Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Cystatin A
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Cystatin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSTA gene.[5][6]
The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins, and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as a cysteine protease inhibitor, forming tight complexes with papain and the cathepsins B, H, and L. The protein is one of the precursor proteins of cornified cell envelope in keratinocytes and plays a role in epidermal development and maintenance. Stefins have been proposed as prognostic and diagnostic tools for cancer.[6]
Remove ads
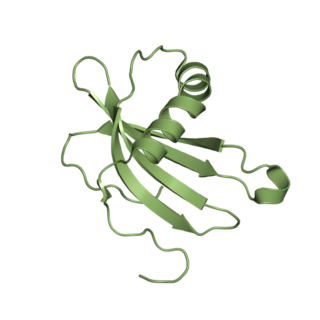
Structure and inhibatory mechanism
The structure of cystatin A features a wedge-like shape that's typical of cysteine protease inhibitors. This shape is critical for how it blocks protease activity.[7] The protein has three main functional regions:
- An N-terminal region with a conserved glycine[7]
- Two β-hairpin loops (the first loop contains the important QVVAG sequence shown in blue in the image)[7]
- A C-terminal region that helps stabilize the structure[7]
These three regions work together to form the functional core that fits into the catalytic cleft of target proteases. The inhibitory mechanism depends on specific structural features:
Remove ads
Function
Cystatin A mainly works as an inhibitor of cysteine proteases, with strong binding to papain and cathepsins B, H, and L. It also serves as a building block for the cornified cell envelope in skin cells and helps with skin growth and maintenance.[10]
In tissues, cystatin A helps regulate protein breakdown by controlling the activity of these proteases. This regulation is important for normal cell function and can be disrupted in certain diseases.
Remove ads
Interactions
Cystatin A has been shown to interact with Cathepsin B[11][12] and CTSL1.[12][13]
Clinical significance
Altered levels of cystatin A have been observed in several disease states, particularly in skin disorders and certain cancers.[14] Its role as a protease inhibitor makes it potentially valuable as both a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.[15]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads