Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Steroid 11β-hydroxylase
Protein found in mammals From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Steroid 11β-hydroxylase, also known as steroid 11β-monooxygenase, is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene.[5][6] The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of adrenal corticosteroids[7] by catalyzing the addition of hydroxyl groups during oxidation reactions.
Remove ads
Gene
The CYP11B1 gene encodes 11β-hydroxylase, a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. The product of this CYP11B1 gene is the 11β-hydroxylase protein. This protein localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane and is involved in the conversion of various steroids in the adrenal cortex. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[6]
The CYP11B1 gene is reversibly inhibited by etomidate[8][9] and metyrapone.
Remove ads
Function
Summarize
Perspective
11β-hydroxylase is a steroidogenic enzyme, i.e. the enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. The enzyme is primarily localized in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. The enzyme functions by introducing a hydroxyl group at carbon position 11β on the steroid nucleus, thereby facilitating the conversion of certain steroids.
Humans have two isozymes with 11β-hydroxylase activity: CYP11B1 and CYP11B2.
CYP11B1 (11β-hydroxylase) is expressed at high levels and is regulated by ACTH, while CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) is usually expressed at low levels and is regulated by angiotensin II. In addition to the 11β-hydroxylase activity, both isozymes have 18-hydroxylase activity.[10] The CYP11B1 isozyme has strong 11β-hydroxylase activity, but the activity of 18-hydroxylase is only one-tenth of CYP11B2.[11] The weak 18-hydroxylase activity of CYP11B1 explains why an adrenal with suppressed CYP11B2 expression continues to synthesize 18-hydroxycorticosterone.[12]
Here are some of the steroids, grouped by catalytic activity of the CYP11B1 isozyme:
Remove ads
Cortisol and corticosterone metabolism
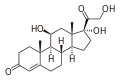
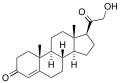
11β-hydroxylase has strong[13] catalytic activity during conversion of 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol and 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone, by catalyzing the hydroxylation of carbon hydrogen bond at 11-beta position. Note the extra "–OH" added at the 11 position (near the center, on ring "C"):
Mechanism of action
As a mitochondrial P450 system, P450c11 is dependent on two electron transfer proteins, adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin that transfer 2 electrons from NADPH to the P450 for each monooxygenase reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. In most respects this process of electron transfer appears similar to that of P450scc system that catalyzes cholesterol side chain cleavage.[25] Similar to P450scc the process of electrons transfer is leaky leading to superoxide production. The rate of electron leakage during metabolism depends on the functional groups of the steroid substrate.[26]
Remove ads
Regulation
The expression of the enzyme in adrenocortical cells is regulated by the trophic hormone corticotropin (ACTH).[27]
Clinical significance
A mutation in genes encoding 11β-hydroxylase is associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
11β-hydroxylase is involved in the metabolism of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone to 21-deoxycortisol,[17] in cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency.[28][29]
See also
Additional images

- Corticosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rat
- Steroid numbering
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads