More information Date, # of cases ...
COVID-19 cases in Togo ()
Deaths Recoveries Active cases
2020202020212021
MarMarAprAprMayMayJunJunJulJulAugAugSepSepOctOctNovNovDecDec
JanJanFebFebMarMarAprAprMayMayJunJunJulJulAugAugSepSepOctOctNovNov
Last 15 daysLast 15 days
Date | | # of cases | # of deaths |
| 2020-03-06 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-07 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-08 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-09 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-10 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-11 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-12 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-13 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-14 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-15 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-16 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-17 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-18 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-19 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-20 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-21 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-22 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-23 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-24 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-25 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-26 | | | 0(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-27 | | | 1(n.a.) |
| 2020-03-28 | | | 1(=) |
| 2020-03-29 | | | 1(=) |
| 2020-03-30 | | | 1(=) |
| 2020-03-31 | | | 1(=) |
| 2020-04-01 | | | 2(+100%) |
| 2020-04-02 | | | 2(=) |
| 2020-04-03 | | | 3(+50%) |
| 2020-04-04 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-05 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-06 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-07 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-08 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-09 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-10 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-11 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-12 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-13 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-14 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-15 | | | 3(=) |
| 2020-04-16 | | | 5(+67%) |
| 2020-04-17 | | | 5(=) |
| 2020-04-18 | | | 5(=) |
| 2020-04-19 | | | 5(=) |
| 2020-04-20 | | | 6(+20%) |
| 2020-04-21 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-22 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-23 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-24 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-25 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-26 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-27 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-28 | | | 6(=) |
| 2020-04-29 | | | 7(+17%) |
| 2020-04-30 | | | 9(+29%) |
| 2020-05-01 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-02 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-03 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-04 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-05 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-06 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-07 | | | 9(=) |
| 2020-05-08 | | | 10(+11%) |
| 2020-05-09 | | | 10(=) |
| 2020-05-10 | | | 11(+10%) |
| 2020-05-11 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-12 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-13 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-14 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-15 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-16 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-17 | | | 11(=) |
| 2020-05-18 | | | 12(+9.1%) |
| 2020-05-19 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-20 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-21 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-22 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-23 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-24 | | | 12(=) |
| 2020-05-25 | | | 13(+8.3%) |
| 2020-05-26 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-05-27 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-05-28 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-05-29 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-05-30 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-05-31 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-01 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-02 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-03 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-04 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-05 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-06 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-07 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-08 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-09 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-10 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-11 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-12 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-13 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-14 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-15 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-16 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-17 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-18 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-19 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-20 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-21 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-22 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-23 | | | 13(=) |
| 2020-06-24 | | | 14(+7.7%) |
| 2020-06-25 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-06-26 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-06-27 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-06-28 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-06-29 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-06-30 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-07-01 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-07-02 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-07-03 | | | 14(=) |
| 2020-07-04 | | | 15(+7.1%) |
| 2020-07-05 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-06 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-07 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-08 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-09 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-10 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-11 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-12 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-13 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-14 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-15 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-16 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-17 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-18 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-19 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-20 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-21 | | | 15(=) |
| 2020-07-22 | | | 16(+6.7%) |
| 2020-07-23 | | | 16(=) |
| 2020-07-24 | | | 17(+6.2%) |
| 2020-07-25 | | | 17(=) |
| 2020-07-26 | | | 18(+5.9%) |
| 2020-07-27 | | | 18(=) |
| 2020-07-28 | | | 18(=) |
| 2020-07-29 | | | 18(=) |
| 2020-07-30 | | | 18(=) |
| 2020-07-31 | | | 19(+5.6%) |
| 2020-08-01 | | | 19(=) |
| 2020-08-02 | | | 19(=) |
| 2020-08-03 | | | 19(=) |
| 2020-08-04 | | | 19(=) |
| 2020-08-05 | | | 21(+11%) |
| 2020-08-06 | | | 22(+4.8%) |
| 2020-08-07 | | | 22(=) |
| 2020-08-08 | | | 23(+4.5%) |
| 2020-08-09 | | | 23(=) |
| 2020-08-10 | | | 25(+8.7%) |
| 2020-08-11 | | | 26(+4%) |
| 2020-08-12 | | | 26(=) |
| 2020-08-13 | | | 26(=) |
| 2020-08-14 | | | 26(=) |
| 2020-08-15 | | | 27(+3.8%) |
| 2020-08-16 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-17 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-18 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-19 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-20 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-21 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-22 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-23 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-24 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-25 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-26 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-27 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-28 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-29 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-30 | | | 27(=) |
| 2020-08-31 | | | 28(+3.7%) |
| 2020-09-01 | | | 28(=) |
| 2020-09-02 | | | 30(+7.1%) |
| 2020-09-03 | | | 31(+3.3%) |
| 2020-09-04 | | | 31(=) |
| 2020-09-05 | | | 32(+3.2%) |
| 2020-09-06 | | | 32(=) |
| 2020-09-07 | | | 33(+3.1%) |
| 2020-09-08 | | | 34(+3%) |
| 2020-09-09 | | | 36(+5.9%) |
| 2020-09-10 | | | 37(+2.8%) |
| 2020-09-11 | | | 37(=) |
| 2020-09-12 | | | 37(=) |
| 2020-09-13 | | | 37(=) |
| 2020-09-14 | | | 40(+8.1%) |
| 2020-09-15 | | | 40(=) |
| 2020-09-16 | | | 40(=) |
| 2020-09-17 | | | 41(+2.5%) |
| 2020-09-18 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-19 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-20 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-21 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-22 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-23 | | | 41(=) |
| 2020-09-24 | | | 44(+7.3%) |
| 2020-09-25 | | | 44(=) |
| 2020-09-26 | | | 46(+4.5%) |
| 2020-09-27 | | | 46(=) |
| 2020-09-28 | | | 47(+2.2%) |
| 2020-09-29 | | | 48(+2.1%) |
| 2020-09-30 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-01 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-02 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-03 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-04 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-05 | | | 48(=) |
| 2020-10-06 | | | 49(+2.1%) |
| 2020-10-07 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-08 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-09 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-10 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-11 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-12 | | | 49(=) |
| 2020-10-13 | | | 50(+2%) |
| 2020-10-14 | | | 51(+2%) |
| 2020-10-15 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-16 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-17 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-18 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-19 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-20 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-21 | | | 51(=) |
| 2020-10-22 | | | 52(+2%) |
| 2020-10-23 | | | 52(=) |
| 2020-10-24 | | | 52(=) |
| 2020-10-25 | | | 52(=) |
| 2020-10-26 | | | 53(+1.9%) |
| 2020-10-27 | | | 54(+1.9%) |
| 2020-10-28 | | | 54(=) |
| 2020-10-29 | | | 55(+1.9%) |
| 2020-10-30 | | | 55(=) |
| 2020-10-31 | | | 57(+3.6%) |
| 2020-11-01 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-02 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-03 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-04 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-05 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-06 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-07 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-08 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-09 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-10 | | | 57(=) |
| 2020-11-11 | | | 59(+3.5%) |
| 2020-11-12 | | | 60(+1.7%) |
| 2020-11-13 | | | 60(=) |
| 2020-11-14 | | | 61(+1.7%) |
| 2020-11-15 | | | 61(=) |
| 2020-11-16 | | | 61(=) |
| 2020-11-17 | | | 62(+1.6%) |
| 2020-11-18 | | | 63(+1.6%) |
| 2020-11-19 | | | 63(=) |
| 2020-11-20 | | | 64(+1.6%) |
| 2020-11-21 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-22 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-23 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-24 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-25 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-26 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-27 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-28 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-29 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-11-30 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-12-01 | | | 64(=) |
| 2020-12-02 | | | 65(+1.6%) |
| 2020-12-03 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-04 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-05 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-06 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-07 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-08 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-09 | | | 65(=) |
| 2020-12-10 | | | 66(+1.5%) |
| 2020-12-11 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-12 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-13 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-14 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-15 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-16 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-17 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-18 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-19 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-20 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-21 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-22 | | | 66(=) |
| 2020-12-23 | | | 68(+3%) |
| 2020-12-24 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-25 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-26 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-27 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-28 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-29 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-30 | | | 68(=) |
| 2020-12-31 | | | 68(=) |
| 2021-01-01 | | | 68(=) |
| 2021-01-02 | | | 68(=) |
| 2021-01-03 | | | 68(=) |
| 2021-01-04 | | | 69(+1.5%) |
| 2021-01-05 | | | 69(=) |
| 2021-01-06 | | | 70(+1.4%) |
| 2021-01-07 | | | 72(+2.9%) |
| 2021-01-08 | | | 72(=) |
| 2021-01-09 | | | 72(=) |
| 2021-01-10 | | | 72(=) |
| 2021-01-11 | | | 73(+1.4%) |
| 2021-01-12 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-13 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-14 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-15 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-16 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-17 | | | 73(=) |
| 2021-01-18 | | | 74(+1.4%) |
| 2021-01-19 | | | 74(=) |
| 2021-01-20 | | | 74(=) |
| 2021-01-21 | | | 74(=) |
| 2021-01-22 | | | 74(=) |
| 2021-01-23 | | | 74(=) |
| 2021-01-24 | | | 75(+1.4%) |
| 2021-01-25 | | | 76(+1.3%) |
| 2021-01-26 | | | 76(=) |
| 2021-01-27 | | | 76(=) |
| 2021-01-28 | | | 76(=) |
| 2021-01-29 | | | 76(=) |
| 2021-01-30 | | | 77(+1.3%) |
| 2021-01-31 | | | 77(=) |
| 2021-02-01 | | | 79(+2.6%) |
| 2021-02-02 | | | 79(=) |
| 2021-02-03 | | | 79(=) |
| 2021-02-04 | | | 79(=) |
| 2021-02-05 | | | 79(=) |
| 2021-02-06 | | | 79(=) |
| 2021-02-07 | | | 80(+1.3%) |
| 2021-02-08 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-09 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-10 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-11 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-12 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-13 | | | 80(=) |
| 2021-02-14 | | | 81(+1.2%) |
| 2021-02-15 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-16 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-17 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-18 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-19 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-20 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-21 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-22 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-23 | | | 81(=) |
| 2021-02-24 | | | 82(+1.2%) |
| 2021-02-25 | | | 82(=) |
| 2021-02-26 | | | 82(=) |
| 2021-02-27 | | | 83(+1.2%) |
| 2021-02-28 | | | 84(+1.2%) |
| 2021-03-01 | | | 85(+1.2%) |
| 2021-03-02 | | | 85(=) |
| 2021-03-03 | | | 85(=) |
| 2021-03-04 | | | 88(+3.5%) |
| 2021-03-05 | | | 88(=) |
| 2021-03-06 | | | 90(+2.3%) |
| 2021-03-07 | | | 92(+2.2%) |
| 2021-03-08 | | | 92(=) |
| 2021-03-09 | | | 92(=) |
| 2021-03-10 | | | 92(=) |
| 2021-03-11 | | | 93(+1.1%) |
| 2021-03-12 | | | 93(=) |
| 2021-03-13 | | | 93(=) |
| 2021-03-14 | | | 95(+2.2%) |
| 2021-03-15 | | | 96(+1.1%) |
| 2021-03-16 | | | 97(+1%) |
| 2021-03-17 | | | 98(+1%) |
| 2021-03-18 | | | 102(+4.1%) |
| 2021-03-19 | | | 102(=) |
| 2021-03-20 | | | 102(=) |
| 2021-03-21 | | | 104(+2%) |
| 2021-03-22 | | | 104(=) |
| 2021-03-23 | | | 105(+0.96%) |
| 2021-03-24 | | | 105(=) |
| 2021-03-25 | | | 107(+1.9%) |
| 2021-03-26 | | | 107(=) |
| 2021-03-27 | | | 107(=) |
| 2021-03-28 | | | 107(=) |
| 2021-03-29 | | | 107(=) |
| 2021-03-30 | | | 109(+1.9%) |
| 2021-03-31 | | | 109(=) |
| 2021-04-01 | | | 110(+0.92%) |
| 2021-04-02 | | | 110(=) |
| 2021-04-03 | | | 110(=) |
| 2021-04-04 | | | 112(+1.8%) |
| 2021-04-05 | | | 112(=) |
| 2021-04-06 | | | 113(+0.89%) |
| 2021-04-07 | | | 113(=) |
| 2021-04-08 | | | 115(+1.8%) |
| 2021-04-09 | | | 116(+0.87%) |
| 2021-04-10 | | | 116(=) |
| 2021-04-11 | | | 116(=) |
| 2021-04-12 | | | 116(=) |
| 2021-04-13 | | | 117(+0.86%) |
| 2021-04-14 | | | 117(=) |
| 2021-04-15 | | | 117(=) |
| 2021-04-16 | | | 119(+1.7%) |
| 2021-04-17 | | | 119(=) |
| 2021-04-18 | | | 119(=) |
| 2021-04-19 | | | 120(+0.84%) |
| 2021-04-20 | | | 121(+0.83%) |
| 2021-04-21 | | | 121(=) |
| 2021-04-22 | | | 121(=) |
| 2021-04-23 | | | 121(=) |
| 2021-04-24 | | | 121(=) |
| 2021-04-25 | | | 121(=) |
| 2021-04-26 | | | 122(+0.83%) |
| 2021-04-27 | | | 122(=) |
| 2021-04-28 | | | 122(=) |
| 2021-04-29 | | | 123(+0.82%) |
| 2021-04-30 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-01 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-02 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-03 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-04 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-05 | | | 123(=) |
| 2021-05-06 | | | 124(+0.81%) |
| 2021-05-07 | | | 124(=) |
| 2021-05-08 | | | 124(=) |
| 2021-05-09 | | | 124(=) |
| 2021-05-10 | | | 125(+0.81%) |
| 2021-05-11 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-12 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-13 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-14 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-15 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-16 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-17 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-18 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-19 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-20 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-21 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-22 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-23 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-24 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-25 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-26 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-27 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-28 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-29 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-30 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-05-31 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-01 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-02 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-03 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-04 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-05 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-06 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-07 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-08 | | | 125(=) |
| 2021-06-09 | | | 126(+0.8%) |
| 2021-06-10 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-11 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-12 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-13 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-14 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-15 | | | 126(=) |
| 2021-06-16 | | | 127(+0.79%) |
| 2021-06-17 | | | 127(=) |
| 2021-06-18 | | | 127(=) |
| 2021-06-19 | | | 127(=) |
| 2021-06-20 | | | 128(+0.79%) |
| 2021-06-21 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-22 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-23 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-24 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-25 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-26 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-27 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-28 | | | 128(=) |
| 2021-06-29 | | | 129(+0.78%) |
| 2021-06-30 | | | 129(=) |
| 2021-07-01 | | | 130(+0.78%) |
| 2021-07-02 | | | 130(=) |
| 2021-07-03 | | | 130(=) |
| 2021-07-04 | | | 131(+0.77%) |
| 2021-07-05 | | | 132(+0.76%) |
| 2021-07-06 | | | 132(=) |
| 2021-07-07 | | | 132(=) |
| 2021-07-08 | | | 133(+0.76%) |
| 2021-07-09 | | | 133(=) |
| 2021-07-10 | | | 133(=) |
| 2021-07-11 | | | 133(=) |
| 2021-07-12 | | | 133(=) |
| 2021-07-13 | | | 134(+0.75%) |
| 2021-07-14 | | | 134(=) |
| 2021-07-15 | | | 134(=) |
| 2021-07-16 | | | 134(=) |
| 2021-07-17 | | | 137(+2.2%) |
| 2021-07-18 | | | 138(+0.73%) |
| 2021-07-19 | | | 138(=) |
| 2021-07-20 | | | 140(+1.4%) |
| 2021-07-21 | | | 140(=) |
| 2021-07-22 | | | 140(=) |
| 2021-07-23 | | | 143(+2.1%) |
| 2021-07-24 | | | 143(=) |
| 2021-07-25 | | | 146(+2.1%) |
| 2021-07-26 | | | 148(+1.4%) |
| 2021-07-27 | | | 148(=) |
| 2021-07-28 | | | 150(+1.4%) |
| 2021-07-29 | | | 150(=) |
| 2021-07-30 | | | 152(+1.3%) |
| 2021-07-31 | | | 152(=) |
| 2021-08-01 | | | 153(+0.66%) |
| 2021-08-02 | | | 154(+0.65%) |
| 2021-08-03 | | | 155(+0.65%) |
| 2021-08-04 | | | 155(=) |
| 2021-08-05 | | | 156(+0.65%) |
| 2021-08-06 | | | 156(=) |
| 2021-08-07 | | | 157(+0.64%) |
| 2021-08-08 | | | 159(+1.3%) |
| 2021-08-09 | | | 161(+1.3%) |
| 2021-08-10 | | | 161(=) |
| 2021-08-11 | | | 162(+0.62%) |
| 2021-08-12 | | | 163(+0.62%) |
| 2021-08-13 | | | 165(+1.2%) |
| 2021-08-14 | | | 165(=) |
| 2021-08-15 | | | 165(=) |
| 2021-08-16 | | | 165(=) |
| 2021-08-17 | | | 170(+3%) |
| 2021-08-18 | | | 172(+1.2%) |
| 2021-08-19 | | | 172(=) |
| 2021-08-20 | | | 172(=) |
| 2021-08-21 | | | 172(=) |
| 2021-08-22 | | | 172(=) |
| 2021-08-23 | | | 173(+0.58%) |
| 2021-08-24 | | | 175(+1.2%) |
| 2021-08-25 | | | 175(=) |
| 2021-08-26 | | | 175(=) |
| 2021-08-27 | | | 177(+1.1%) |
| 2021-08-28 | | | 180(+1.7%) |
| 2021-08-29 | | | 180(=) |
| 2021-08-30 | | | 185(+2.8%) |
| 2021-08-31 | | | 185(=) |
| 2021-09-01 | | | 187(+1.1%) |
| 2021-09-02 | | | 190(+1.6%) |
| 2021-09-03 | | | 193(+1.6%) |
| 2021-09-04 | | | 194(+0.52%) |
| 2021-09-05 | | | 196(+1%) |
| 2021-09-06 | | | 197(+0.51%) |
| 2021-09-07 | | | 200(+1.5%) |
| 2021-09-08 | | | 203(+1.5%) |
| 2021-09-09 | | | 203(=) |
| 2021-09-10 | | | 204(+0.49%) |
| 2021-09-11 | | | 205(+0.49%) |
| 2021-09-12 | | | 205(=) |
| 2021-09-13 | | | 207(+0.98%) |
| 2021-09-14 | | | 208(+0.48%) |
| 2021-09-15 | | | 209(+0.48%) |
| 2021-09-16 | | | 209(=) |
| 2021-09-17 | | | 211(+0.96%) |
| 2021-09-18 | | | 213(+0.95%) |
| 2021-09-19 | | | 213(=) |
| 2021-09-20 | | | 215(+0.94%) |
| 2021-09-21 | | | 216(+0.47%) |
| 2021-09-22 | | | 216(=) |
| 2021-09-23 | | | 216(=) |
| 2021-09-24 | | | 219(+1.4%) |
| 2021-09-25 | | | 222(+1.4%) |
| 2021-09-26 | | | 226(+1.8%) |
| 2021-09-27 | | | 227(+0.44%) |
| 2021-09-28 | | | 227(=) |
| 2021-09-29 | | | 228(+0.44%) |
| 2021-09-30 | | | 229(+0.44%) |
| 2021-10-01 | | | 229(=) |
| 2021-10-02 | | | 230(+0.44%) |
| 2021-10-03 | | | 233(+1.3%) |
| 2021-10-04 | | | 234(+0.43%) |
| 2021-10-05 | | | 234(=) |
| 2021-10-06 | | | 234(=) |
| 2021-10-07 | | | 235(+0.43%) |
| 2021-10-08 | | | 235(=) |
| 2021-10-09 | | | 235(=) |
| 2021-10-10 | | | 236(+0.43%) |
| 2021-10-11 | | | 236(=) |
| 2021-10-12 | | | 237(+0.42%) |
| 2021-10-13 | | | 237(=) |
| 2021-10-14 | | | 237(=) |
| 2021-10-15 | | | 238(+0.42%) |
| 2021-10-16 | | | 238(=) |
| 2021-10-17 | | | 239(+0.42%) |
| 2021-10-18 | | | 239(=) |
| 2021-10-19 | | | 240(+0.42%) |
| 2021-10-20 | | | 240(=) |
| 2021-10-21 | | | 240(=) |
| 2021-10-22 | | | 240(=) |
| 2021-10-23 | | | 242(+0.83%) |
| 2021-10-24 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-25 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-26 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-27 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-28 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-29 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-30 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-10-31 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-11-01 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-11-02 | | | 242(=) |
| 2021-11-03 | | | 243(+0.41%) |
| 2021-11-04 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-05 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-06 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-07 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-08 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-09 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-10 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-11 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-12 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-13 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-14 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-15 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-16 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-17 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-18 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-19 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-20 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-21 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-22 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-23 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-24 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-25 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-26 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-27 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-28 | | | 243(=) |
| 2021-11-29 | | | 243(=) |
| Sources: various news sources and state health department websites. See Timeline Table and Timeline narrative for sources. |
Close
March 2020
- On 6 March, Togolese authorities announced the first COVID-19 case, a 42-year-old Togolese woman who travelled between Germany, France, Turkey, and Benin before returning to Togo.[8] On this date, it was reported that she was being treated in isolation and her condition was stable.[9]
- On 20 March, nine more cases were confirmed in Togo. On this day, the first case recovered, as indicated by the Ministry of Health.[10][11]
- On 21 March, seven more cases were confirmed. In an attempt to control the spread of the virus in Togo, all borders to the country were closed. The cities of Lomé, Tsévié, Kpalimé, and Sokodé were quarantined starting on 20 March for two weeks.[12][13]
- On 27 March, the first death occurred.[14]
- By the end of March there had been 34 confirmed cases, of which 1 patient had died and 10 had recovered, leaving 23 active cases.[15]
Subsequent cases
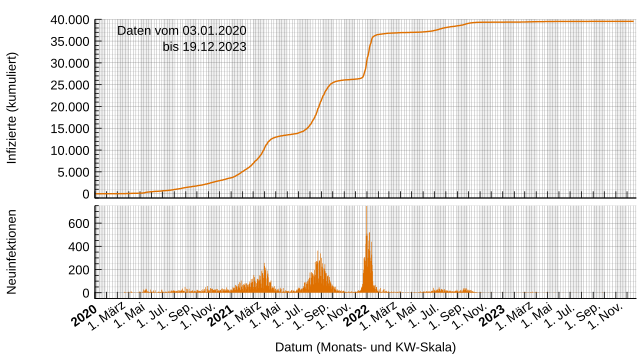
There were 3,611 confirmed cases in 2020. 3,384 patients recovered while 68 persons died. At the end of 2020 there were 159 active cases.
Vaccinations started on 10 March, initially with 156,000 doses of AstraZeneca's Covishield vaccine delivered through the COVAX mechanism.[16] Togo subsequently received 140,000 doses of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine which the Democratic Republic of Congo had been unable to use before the expiry date.[17]
Togo's first cases of the omicron variant were announced on 20 December.[18]
There were 27,062 confirmed cases in 2021, bringing the total number of cases to 30,673. 22,783 patients recovered in 2021 while 180 persons died, bringing the total death toll to 248. At the end of 2021 there were 4,258 active cases.
Modelling by WHO's Regional Office for Africa suggests that due to under-reporting, the true number of infections by the end of 2021 was around 3.7 million while the true number of COVID-19 deaths was around one thousand.[19]
There were 8,671 confirmed cases in 2022, bringing the total number of cases to 39,344. 12,881 patients recovered in 2022 while 42 persons died, bringing the total death toll to 290. At the end of 2022 there were 6 active cases.[20]
There were 209 confirmed cases in 2023, bringing the total number of confirmed cases to 39,553. 214 patients recovered in 2023 while the death toll remained unchanged. At the end of 2023 there was one active case.[21]