Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Triangular prism
Prism with a 3-sided base From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
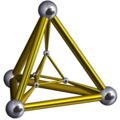
A triangular prism or trigonal prism[1] is a prism with two triangular bases in geometry. If the edges pair with each triangle's vertex and if they are perpendicular to the base, it is a right triangular prism. A right triangular prism may be both semiregular and uniform.
The triangular prism can be used as the core of constructing other polyhedra, examples are some of the Johnson solids and Schönhardt polyhedron. It has a relationship with the honeycombs and polytopes. It can be found in many real life applications as in architecture and natural science.
Remove ads
Special cases
Summarize
Perspective
A triangular prism has six vertices, nine edges, and five faces. Every prism has two congruent faces known as its bases, and the bases of a triangular prism are triangles. The triangle has three vertices, each of which pairs with another triangle's vertex, forming three edges. These edges form three parallelograms as other faces.[2] If the prism's edges are perpendicular to the base, the lateral faces are rectangles. The prism is called a right triangular prism.[3] This prism may also be considered a special case of a wedge.[4] Topologically a triangular frustum is the same polyhedron. Still, the two triangles are different sizes, and the sides are slanted trapezoids.
The vertices and edges of a triangular prism can give rise to a graph. This is due to Steinitz's theorem, stating that any convex polyhedron can be drawn into planar graph that is 3-connected, meaning the edges of a graph do not cross each other, and the vertices are impossible to disconnect whenever picking any two vertices to be removed. Classifying into a family, the graph of a triangular prism is the prism graph Π3, where the symbol Πn represents the graph of an n-sided prism.[5] The graph of a triangular prism is a type of planar graph formed from a tree with no degree-two vertices by adding a cycle connecting its leaves, an example of Halin graph.[6]
As a uniform prism
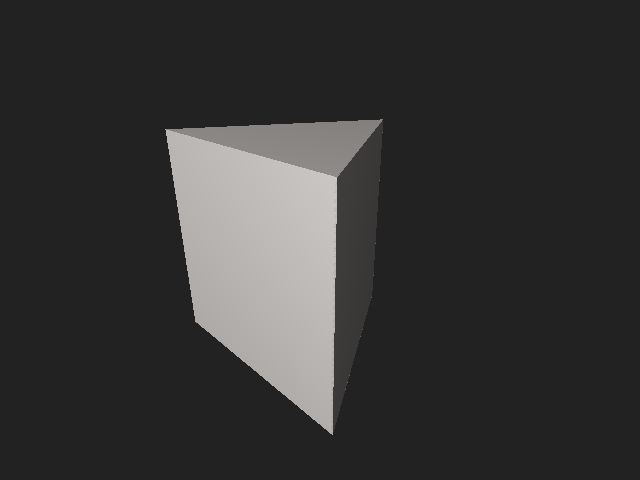
When all edges are equal in length, its bases and its lateral faces are all equilaterals and squares, respectively. Hence, the right triangular prism is semiregular. A semiregular prism means that the number of its polygonal base's edges equals the number of its square faces.[7] More generally, the triangular prism is uniform. This means that a triangular prism has regular faces and has a symmetry of mapping any two vertices known as isogonal.[8] The dihedral angle between two adjacent square faces is the internal angle of an equilateral triangle π/3 = 60°, and that between a square and a triangle is π/2 = 90°.[9]
The volume of any prism is the product of the area of the base and the distance between the two bases.[10] In the case of a triangular prism, its base is a triangle. The area of a triangle is the half product of its base b and its height h, formulated as 1/2bh. Since the triangular prism has a distance l between two triangular bases, the general formula for its volume is:[11] In the case of a right triangular prism, where all its edges are equal in length l, its volume can be calculated as the product of the equilateral triangle's area and the distance between bases:[12]
The three-dimensional symmetry group of a triangular prism is dihedral group D3h of order 12: the appearance is unchanged if the triangular prism is rotated one- and two- thirds of a full angle around its axis of symmetry passing through the center's base, and reflecting across a horizontal plane.[9] The dual polyhedron of any prism is a bipyramid, a polyhedron formed by fusing two pyramids base-to-base. In the case of a triangular prism, its dual is a triangular bipyramid, both of which have a common three-dimensional symmetry group.[1]
Remove ads
Applications
Triangular prism as an optical object
A triangular prism is commonly designed as a transparent optical object to refract light.[13] The cluster of a chemical compound known as trigonal prismatic molecular geometry resembles the structure of a triangular prism, with an example compound being hexamethyltungsten.[14] In architecture, an example of a building with a triangular prism shape is Flatiron Building in New York City.[15] An instance of food that resembles the shape of a triangular prism is a Swiss chocolate brand of Toblerone.[16]
Remove ads
Related figures
Summarize
Perspective
In the construction of polyhedra
Left to right: triaugmented triangular prism, a right triangular prism with cutting off its part at an oblique angle, Schönhardt polyhedron, rectified triangular prism
Beyond the triangular bipyramid as its dual polyhedron, many other polyhedra are related to the triangular prism. A Johnson solid is a convex polyhedron with regular faces, and this definition sometimes omits uniform polyhedra such as Archimedean solids, Catalan solids, prisms, and antiprisms.[17] There are six Johnson solids with their construction involving the triangular prism: elongated triangular pyramid, elongated triangular bipyramid, gyrobifastigium, augmented triangular prism, biaugmented triangular prism, and triaugmented triangular prism. The elongated triangular pyramid and the gyroelongated triangular pyramid are constructed by attaching tetrahedron onto the base of a triangular prism. The augmented triangular prism, biaugmented triangular prism, and triaugmented triangular prism are constructed by attaching equilateral square pyramids onto the square face of the prism. The gyrobifastigium is constructed by attaching two triangular prisms along one of its square faces.[18]
One can cut the part of a triangular prism at an oblique angle. The result has two bases that are not parallel, such that every distance between those bases has a different edge length. If the edges connecting bases are perpendicular to one of its bases, this prism can have a version of a right triangular prism. Given that A is the area of the triangular prism's base, and the three heights h1, h2, and h3, its volume can be determined in the following formula:[19]
Schönhardt polyhedron is another polyhedron constructed from a triangular prism with equilateral triangle bases. This way, one of its bases rotates around the prism's centerline and breaks the square faces into skew polygons. Each square face can be re-triangulated with two triangles to form a non-convex dihedral angle.[20] As a result, the Schönhardt polyhedron cannot be triangulated by a partition into tetrahedra. It is also that the Schönhardt polyhedron has no internal diagonals.[21] It is named after German mathematician Erich Schönhardt, who described it in 1928, although artist Karlis Johansons exhibited the related structure in 1921.[22]
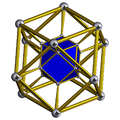
The triangular prism can be rectified from the convex hull of its midpoints' edges. The resulting construction yields three square faces on the same planes as the square faces of the prism, two equilateral triangle faces on the planes of the triangular ends of the prism, and six more isosceles triangle faces. By giving rise to a graph, its dual forms another convex polyhedron called Herschel enneahedron.[23]
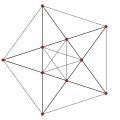
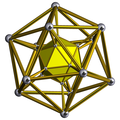
The number of triangular prisms can be composed by sharing a common center. Four uniform compounds of triangular prisms, they are compound of four triangular prisms, compound of eight triangular prisms, compound of ten triangular prisms, compound of twenty triangular prisms.[24]
Honeycombs
The honeycomb by triangular prism and gyrobifastigium
The triangular prism is a plesiohedron, a space-filling polyhedron that can be defined as the Voronoi cell of a symmetric Delone set in order to create a honeycomb. The triangular prism is a prototile of the triangular prismatic honeycomb.[25] Relatedly, the gyrobifastigium, constructed by two triangular prisms alongside a square face, is the Johnson solid that can tile a space of gyrated triangular prismatic honeycomb. Nonetheless, it is a stereohedron instead of a plesiohedron, because the points at the centers of the cells of its face-to-face tiling (where they are forced to go by symmetry) have differently-shaped Voronoi cells. If the gyrobifastigium has isosceles right triangles and silver rectangles, then it is a plesiohedron.
Related polytopes
The triangular prism is first in a dimensional series of semiregular polytopes. Each progressive uniform polytope is constructed vertex figure of the previous polytope. Thorold Gosset identified this series in 1900 as containing all regular polytope facets, containing all simplexes and orthoplexes (equilateral triangles and squares in the case of the triangular prism). In Coxeter's notation the triangular prism is given the symbol −121.
Four dimensional space
The triangular prism exists as cells of a number of four-dimensional uniform 4-polytopes, including:
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads














 ...
...