Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
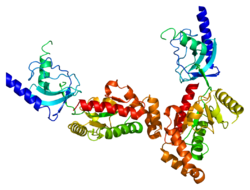
CACNB4
Protein-coding gene in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNB4 gene.[5][6]
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (November 2009) |
Remove ads
Function
This gene encodes a member of the beta subunit family, a protein in the voltage-dependent calcium channel complex. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Various versions of each of these subunits exist, either expressed from similar genes or the result of alternative splicing. The protein described in this record plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized.[6]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Certain mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME).[6]
Interactions
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads