Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Delta Canis Majoris
Star in the constellation Canis Major From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Delta Canis Majoris is a supergiant star in the constellation of Canis Major. It is formally named Wezen (/ˈwiːzən/);[12] Delta Canis Majoris is its Bayer designation. At an apparent magnitude of +1.83, it is the third-brightest star in the constellation. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately 1,600 light years. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified.[13]
Remove ads
Observation
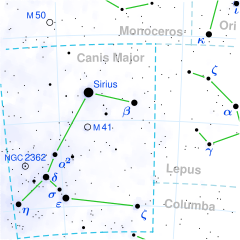
Delta Canis Majoris is the third-brightest star in the constellation after Sirius and ε Canis Majoris (Adhara), with an apparent magnitude of +1.83, and is white or yellow-white in colour. Lying about 10 degrees south southeast of Sirius, it only rises to about 11 degrees above the horizon at the latitude of the United Kingdom.[14] The open cluster NGC 2354 is located only 1.3 degrees east of Delta Canis Majoris.[15] As with the rest of Canis Major, Delta Canis Majoris is most visible in winter skies in the northern hemisphere, and summer skies in the southern. In Bayer's Uranometria, it is in the Great Dog's hind quarter.[16]
Remove ads
History and naming
Summarize
Perspective
δ Canis Majoris (Latinised to Delta Canis Majoris) is the star's Bayer designation, abbreviated δ CMa or Delta CMa.
The traditional name, Wezen (alternatively Wesen, or Wezea), is derived from the medieval Arabic وزن al-wazn, which means 'weight' in modern Arabic. The name was for one of a pair of stars, the other being Hadar, which has now come to refer to Beta Centauri. It is unclear whether the pair of stars was originally Alpha and Beta Centauri or Alpha and Beta Columbae. In any case, the name was somehow applied to both Delta Canis Majoris and Beta Columbae.[17] Richard Hinckley Allen muses that the name alludes to the difficulty the star has rising above the horizon in the northern hemisphere.[16] Astronomer Jim Kaler has noted the aptness of the traditional name given the star's massive nature.[18]
In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[19] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[20] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Wezen for this star.
In Chinese, 弧矢 (Hú Shǐ), meaning Bow and Arrow,[21] refers to an asterism consisting of δ Canis Majoris, ε Canis Majoris, η Canis Majoris, κ Canis Majoris, ο Puppis, π Puppis, χ Puppis, c Puppis and k Puppis. Consequently, δ Canis Majoris itself is known as 弧矢一 (Hú Shǐ yī, English: the First Star of Bow and Arrow.)[22]
In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket, this star was designated Thalath al Adzari (تالت ألعذاري - taalit al-aðārii), which was translated into Latin as Tertia Virginum, meaning the third virgin.[23] This star, along with ε Canis Majoris (Adhara), η Canis Majoris (Aludra) and ο2 Canis Majoris (Thanih al Adzari), were Al ʽAdhārā (ألعذاري), the Virgins.[24][25]
Remove ads
Physical properties

Delta Canis Majoris is a supergiant star with a stellar classification of F8 Ia.[3] It is 14 to 15 times more massive than the Sun,[8] but around 190 times larger. It lies at a distance of 1,600 light-years from Earth and has 35,000 times the Sun's luminosity.[9] The effective temperature of 5,818 K[10] is similar to the Sun's temperature of 5,772 K. It is rotating with an equatorial speed of around 28 km/s, and hence may take a year to rotate fully. Only around 12 million years old, Delta Canis Majoris has stopped fusing hydrogen in its core. Its outer envelope is beginning to expand and cool, and in the next 100,000 years it will become a red supergiant as its core fuses heavier and heavier elements. After it develops an inert iron core, it will collapse and explode as a supernova.[18]
If Delta Canis Majoris were as close to Earth as Sirius is, it would be as bright as a half-full moon.[26]
Modern legacy
Delta Canis Majoris appears on the flag of Brazil, symbolising the state of Roraima.[27]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads