Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
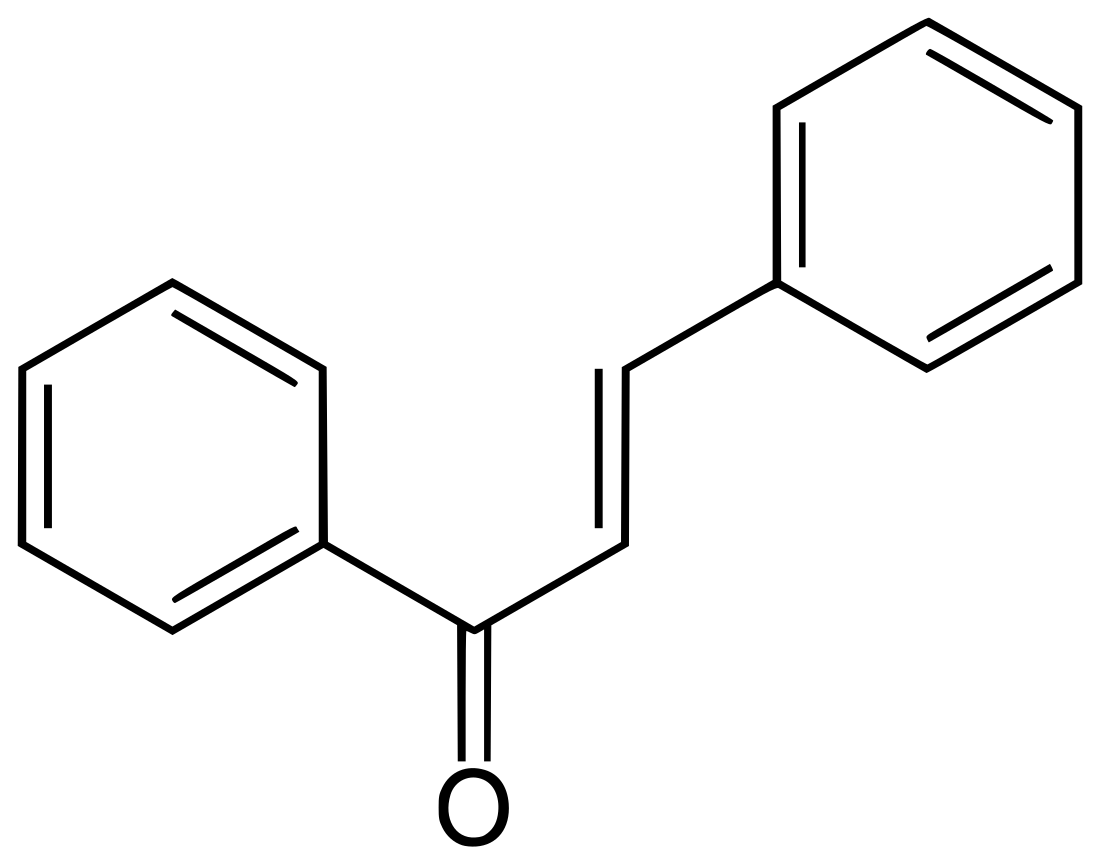
Chalcone
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Chalcone is the organic compound C6H5C(O)CH=CHC6H5. It is an α,β-unsaturated ketone. A variety of important biological compounds are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids.[3] They are widely known bioactive substances, fluorescent materials, and chemical intermediates.
Remove ads
Chemical properties
Chalcones have two absorption maxima at 280 nm and 340 nm.[4]
Biosynthesis
Chalcones and chalconoids are synthesized in plants as secondary metabolites. The enzyme chalcone synthase, a type III polyketide synthase, is responsible for the biosynthesis of these compounds. The enzyme is found in all "higher" (vascular) and several "lower" (non-vascular) plants.[5]
Laboratory synthesis
Chalcone is usually prepared by an aldol condensation between benzaldehyde and acetophenone.[6]
This reaction, which can be carried out without any solvent, is so reliable that it is often given as an example of green chemistry in undergraduate education.[7]
Potential pharmacology
Chalcones and their derivatives demonstrate a wide range of biological activities including anti-inflammation.[8] Some 2′-amino chalcones have been studied as potential antitumor agents.[9][10] Chalcones are of interest in medicinal chemistry and have been described as a privileged scaffold.[5]
Uses
Summarize
Perspective
Medicinal uses
In medicinal chemistry, chalcones have been used as:
Industrial uses
In chemical industries, they are employed as:
- liquid crystals
- fluorescent chemical scaffolds
- metal sensors
- corrosion inhibitors
- plant hormones[11]
Uses in organic chemistry
Chalcones have been used as intermediates in heterocyclic synthesis, especially in the synthesis of pyrazoles and aurones.[11]
In the Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction, chalcone reacts with dimethylsulfoxonium methylide to give 1-phenyl-2-benzoylcyclopropane [15295-43-9] [1145-91-1] in 95% yield.[12] A Leuckart reaction or ammonium acetate in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride would be predicted to give Phenyl(2-phenylcyclopropyl)methanamine [1559116-96-9]. Alternatively if a reductive amination of the ketone with methylamine is performed one would instead get the secondary amine N-Me [1559367-56-4].

These compounds have the same trans-stereochemistry as was observed for tranylcypromine although their exact mode of pharmacology is still lacking. Lastly, it was discovered that if a hydrazine is prepared from the ketone (ala pheniprazine) one gets a compound that is called [Phenyl-(2-phenylcyclopropyl)methyl]hydrazine (PC105199424).
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads