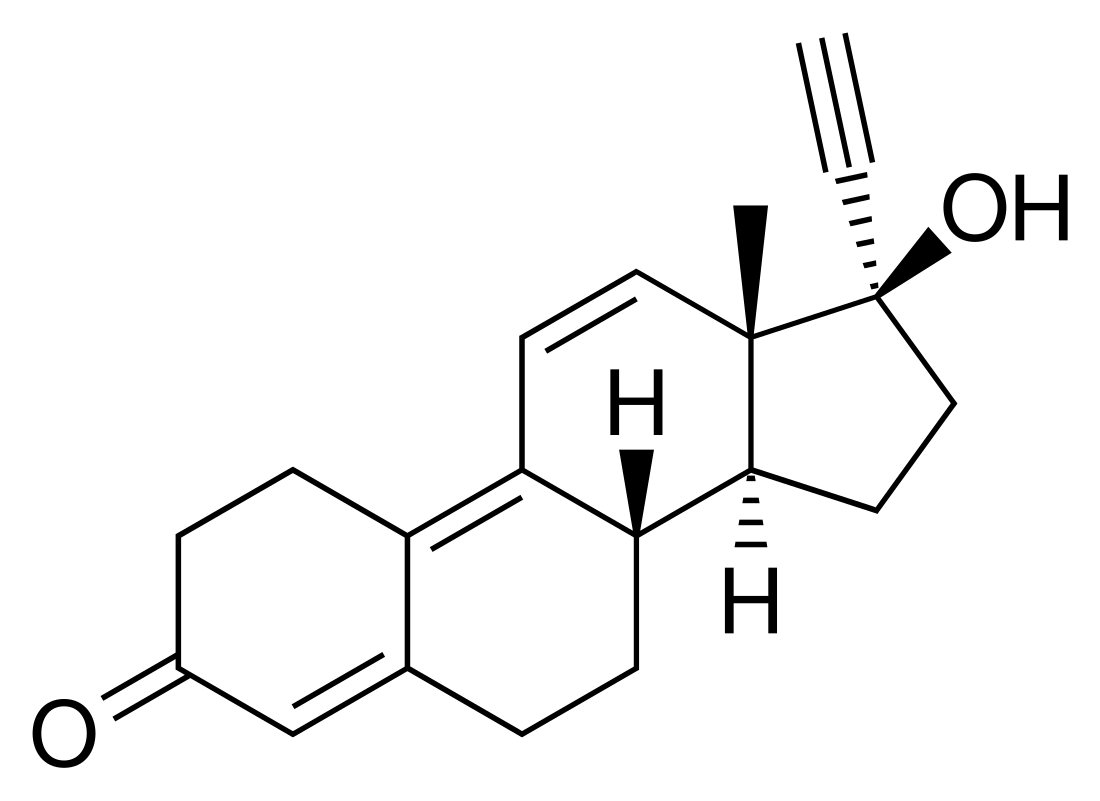
Norgestrienone, also known as 17α-ethynyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone or as 17α-ethynylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one, as well as δ9,11-norethisterone or 17α-ethynyltrienolone (17α-ethynyltrenbolone), is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of testosterone and 19-nortestosterone.[1][4][19] It is structurally related to the anabolic steroid trenbolone (19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone; the non-17α-ethynylated analogue of norgestrienone), the progestogenic and androgenic steroid gestrinone (the 13β-ethyl variant or 18-methyl derivative of norgestrienone), and the anabolic steroid tetrahydrogestrinone (the 18-methyl and 17α-ethyl variant of norgestrienone).[1][4][20]
Remove ads
History
Norgestrienone was first described in the literature in 1965.[10] It is sometimes referred to as a "second-generation" progestin based on its time of introduction.[13]
Society and culture
Generic names
Norgestrienone is the generic name of the drug and its INN.[1][2][4] It is also known by its developmental code names RU-2010 and A-301.[1][2][4]
Brand names
Norgestrienone has been marketed under the brand names Ogyline, Planor, and Miniplanor.[1][2][4]
Availability
Norgestrienone is no longer marketed and hence is no longer available in any country.[citation needed] It was previously used in France.[4] The medication was never marketed in the United States.[21]
Remove ads
Research
Norgestrienone has been studied for use in male hormonal contraception.[22]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads