Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Cantellation (geometry)
Geometric operation on a regular polytope From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In geometry, a cantellation is a 2nd-order truncation in any dimension that bevels a regular polytope at its edges and at its vertices, creating a new facet in place of each edge and of each vertex. Cantellation also applies to regular tilings and honeycombs. Cantellating a polyhedron is also rectifying its rectification.


Cantellation (for polyhedra and tilings) is also called expansion by Alicia Boole Stott: it corresponds to moving the faces of the regular form away from the center, and filling in a new face in the gap for each opened edge and for each opened vertex.
Remove ads
Notation
A cantellated polytope is represented by an extended Schläfli symbol t0,2{p,q,...} or r or rr{p,q,...}.
For polyhedra, a cantellation offers a direct sequence from a regular polyhedron to its dual.
Example: cantellation sequence between cube and octahedron:
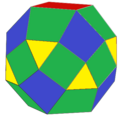
Example: a cuboctahedron is a cantellated tetrahedron.
For higher-dimensional polytopes, a cantellation offers a direct sequence from a regular polytope to its birectified form.
Remove ads
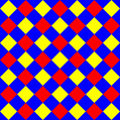
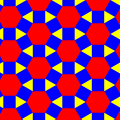
Examples: cantellating polyhedra, tilings
Remove ads
See also
References
- Coxeter, H.S.M. Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8 (pp.145-154 Chapter 8: Truncation, p 210 Expansion)
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads