Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
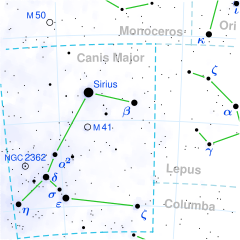
Eta Canis Majoris
Blue supergiant star in the constellation Canis Major From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Eta Canis Majoris is a blue supergiant star in the constellation of Canis Major. It has the proper name Aludra, pronounced /əˈluːdrə, əˈljuːdrə/;[10] Eta Canis Majoris is its Bayer designation. This star has an apparent visual magnitude that varies between 2.38 and 2.48, which makes it the fifth-brightest in the constellation. Parallax measurements from the Hipparcos mission estimate a large distance of 2,000 light-years. It is drifting further away from the Sun with a line of sight velocity of 41 km/s.[6]
Remove ads
Nomenclature
η Canis Majoris, Latinised to Eta Canis Majoris, is the star's Bayer designation, abbreviated Eta CMa or η CMa.
The traditional name Aludra originates from the Arabic: العذراء al-adhraa, 'the virgin'. This star, along with Epsilon Canis Majoris (Adhara), Delta Canis Majoris (Wezen) and Omicron2 Canis Majoris (Thanih al Adzari), were Al 'Adhārā (العذاري), 'the Virgins'.[11] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[12] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[13] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Aludra for this star.
In Chinese, 弧矢 (Hú Shǐ), meaning Bow and Arrow,[14] refers to an asterism consisting of Eta Canis Majoris, Delta Canis Majoris, HD 63032, HD 65456, Omicron Puppis, k Puppis, Epsilon Canis Majoris, Kappa Canis Majoris and Pi Puppis. Consequently, Eta Canis Majoris itself is known as 弧矢二 (Hú Shǐ èr, English: the Second Star of Bow and Arrow).[15]
Remove ads
Properties
Summarize
Perspective

Eta Canis Majoris is a blue supergiant star with a spectral type of B5Ia.[3] It has been the standard for this spectral class in the Morgan–Keenan system, and since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified.[17][18]
This is likely a post-red supergiant, a star which left its red supergiant phase and is near the end of its life. As a consequence, Aludra has lost significant part of its mass. It formed with a mass of 22 M☉ and now has either 5.5 or 9.5 M☉, depending on the estimate.[3] The present day mass loss rate is estimated at (0.12±0.01)×10−6 M☉·yr−1, or one solar mass every 8.3 million years.[8]
Aludra shines brightly in the skies in spite of a large distance from Earth due to being intrinsically many times brighter than the Sun. It has a luminosity over 100,000 times and a radius around 54 times that of the Sun. The star has only existed for a fraction of the time the Sun has, less than 10 million years, yet is already in the final stages of its life.[8][3]
The star is classified as an Alpha Cygni-type variable star and its brightness varies from magnitude +2.38 to +2.48 over a period of 4.7 days.[2][19]
Remove ads
Namesakes
Both USS Aludra (AF-55), an Alstede-class stores ship, and USS Aludra (AK-72), a Crater-class cargo ship, were U.S. Navy vessels named after the star.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads