Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Dresden
Capital city of Saxony, Germany From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Dresden (/ˈdrɛzdən/; German: [ˈdʁeːsdn̩] ⓘ; Upper Saxon: Dräsdn; Upper Sorbian: Drježdźany, pronounced [ˈdʁʲɛʒdʒanɨ]) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants.[3] The Dresden metropolitan area has over 1.3 million inhabitants.[4]
Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the Ore Mountain Foreland, as well as in the valleys of the rivers rising there and flowing through Dresden, the longest of which are the Weißeritz and the Lockwitzbach. The name of the city as well as the names of most of its boroughs and rivers are of Sorbian origin.
Dresden has a long history as the capital and royal residence for the Electors and Kings of Saxony, who for centuries furnished the city with cultural and artistic splendor, and was once by personal union the family seat of Polish monarchs. The city was known as the Jewel Box, because of its Baroque and Rococo city centre. The controversial American and British bombing of Dresden towards the end of World War II killed approximately 25,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and destroyed the entire city centre. After the war, restoration work has helped to reconstruct parts of the historic inner city.
Since German reunification in 1990, Dresden has once again become a cultural, educational and political centre of Germany.[5] The Dresden University of Technology (TU Dresden) is one of the 10 largest universities in Germany and part of the German Universities Excellence Initiative. The economy of Dresden and its agglomeration is one of the most dynamic in Germany and ranks first in Saxony.[6] It is dominated by high-tech branches, often called "Silicon Saxony". According to the Hamburg Institute of International Economics (HWWI) and Berenberg Bank in 2019, Dresden had the seventh best prospects for the future of all cities in Germany.[7]
Dresden is one of the most visited cities in Germany with 4.7 million overnight stays per year.[8][9] Its most prominent building is the Frauenkirche located at the Neumarkt. Built in the 18th century, the church was destroyed during World War II. The remaining ruins were left for 50 years as a war memorial, before being rebuilt between 1994 and 2005. Other famous landmarks include the Zwinger, the Semperoper and Dresden Castle. Furthermore, the city is home to the Dresden State Art Collections, originating from the collections of the Saxon electors in the 16th century. Dresden's Striezelmarkt is one of the largest Christmas markets in Germany and is considered the first genuine Christmas market in the world.[10] Nearby sights include the National Park of Saxon Switzerland, the Ore Mountains and the countryside around Elbe Valley, Moritzburg Castle and Meissen, home of Meissen porcelain.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Timeline of Dresden
Historical affiliations
Historical affiliations
Margravate of Meissen, 1206–1316
Margraviate of Brandenburg 1316–1319
Margravate of Meissen, 1319–1423
Electorate of Saxony, 1423–1485
Duchy of Saxony, 1485–1547
Electorate of Saxony, 1547–1806
Kingdom of Saxony, 1806–1848
German Empire, 1848–1849
Kingdom of Saxony, 1849–1918
North German Confederation (Kingdom of Saxony), 1867–1871
German Empire (Kingdom of Saxony), 1867–1918
Weimar Republic (Free State of Saxony), 1918–1933
Nazi Germany, 1933–1945
Soviet occupation zone of Germany, 1945–1949
East Germany, 1949–1990
Germany (Free State of Saxony), 1990–present
The area had been settled in the Neolithic era by Linear Pottery culture tribes c. 7500 BC.[11] Dresden's founding and early growth is associated with the eastward expansion of Germanic peoples,[12] mining in the nearby Ore Mountains, and the establishment of the Margraviate of Meissen. Its name comes from Sorbian Drežďany[13] (meaning either "woods" or "lowland forest-dweller"[14]). Dresden later evolved into the capital of Saxony. Beginning in the 17th century, it became one of Europe’s leading centres of culture and the arts.[15]
Early history
Dresden developed as a German trading settlement on the south bank of the Elbe, established by the Margrave of Meissen Dietrich.[15] The first documentary evidence of Dresden as a town dates to 1206.[15] Dietrich chose Dresden as his interim residence in 1206, as documented in a record calling the place "Civitas Dresdene". In 1220, a stone bridge was constructed over the Elbe at the same location as today’s Augustus Bridge.[15] The bridge connected the town with a Sorbian settlement called Drezdany on the northern bank.[15] It was known as Antiqua Dresdin by 1350, and later as Altendresden,[13][16] both literally "old Dresden".
Dresden was given to Friedrich Clem after the death of Henry the Illustrious in 1288. It was taken by the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1316 and was restored to the Wettin dynasty after the death of Valdemar the Great in 1319. In 1485, the Saxon Wettin brothers divided their lands under the Treaty of Leipzig, with Ernest retaining the Elector title and the western and northern territories, while Albert received the Meissen area and established Dresden as the capital of the Duchy of Saxony.[17] Following the Schmalkaldic War, in 1547 Duke Moritz was granted the title of Elector and Dresden became the capital of the Electorate of Saxony.
Early modern age

The Elector and ruler of Saxony Frederick Augustus I became King Augustus II the Strong of Poland in 1697. He gathered many of the best musicians,[18] architects and painters from all over Europe to Dresden.[19] His reign marked the beginning of Dresden's emergence as a leading European city for technology and art. During the reign of Kings Augustus II the Strong and Augustus III of Poland most of the city's baroque landmarks were built. These include the Zwinger Royal Palace, the Japanese Palace, the Taschenbergpalais, the Pillnitz Castle and the two landmark churches: the Catholic Hofkirche and the Lutheran Frauenkirche. In addition, significant art collections and museums were founded. Notable examples include the Dresden Porcelain Collection, the Collection of Prints, Drawings and Photographs, the Grünes Gewölbe and the Mathematisch-Physikalischer Salon. Strengthening ties with Poland, postal routes to Poznań, Toruń and Warsaw were established under Augustus II the Strong.[20]
In 1726, there was a riot for two days after a Protestant clergyman was killed by a soldier who had recently converted from Catholicism.[21] In 1745, the Treaty of Dresden between Prussia, Saxony, and Austria ended the Second Silesian War. Only a few years later, Dresden suffered heavy destruction in the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), following its capture by Prussian forces, its subsequent re-capture, and a failed Prussian siege in 1760. Friedrich Schiller completed his Ode to Joy (the literary base of the European anthem) in Dresden in 1785.[22] In 1793, preparations for the Polish Kościuszko Uprising started in the city by Tadeusz Kościuszko in response to the Second Partition of Poland.[23]
19th and early 20th century
In 1806, Dresden became the capital of the Kingdom of Saxony established by Napoleon. During the Napoleonic Wars the French Emperor made it a base of operations, winning there the Battle of Dresden on 27 August 1813. As a result of the Congress of Vienna, the Kingdom of Saxony became part of the German Confederation in 1815. In 1838, the Dresden Coinage Convention took place in the city which attempted to bring some degree of standardisation to the currencies used in the Zollverein (German Customs Union). Steamboat transport on the Elbe was established in 1837, followed in 1839 by the opening of Dresden’s first railway, providing a direct connection to Leipzig.[24]

Dresden was a centre of the German Revolutions in 1848–1849. The May Uprising saw rebel Saxon troops supported by students, democrats, miners, and workers declaring a provisional government at the Town Hall.[25] During the street fighting the city’s first opera house was destroyed.[24] Prussian forces, aided by loyal Saxon troops, suppressed the revolt, leaving over 150 dead and many imprisoned.[24] The uprising forced Frederick Augustus II of Saxony to flee from Dresden, but he soon after regained control over the city with the help of Prussia. In 1852, the population of Dresden grew to 100,000 inhabitants, making it one of the biggest cities within the German Confederation. Following the Polish uprisings of 1831, 1848 and 1863, many Poles fled to Dresden, including the artistic and political elite, such as composer Frédéric Chopin, war hero Józef Bem and writer Adam Mickiewicz.[26] Mickiewicz wrote one of his greatest works, Dziady, Part III, there.[26]
As the capital of the Kingdom of Saxony, Dresden became part of the newly founded German Empire in 1871. In the following years, the city became a major centre of economy, including motor car production, food processing, banking and the manufacture of medical equipment. In the early 20th century, Dresden was particularly well known for its camera works and its cigarette factories. During World War I, the city did not suffer any war damage, but lost many of its inhabitants. Between 1918 and 1934, Dresden was the capital of the first Free State of Saxony as well as a cultural and economic centre of the Weimar Republic. The city was also a centre of European modern art until 1933.
Military history

During the foundation of the German Empire in 1871, a large military facility called Albertstadt was built.[27] It had a capacity of up to 20,000 military personnel at the beginning of the First World War. The garrison saw only limited use between 1918 and 1934, but was then reactivated in preparation for the Second World War.
Its usefulness was limited by attacks on 13–15 February and 17 April 1945, the former of which destroyed large areas of the city. However, the garrison itself was not specifically targeted.[28][29] Soldiers had been deployed as late as March 1945 in the Albertstadt garrison.
The Albertstadt garrison became the headquarters of the Soviet 1st Guards Tank Army in the Group of Soviet Forces in Germany after the war. Apart from the German army officers' school (Offizierschule des Heeres), there have been no more military units in Dresden since the army merger during German reunification, and the withdrawal of Soviet forces in 1992. Nowadays, the Bundeswehr operates the Military History Museum of the Federal Republic of Germany in the former Albertstadt garrison.
Nazi era, Second World War

After the Nazi seizure of power, two book burnings were organised in the city in 1933, one by the SA on Wettiner Platz, the second one by German Student Union at the Bismarck Column on Räcknitzhöhe.[30]
From 1933 to 1945, the Jewish community of Dresden was reduced from over 6,000 (7,100 people were persecuted as Jews) to 41, mostly as a result of emigration, but later also deportation and murder.[31][32] One of the survivors was Victor Klemperer with his non-Jewish wife, who believed that the bombing saved their lives. The Semper Synagogue was destroyed in November 1938 on Kristallnacht.[33]
During the German invasion of Poland at the start of World War II, in September 1939, the Gestapo carried out mass arrests of local Polish activists.[34] Other non-Jews were also targeted, and over 1,300 people were executed by the Nazis at the Münchner Platz, a courthouse in Dresden, including labour leaders, undesirables, resistance fighters and anyone caught listening to foreign radio broadcasts.[35] The bombing stopped prisoners who were busy digging a large hole into which an additional 4,000 prisoners were to be disposed of.[36]
During the war, Dresden was the location of several forced labour subcamps of the Stalag IV-A prisoner-of-war camp for Allied POWs,[37] and seven subcamps of the Flossenbürg concentration camp, in which some 3,600 men, women and children were imprisoned, mostly Polish, Jewish and Russian.[38] In April 1945, most surviving prisoners were sent on death marches to various destinations in Saxony and German-occupied Czechoslovakia, whereas some women were probably murdered and some managed to escape.[38]
Dresden in the 20th century was a major communications hub and manufacturing centre with 127 factories and major workshops and was designated by the German military as a defensive strongpoint, with which to hinder the Soviet advance.[39] Being the capital of the German state of Saxony, Dresden not only had garrisons but a whole military borough, the Albertstadt.[40] This military complex, named after Saxon King Albert, was not specifically targeted in the bombing of Dresden.
During the final months of the Second World War, Dresden harboured some 600,000 refugees, with a total population of 1.2 million. Dresden was attacked seven times between 1944 and 1945, and was occupied by the Red Army after the German capitulation.
Fire-bombing
The bombing of Dresden by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) between 13 and 15 February 1945 was controversial. On the night of 13–14 February 1945, 773 RAF Lancaster bombers dropped 1,181.6 tons of incendiary bombs and 1,477.7 tons of high explosive bombs, targeting the rail yards at the centre of the city. The inner city of Dresden was largely destroyed.[41][42] Widely quoted Nazi propaganda reports claimed 200,000 deaths, but the German Dresden Historians' Commission, made up of 13 prominent German historians, in an official 2010 report published after five years of research concluded that casualties numbered between 22,500 and 25,000.[43]
The destruction of Dresden allowed Hildebrand Gurlitt, a major Nazi Museum director and art dealer, to hide a large collection of artwork worth tens of millions of dollars that had been stolen during the Nazi era, as he claimed it had been destroyed along with his house which was located in Dresden.[44]
The Allies described the operation as the legitimate bombing of a military and industrial target.[28] Several researchers have argued that the February attacks were disproportionate. As a result of the bombings, mostly women and children died.[45]
American author Kurt Vonnegut's novel Slaughterhouse Five is loosely based on his first-hand experience of the raid as a prisoner of war.[46]
In remembrance of the victims, the anniversaries of the bombing of Dresden are marked with peace demonstrations, devotions and marches.[47][48]
Post-war
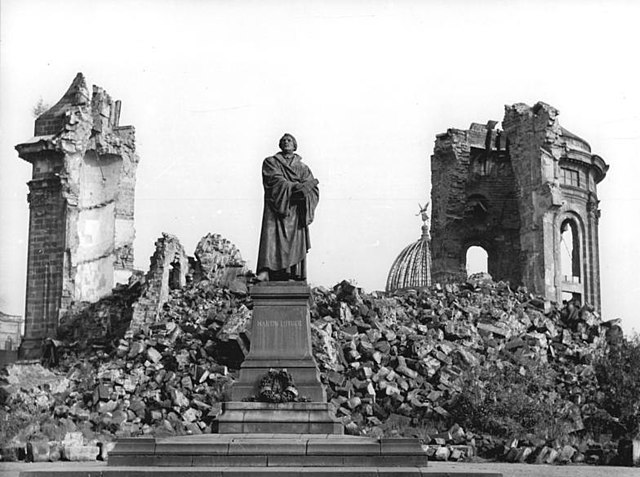

After the war, Dresden became part of the Soviet occupation zone in Germany. Following his military service the German press photographer and photojournalist Richard Peter returned to Dresden and began to document the ruined city. Among his best known works Blick auf Dresden vom Rathausturm (View of Dresden from the Rathaus Tower). It has become one of the best known photographs of a ruined post-war Germany following its appearance in 1949 in his book Dresden, eine Kamera klagt an ("Dresden, a photographic accusation", ISBN 3-930195-03-8).[49]
When a skeleton previously used as a model for drawing art classes was found in the ruins of the Dresden Art Academy, the photographer Edmund Kesting with the assistance of Peter posed it in a number of different locations to produce a series of haunting photographic images to give the impression that Death was wandering through the city in search of the dead.[49] Kesting subsequently published them in the book Dresdner Totentanz (Dresden's Death Dance).
The damage from Allied air raids was so extensive that a narrow-gauge light railway system was constructed after the war to remove the debris, though being makeshift there were frequent derailments. This seven-line railway system employed 5,000 staff and 40 locomotives, all of which bore women's names. The last train remained in service until 1958, though the last official debris clearance team was only disbanded in 1977.[49]
Rather than repair them, German Democratic Republic (East Germany) authorities razed the ruins of many churches, royal buildings and palaces in the 1950s and 1960s, such as the Gothic Sophienkirche, the Alberttheater and the Wackerbarth-Palais as well as many historic residential buildings. The surroundings of the once lively Prager Straße resembled a wasteland before it was rebuilt in the socialist style at the beginning of the 1960s.
However, the majority of historic landmarks were saved or reconstructed. Among them were the Ständehaus (1946), the Augustusbrücke (1949), the Kreuzkirche (completed 1955), the Zwinger (completed 1963), the Catholic Court Church (completed 1965), the Semperoper (completed 1985), the Japanese Palace (completed 1987) and the two largest train stations. Some of this work dragged on for decades, often interrupted by the overall economic situation in the GDR. The ruins of the Frauenkirche were allowed to remain on the Neumarkt as a war memorial.
While the Theater and Schloßplatz were rebuilt in accordance with the historical model in 1990, the Neumarkt remained completely undeveloped. On the other hand, buildings of socialist classicism and spatial design and orientation according to socialist ideals (e.g. the Kulturpalast) were built at the Altmarkt.

From 1955 to 1958, a large part of the art treasures looted by the Soviet Union was returned, which meant that from 1960 onwards many state art collections could be opened in reconstructed facilities or interim exhibitions. Important orchestras such as the Staatskapelle performed in alternative venues (for example in the Kulturpalast from 1969). Some cultural institutions were moved out of the city center (for example the state library in Albertstadt). The Outer Neustadt, which was almost undamaged during the war was threatened with demolition in the 1980s following years of neglect, but was preserved following public protests.
To house the homeless, large prefabricated housing estates were built on previously undeveloped land In Prohlis and Gorbitz. Damaged housing in the Johannstadt and other areas in the city center were demolished and replaced with large apartment blocks. The villa districts in Blasewitz, Striesen, Kleinzschachwitz, Loschwitz and on the Weißen Hirsch were largely preserved.
Dresden became a major industrial centre of East Germany, with a great deal of research infrastructure. It was the centre of Bezirk Dresden (Dresden District) between 1952 and 1990. Many of the city's important historic buildings were reconstructed, including the Semper Opera House and the Zwinger Palace, although the city leaders chose to rebuild large areas of the city in a "socialist modern" style, partly for economic reasons, but also to break away from the city's past as the royal capital of Saxony and a stronghold of the German bourgeoisie.
Until the end of the Cold War, the 1st Guards Tank Army of the Soviet Army and the 7th Panzer Division of the National People's Army were stationed in and around Dresden. Following reunification in 1989, the Soviet / Russian troops were withdrawn from Germany in the early 1990s and the NVA dissolved in accordance with the provisions of the Two-Plus-Four Treaty of 1990.
From 1985 to 1990, the future President of Russia, Vladimir Putin, was stationed in Dresden by the KGB, where he worked for Lazar Matveev, the senior KGB liaison officer there. On 3 October 1989 (the so-called "battle of Dresden"), a convoy of trains carrying East German refugees from Prague passed through Dresden on its way to the Federal Republic of Germany. Local activists and residents joined in the growing civil disobedience movement spreading across the German Democratic Republic, by staging demonstrations and demanding the removal of the communist government.
Post-reunification

Dresden has experienced dramatic changes since the reunification of Germany in the early 1990s. The city still bears many wounds from the bombing raids of 1945, but it has undergone significant reconstruction. Restoration of the Dresden Frauenkirche, a Lutheran church, began in 1994 and was completed in 2005, a year before Dresden's 800th anniversary; this was done with the help of privately raised funds. The gold cross on the top of the church was funded officially by "the British people and the House of Windsor". The urban renewal process, which includes the reconstruction of the area around the Neumarkt square on which the Frauenkirche is situated, was expected to take decades, but numerous large projects were under way in the first part of the 21st century.
Dresden remains a major cultural centre of historical memory, owing to the city's destruction in World War II. Each year on 13 February, the anniversary of the British and American fire-bombing raid that destroyed most of the city, tens of thousands of demonstrators gather to commemorate the event. Since reunification, the ceremony has taken on a more neutral and pacifist tone (after being used more politically during the Cold War). Beginning in 1999, right-wing Neo-Nazi white nationalist groups have organised demonstrations in Dresden that have been among the largest of their type in the post-war history of Germany. Each year around the anniversary of the city's destruction, people convene in the memory of those who died in the fire-bombing.
The completion of the reconstructed Dresden Frauenkirche in 2005 marked the first step in rebuilding the Neumarkt area. The areas around the square were divided into eight "quarters", with each being rebuilt as a separate project. The majority of buildings were rebuilt either in their original form or at least with a façade resembling the original.
In 2002, torrential rains caused the Elbe to flood 9 metres (30 ft) above its normal height, i.e., even higher than the old record height from 1845, damaging many landmarks (see 2002 European floods). The destruction from this "millennium flood" is no longer visible, due to the speed of reconstruction.
The United Nations' cultural organization UNESCO declared the Dresden Elbe Valley to be a World Heritage Site in 2004.[50] After being placed on the list of endangered World Heritage Sites in 2006, the city lost the title in June 2009,[51][52] due to the construction of the Waldschlößchenbrücke, making it only the second ever World Heritage Site to be removed from the register.[51][52] UNESCO stated in 2006 that the bridge would destroy the cultural landscape. The city council's legal moves, meant to prevent the bridge from being built, failed.[53][54]
Remove ads
Geography
Summarize
Perspective
Location
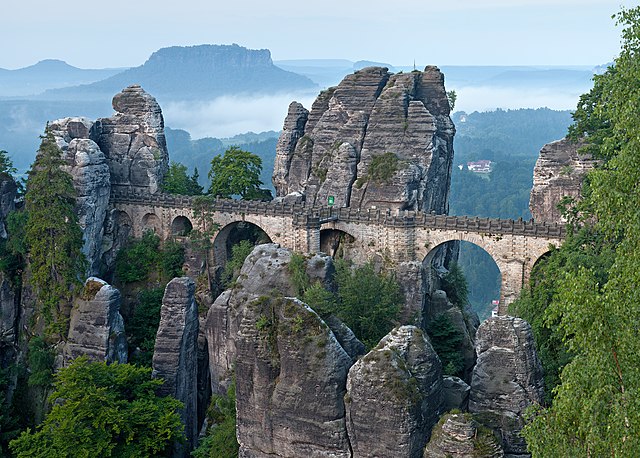


Dresden lies on both banks of the Elbe, mostly in the Dresden Basin, with the further reaches of the eastern Ore Mountains to the south, the steep slope of the Lusatian granitic crust to the north, and the Elbe Sandstone Mountains to the east at an altitude of about 113 metres (371 feet). Triebenberg is the highest point in Dresden at 384 metres (1,260 feet).[55]
With a pleasant location and a mild climate on the Elbe, as well as Baroque-style architecture and numerous museums and art collections, Dresden has been called "Elbflorenz" (Florence on the Elbe). The incorporation of neighbouring rural communities over the past 60 years has made Dresden the fourth largest urban district by area in Germany after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne.[56]
The nearest German cities are Chemnitz 62 kilometres (39 miles)[57] to the southwest, Leipzig 100 kilometres (62 miles)[58] to the northwest and Berlin 165 kilometres (103 miles)[59] to the north. Prague (Czech Republic) is about 150 kilometres (93 miles) to the south and Wrocław (Poland) 200 kilometres (120 miles) to the east.
Nature
Dresden is one of the greenest cities in all of Europe, with 62% of the city being green areas and forests.[60] The Dresden Heath (Dresdner Heide) to the north is a forest 50 km2 (19 sq mi) in size. There are four nature reserves. The additional Special Conservation Areas cover 18 km2 (6.9 sq mi). The protected gardens, parkways, parks and old graveyards host 110 natural monuments in the city.[61] The Dresden Elbe Valley is a former world heritage site which is focused on the conservation of the cultural landscape in Dresden. One important part of that landscape is the Elbe meadows, which cross the city in a 20 kilometre swath. Saxon Switzerland is located south-east of the city.
Climate
Like most of eastern Germany, Dresden has an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb), with significant continental influences due to its inland location. The summers are warm, averaging 19.0 °C (66.2 °F) in July. The winters are slightly colder than the German average, with a January average temperature of 0.1 °C (32.18 °F). The driest months are February, March and April, with precipitation of around 40 mm (1.6 in). The wettest months are July and August, with more than 80 mm (3.1 in) per month.
The microclimate in the Elbe valley differs from that on the slopes and in the higher areas, where the Dresden district Klotzsche, at 227 metres above sea level, hosts the Dresden weather station. The weather in Klotzsche is 1 to 3 °C (1.8 to 5.4 °F) colder than in the inner city at 112 metres above sea level.
Flood protection
Because of its location on the banks of the Elbe, into which some water sources from the Ore Mountains flow, flood protection is important. Large areas are kept free of buildings to provide a flood plain. Two additional trenches, about 50 metres wide, have been built to keep the inner city free of water from the Elbe, by dissipating the water downstream through the inner city's gorge portion. Flood regulation systems like detention basins and water reservoirs are almost all outside the city area.[citation needed]
The Weißeritz, normally a rather small river, suddenly ran directly into the main station of Dresden during the 2002 European floods. This was largely because the river returned to its former route; it had been diverted so that a railway could run along the river bed.[citation needed]
Many locations and areas need to be protected by walls and sheet pilings during floods. A number of districts become waterlogged if the Elbe overflows across some of its former floodplains.[67]
- Floods in 2002
- Semperoper during 2005 floods
- Elbe flood in April 2006
- Dresden skyline in 2006
City structuring
Dresden is a spacious city. Its boroughs differ in their structure and appearance. Many parts still contain an old village core, while some quarters are almost completely preserved as rural settings. Other characteristic kinds of urban areas are the historic outskirts of the city, and the former suburbs with scattered housing. During the German Democratic Republic, many apartment blocks were built. The original parts of the city are almost all in the boroughs of Altstadt (Old town) and Neustadt (New town). Growing outside the city walls, the historic outskirts were built in the 18th and 19th century. They were planned and constructed on the orders of the Saxon monarchs and many of them are named after Saxon sovereigns (e.g. Friedrichstadt and Albertstadt). Dresden has been divided into ten boroughs called "Stadtbezirk" and nine former municipalities ("Ortschaften") which have been incorporated since 1990.[68]
Remove ads
Demographics
Summarize
Perspective
The population of Dresden grew to 100,000 inhabitants in 1852, making it one of the first German cities after Hamburg, Berlin and Breslau (Wrocław) to reach that number. The population peaked at 649,252 in 1933, and dropped to 368,519 in 1945 because of World War II, during which large residential areas of the city were destroyed. After large incorporations and city restoration, the population grew to 522,532 again between 1946 and 1983.[71]
Since German reunification, demographic development has been very unsteady. The city has struggled with migration and suburbanisation. During the 1990s the population increased to 480,000 because of several incorporations, and decreased to 452,827 in 1998. Between 2000 and 2010, the population grew quickly by more than 45,000 inhabitants (about 9.5%) due to a stabilised economy and re-urbanisation. Along with Munich and Potsdam, Dresden is one of the ten fastest-growing cities in Germany.[56]
As of 2019[update] the population of the city of Dresden was 557,075,[72] the population of the Dresden agglomeration was 790,400 as of 2018[update],[3] and as of 2019[update] the population of the Dresden metropolitan area, which includes the neighbouring districts of Meißen, Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge, Bautzen and Görlitz, was 1,343,305.[4]
As of 2018 about 50.0% of the population was female.[73] As of 2007[update] the mean age of the population was 43 years, which is the lowest among the urban districts in Saxony.[74] As of 31 December 2018[update] there were 67,841 people with a migration background (12.1% of the population, increased from 7.2% in 2010), and about two-thirds of these, 44,665 or about 8.0% of all Dresden citizens were foreigners.[73] This percentage increased from 4.1% in 2010.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Governance
Summarize
Perspective
Dresden is one of Germany's 16 political centres[clarification needed] and the capital of Saxony. It has institutions of democratic local self-administration that are independent from the capital functions.[75]
Dresden hosted some international summits in recent years, such as the Petersburg Dialogue between Russia and Germany,[76] the European Union's Minister of the Interior conference[77] and the G8 labour ministers conference.[78]
Mayor
The city council is the legislative branch of the city government. The council gives orders to the mayor (German: Bürgermeister) via resolutions and decrees, and thus also has some degree of executive power.[79][80]

The first freely elected mayor after German reunification was Herbert Wagner of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), who served from 1990 to 2001. The mayor was originally chosen by the city council, but since 1994 has been directly elected. Ingolf Roßberg of the Free Democratic Party (FDP) served from 2001 until 2008. He was succeeded by Helma Orosz (CDU). Dirk Hilbert was elected mayor in 2015 under the banner "Independent Citizens for Dresden". He was nominated by the FDP and Free Voters, and was endorsed by the CDU and AfD in the runoff. The most recent mayoral election was held on 12 June 2022, with a runoff held on 10 July, and the results were as follows:
City council

The most recent city council election was held on 9 June 2024, and the results were as follows:
Public institutions

As the capital of Saxony, Dresden is home to the Saxon state parliament (Landtag)[84] and the ministries of the Saxon Government. The controlling Constitutional Court of Saxony is in Leipzig. The highest Saxon court in civil and criminal law, is the Higher Regional Court of Dresden.[85]
Most of the Saxon state authorities are located in Dresden. Dresden is home to the Regional Commission of the Dresden Regierungsbezirk, which is a controlling authority for the Saxon Government.
Like many cities in Germany, Dresden is also home to a local court, has a trade corporation and a Chamber of Industry and Trade and many subsidiaries of federal agencies (such as the Federal Labour Office or the Federal Agency for Technical Relief). It hosts some divisions of the German Customs and Waterways and Shipping Office.[86]
Dresden is home to a military subdistrict command, but no longer has large military units as it did in the past. Dresden is the traditional location for army officer schooling in Germany, today carried out in the Offizierschule des Heeres.[87]
Local affairs

Local affairs in Dresden often centre around the urban development of the city and its spaces. Architecture and the design of public places is a controversial subject. Discussions about the Waldschlößchenbrücke, a bridge under construction across the Elbe, received international attention because of its position across the Dresden Elbe Valley World Heritage Site. The city held a public referendum in 2005 on whether to build the bridge, prior to UNESCO expressing doubts about the compatibility between bridge and heritage. Its construction caused loss of World Heritage site status in 2009.[88]
In 2006, the city of Dresden sold its publicly subsidized housing organization, WOBA Dresden GmbH, to the US-based private investment company Fortress Investment Group. The city received 987.1 million euro and paid off its remaining loans, making it the first large city in Germany to become debt-free. Opponents of the sale were concerned about Dresden's loss of control over the subsidized housing market.[89]
Dresden has been the center of groups and activities of far-right movements. Politicians and politics of Alternative for Germany (AfD) have a strong backing.[90] Starting in October 2014, PEGIDA, a nationalistic political movement based in Dresden has been organizing weekly demonstrations against what it perceives as the Islamization of Europe at the height of the European migrant crisis. As the number of demonstrators increased to 15,000 in December 2014, so has the international media coverage of it.[91] However, since 2015, the number of demonstrators has decreased significantly.[92]
In 2019, the Dresden City Council passed a policy statement against "anti-democratic, anti-pluralist, misanthropic and right-wing-extremist developments".[93] The motion was originally put forward by the satirical political party Die Partei.[94] Bündnis 90/Die Grünen, Die Linke, SPD and Die Partei voted in favour of the statement. The CDU and AfD voted against it. Among other things, the statement calls on strengthening democracy, protecting human rights and raising spending on (political) education.[95]
Remove ads
Twin towns – sister cities
Dresden and Coventry became twins after World War II in an act of reconciliation, as both had suffered near-total destruction from massive aerial bombings.[96] Similar symbolism occurred in 1988, when Dresden twinned with the Dutch city of Rotterdam. The Coventry Blitz and Rotterdam Blitz bombardments by the German Luftwaffe are also considered to be disproportional.[97]
Dresden has had a triangular partnership with Saint Petersburg and Hamburg since 1987. Dresden is twinned with:[98]
- Coventry, England (1959)
- Saint Petersburg, Russia (1961, suspended)
- Wrocław, Poland (1963)
- Skopje, North Macedonia (1967)
- Ostrava, Czech Republic (1971)
- Brazzaville, Congo (1975)
- Florence, Italy (1978)
- Hamburg, Germany (1987)
- Rotterdam, Netherlands (1988)
- Strasbourg, France (1990)
- Salzburg, Austria (1991)
- Columbus, United States (1992)
- Rouen, France (1994)
- Hangzhou, China (2009)
Friendly cities
Dresden also has friendly relations with:[99]
Remove ads
Cityscape
Summarize
Perspective

Architecture
Although Dresden is often said to be a Baroque city, its architecture is influenced by more than one style. Other eras of importance are the Renaissance and Historicism, as well as the contemporary styles of Modernism and Postmodernism.[100]
Dresden has some 13,000 listed cultural monuments and eight districts under general preservation orders.[101]
Royal household

The Dresden Castle was the seat of the royal household from 1485. The wings of the building have been renewed, built upon and restored many times. Due to this integration of styles, the castle is made up of elements of the Renaissance, Baroque and Classicist styles.[102]
The Zwinger Palace is across the road from the castle. It was built on the old stronghold of the city and was converted to a centre for the royal art collections and a place to hold festivals. Its gate by the moat is surmounted by a golden crown.[103]
Other royal buildings and ensembles:
- Brühl's Terrace was a gift to Heinrich, count von Brühl, and became an ensemble of buildings above the river Elbe.
- Dresden Elbe Valley with the Pillnitz Castle and other castles
Sacred buildings

The Hofkirche was the church of the royal household. Augustus the Strong, who desired to be King of Poland, converted to Catholicism, as Polish kings had to be Catholic. At that time Dresden was strictly Protestant. Augustus the Strong ordered the building of the Hofkirche, the Roman Catholic Cathedral, to establish a sign of Roman Catholic religious importance in Dresden. The church is the cathedral "Sanctissimae Trinitatis" since 1980. The crypt of the Wettin Dynasty is located within the church.[104] King Augustus III of Poland is buried in the cathedral, as one of the very few Polish kings to be buried outside the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków.
In contrast to the Hofkirche, the Lutheran Frauenkirche located at the Neumarkt was built almost contemporaneously by the citizens of Dresden. The city's historic Kreuzkirche was reconsecrated in 1388.[105]
There are also other churches in Dresden, like the Russian Orthodox St. Simeon of the Wonderful Mountain Church in the Südvorstadt district.
Historicism

Historicist buildings made their presence felt on the cityscape until the 1920s.
Notable examples of Renaissance Revival architecture in Dresden include the Albertinum located at Brühl's Terrace as well as the Saxon State Chancellery and the Saxon State Ministry of Finance located on the northern Elbe river banks. The Ehrlichsche Gestiftskirche, constructed in 1907, was a historicist church building that was demolished in August 1951.[106]
The Villa Rosa was built in 1839 and was considered one of the most important villa buildings in Dresden, due to its Renaissance Revival architecture.[107]
Yenidze is a former cigarette factory building built in the style of a mosque between 1907 and 1909.
The most recent historicist buildings in Dresden date from the short era of Stalinist architecture in the 1950s, e.g. at the Altmarkt.[108]

Modernism
The Garden City of Hellerau, at that time a suburb of Dresden, was founded in 1909. It was Germany's first garden city.[109] In 1911, Heinrich Tessenow built the Hellerau Festspielhaus (festival theatre). Until the outbreak of World War I, Hellerau was a centre for European modernism with international standing.[110][111] In 1950, Hellerau was incorporated into the city of Dresden. Today, the Hellerau reform architecture is recognized as exemplary. In the 1990s, the garden city of Hellerau became a conservation area.[112]
The German Hygiene Museum (built 1928–1930) is a signal example of modern architecture in Dresden in the interwar period. The building is designed in an impressively monumental style, but employs plain façades and simple structures.[citation needed]
Important modernist buildings erected between 1945 and 1990 are the Centrum-Warenhaus (a large department store), representing the international Style, and the multi-purpose hall Kulturpalast.[citation needed]
Contemporary architecture

After 1990 and German reunification, new styles emerged. Important contemporary buildings include the New Synagogue, a postmodern building with few windows, the Transparent Factory, the Saxon State Parliament and the New Terrace, the UFA-Kristallpalast cinema by Coop Himmelb(l)au (one of the biggest buildings of Deconstructivism in Germany), and the Saxon State Library.
Daniel Libeskind and Norman Foster both modified existing buildings. Foster roofed the main railway station with translucent Teflon-coated synthetics. Libeskind changed the whole structure of the Bundeswehr Military History Museum by placing a wedge through the historical arsenal building. According to Libeskind's studio, "[t]he façade's openness and transparency is intended to contrast with the opacity and rigidity of the existing building."[113]
Bridges
Important bridges crossing the Elbe river are the Blaues Wunder bridge and the Augustus Bridge.
Statues
Jean-Joseph Vinache's golden equestrian statue of August the Strong, the Goldener Reiter (Golden Cavalier), is on the Neustädter Markt square. It shows August at the beginning of the Hauptstraße (Main street) on his way to Warsaw, where he was King of Poland in personal union. Another statue is the memorial of Martin Luther in front of the Frauenkirche.[114]
Parks and gardens
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2020) |
Großer Garten is a Baroque garden in central Dresden. It includes the Dresden Zoo and the Dresden Botanical Garden.
The Dresden Heath is a large forest located in the northeast of Dresden and one of the city's most important recreation areas.
The park of Pillnitz Palace is famous for its botanical treasures, including a more than 230-year-old Japanese camellia and about 400 potted plants.[115]
Main sights
Remove ads
Culture
Summarize
Perspective

Carl Maria von Weber and Richard Wagner had a number of their works performed for the first time in Dresden.[116] Other artists, such as Ernst Ludwig Kirchner,[117] Otto Dix,[118] Oskar Kokoschka,[119] Richard Strauss,[120][121] Gottfried Semper[122] and Gret Palucca,[123] were also active in the city. Dresden is also home to several art collections and musical ensembles.
Entertainment

The Saxon State Opera descends from the opera company of the former electors and Kings of Saxony. Their first opera house was the Opernhaus am Taschenberg, opened in 1667. The Opernhaus am Zwinger presented opera from 1719 to 1756, when the Seven Years' War began. The later Semperoper was completely destroyed during the bombing of Dresden during the second world war. The opera's reconstruction was completed exactly 40 years later, on 13 February 1985. Its musical ensemble is the Sächsische Staatskapelle Dresden, founded in 1548.[124] The Dresden State Theatre runs a number of smaller theatres. The Dresden State Operetta is the only independent operetta in Germany.[125] The Herkuleskeule (Hercules club) is an important site in German-speaking political cabaret.
There are several choirs in Dresden, the best-known of which is the Dresdner Kreuzchor (Choir of The Holy Cross). It is a boys' choir drawn from pupils of the Kreuzschule, and was founded in the 13th century.[126] The Dresdner Kapellknaben are not related to the Staatskapelle, but to the former Hofkapelle, the Catholic cathedral, since 1980. The Dresden Philharmonic Orchestra is the orchestra of the city of Dresden.
Throughout the summer, the outdoor concert series "Zwingerkonzerte und Mehr" is held in the Zwingerhof. Performances include dance and music.[127]
There are several small cinemas presenting cult films and low-budget or low-profile films chosen for their cultural value. Dresden also has a few multiplex cinemas, of which the Rundkino is one the known.
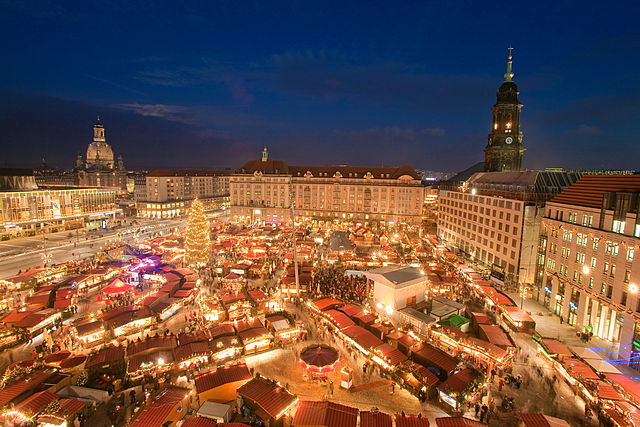
Dresden's Striezelmarkt is one of the largest Christmas markets in Germany. Founded as a one-day market in 1434, it is considered the first genuine Christmas market in the world.[10]
A big event each year in June is the Bunte Republik Neustadt,[128] a culture festival lasting three days in the city district of Dresden-Neustadt. Bands play live concerts for free in the streets and there are refreshments and food.
Museums

Dresden hosts the Staatliche Kunstsammlungen Dresden (Dresden State Art Collections) which, according to the institution's own statements, place it among the most important museums presently in existence. The art collections consist of twelve museums, including the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister (Old Masters Gallery) and the Grünes Gewölbe (Green Vault) and the Japanese Palace (Japanisches Palais).[129] Also known are Galerie Neue Meister (New Masters Gallery), Rüstkammer (Armoury) with the Turkish Chamber, and the Museum für Völkerkunde Dresden (Museum of Ethnology). Other museums and collections owned by the Free State of Saxony in Dresden are:
- The Deutsche Hygiene-Museum, founded for mass education in hygiene, health, human biology and medicine[130]
- The Landesmuseum für Vorgeschichte (State Museum of Prehistory)[131]
- The Senckenberg Naturhistorische Sammlungen Dresden (Senckenberg Natural History Collections Dresden)[132]
- The Universitätssammlung Kunst + Technik (Collection of Art and Technology of the Dresden University of Technology)[133]
- Verkehrsmuseum Dresden (Transport Museum)
- Festung Dresden (Dresden Fortress)[134][135]
- Panometer Dresden (Dresden Panometer) (Panorama museum)[136][137]
The Dresden City Museum is run by the city of Dresden and focused on the city's history.
The Bundeswehr Military History Museum is placed in the former garrison in the Albertstadt.
The book museum of the Saxon State Library presents the Dresden Codex.[138]
The Kraszewski Museum is a museum dedicated to the most prolific Polish writer Józef Ignacy Kraszewski, who lived in Dresden from 1863 to 1883.[139]
Remove ads
Transport
Summarize
Perspective

Bus
DVB is the municipal company in charge of transport in the city of Dresden.[140] DVB provides a night service named GuteNachtLinie ('goodnight lines'), which operates Monday-Sunday, although the frequency of the buses is greater on Friday, Saturday and before holidays when the routes run every 30 minutes between 22:45 and 04:45.[141] Postplatz is the most important hub for night-time travel in Dresden. Most GuteNachtLinie routes meet here at the same time to allow people to switch routes.[141][142]
Roads
The Bundesautobahn 4 (European route E40) crosses Dresden in the northwest from west to east. The Bundesautobahn 17 leaves the A4 in a south-eastern direction. In Dresden it begins to cross the Ore Mountains towards Prague. The Bundesautobahn 13 leaves from the three-point interchange "Dresden-Nord" and goes to Berlin. The A13 and the A17 are on the European route E55. In addition, several Bundesstraßen (federal highways) run through Dresden.
Rail

There are two main inter-city transit hubs in the railway network in Dresden: Dresden Hauptbahnhof and Dresden-Neustadt railway station. The most important railway lines run to Berlin, Prague, Leipzig and Chemnitz. A commuter train system (Dresden S-Bahn) operates on three lines alongside the long-distance routes.
Air
Dresden Airport is the city's international airport, located at the north-western outskirts of the city. After German reunification the airport's infrastructure has been considerably improved. In 1998, a motorway access route was opened.[143] In March 2001, a new terminal building was opened along with the underground S-Bahn station Dresden Flughafen, a multi-storey car park and a new aircraft handling ramp.[144]
Dresden is also directly connected to Berlin Brandenburg Airport by the IC 17.
Trams
Dresden has a large tramway network operated by Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe, the municipal transport company. The Transport Authority operates twelve lines on a 200 km (124 mi) network.[145] Many of the new low-floor vehicles are up to 45 metres long and produced by Bombardier Transportation in Bautzen. While about 30% of the system's lines are on reserved track (often sown with grass to avoid noise), many tracks still run on the streets, especially in the inner city.[146]
The CarGoTram was a tram that supplied Volkswagen's Transparent Factory, crossing the city. The transparent factory is located not far from the city centre next to the city's largest park.[147]
The districts of Loschwitz and Weisser Hirsch are connected by the Dresden Funicular Railway, which has been carrying passengers back and forth since 1895.[148]
Remove ads
Economy
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (June 2020) |


Until enterprises like Dresdner Bank left Dresden in the communist era to avoid nationalisation, Dresden was one of the most important German cities, an important industrial centre of the German Democratic Republic.[citation needed] The period of the GDR until 1990 was characterized by low economic growth in comparison to western German cities.[149] In 1990 Dresden had to struggle with the economic collapse of the Soviet Union and the other export markets in Eastern Europe. After reunification enterprises and production sites broke down almost completely as they entered the social market economy, facing competition from the Federal Republic of Germany. After 1990 a completely new legal system and currency system was introduced and infrastructure was largely rebuilt with funds from the Federal Republic of Germany. Dresden as a major urban centre has developed much faster and more consistently than most other regions in the former German Democratic Republic.
Between 1990 and 2010 the unemployment rate fluctuated between 13% and 15%, but has decreased significantly ever since. In December 2019 the unemployment rate was 5.3%, the fourth lowest among the 15 largest cities of Germany (after Munich, Stuttgart and Nuremberg).[150] In 2017, the GDP per capita of Dresden was 39,134 euros, the highest in Saxony.[151]
Thanks to the presence of public administration centres, a high density of semi-public research institutes and an extension of publicly funded high technology sectors, the proportion of highly qualified workers Dresden is again among the highest in Germany and by European criteria.[152]
In 2019, Dresden had the seventh-best future prospects of all cities in Germany, after being ranked fourth in 2017.[7] According to the 2019 study by Forschungsinstitut Prognos, Dresden is one of the most dynamic regions in Germany. It ranks at number 41 of all 401 German regions and second of all regions in former East Germany (only surpassed by Jena).[153][154][155]
Enterprises
Three major sectors dominate Dresden's economy:
Silicon Saxony Saxony's semiconductor industry was built up in 1969. Major enterprises today include AMD's semiconductor fabrication spin-off GlobalFoundries, Infineon Technologies, ZMDI and Toppan Photomasks. Their factories attract many suppliers of material and cleanroom technology enterprises to Dresden.
The pharmaceutical sector developed at the end of the 19th century. The 'Sächsisches Serumwerk Dresden' (Saxon Serum Plant, Dresden), owned by GlaxoSmithKline, is a global leader in vaccine production.[156] Another traditional pharmaceuticals producer is Arzneimittelwerke Dresden (Pharmaceutical Works, Dresden).[157]
A third traditional branch is that of mechanical and electrical engineering. Major employers are the Volkswagen Transparent Factory, Elbe Flugzeugwerke (Elbe Aircraft Works), Siemens and Linde-KCA-Dresden.[citation needed] The tourism industry enjoys high revenue and supports many employees. There are around one hundred bigger hotels in Dresden, many of which cater in the upscale range.[citation needed]
Media
The media in Dresden include two major newspapers of regional record: the Sächsische Zeitung (Saxon Newspaper, circulation around 228,000) and the Dresdner Neueste Nachrichten (Dresden's Latest News, circulation around 50,000). Dresden has a broadcasting centre belonging to the Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk. The Dresdner Druck- und Verlagshaus (Dresden printing plant and publishing house) produces part of Spiegel's print run, amongst other newspapers and magazines.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Education and science
Summarize
Perspective


Universities
Dresden is home to a number of renowned universities, but among German cities it is a more recent location for academic education.
- The Dresden University of Technology (Technische Universität Dresden, abbreviated as TU Dresden or TUD) with more than 36,000 students (2011)[158] was founded in 1828 and is among the oldest and largest Universities of Technology in Germany. It is currently the university of technology in Germany with the largest number of students but also has many courses in social studies, economics and other non-technical sciences. It offers 126 courses. In 2006, the TU Dresden was successful in the German Universities Excellence Initiative of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Germany).
- The Dresden University of Applied Sciences (Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Dresden) was founded in 1992 and had about 5,300 students in 2005.[159]
- The Dresden Academy of Fine Arts (Hochschule für Bildende Künste Dresden) was founded in 1764 and is known for its former professors and artists such as George Grosz, Sascha Schneider, Otto Dix, Oskar Kokoschka, Bernardo Bellotto, Carl-Gustav Carus, Caspar David Friedrich and Gerhard Richter.
- The Palucca School of Dance (Palucca Hochschule für Tanz)[160] was founded by Gret Palucca in 1925 and is a major European school of free dance.
- The Carl Maria von Weber College of Music was founded in 1856.
Other universities include the Hochschule für Kirchenmusik, a school specialising in church music, and the Evangelische Hochschule für Sozialarbeit, an education institution for social work.[citation needed] The Dresden International University is a private postgraduate university, founded in 2003 in cooperation with the Dresden University of Technology.[161]
Research institutes
Dresden hosts many research institutes, some of which have gained an international standing. The domains of most importance are micro- and nanoelectronics, transport and infrastructure systems, material and photonic technology, and bio-engineering. The institutes are well connected among one other as well as with the academic education institutions.[162]
Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf is the largest complex of research facilities in Dresden, a short distance outside the urban areas. It focuses on nuclear medicine and physics. As part of the Helmholtz Association it is one of the German Big Science research centres.
The Max Planck Society focuses on fundamental research. There are three Max Planck Institutes (MPI) in Dresden: the MPI of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, the MPI for Chemical Physics of Solids, and the MPI for the Physics of Complex Systems.[163]
The Fraunhofer Society hosts institutes of applied research that also offer mission-oriented research to enterprises. With eleven institutions or parts of institutes, Dresden is the largest location of the Fraunhofer Society worldwide.[164] The Fraunhofer Society has become an important factor in location decisions and is seen as a useful part of the "knowledge infrastructure".[165]
The Leibniz Community is a union of institutes with science covering fundamental research and applied research. In Dresden there are three Leibniz Institutes. The Leibniz Institute for Polymer Research[166] and the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research[167] are both in the material and high-technology domain, while the Leibniz Institute for Ecological Urban and Regional Development is focused on more fundamental research into urban planning.[168] The Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf was member of the Leibniz Community until the end of 2010.[169]
Higher secondary education
Dresden has more than 20 gymnasia which prepare for a tertiary education, five of which are private.[170] The Sächsisches Landesgymnasium für Musik with a focus on music is supported, as its name implies by the State of Saxony, rather than by the city.[171] There are some Berufliche Gymnasien which combine vocational education and secondary education and an Abendgymnasium which prepares higher education of adults avocational.[172]
Remove ads
Sport
Summarize
Perspective

Dresden is home to Dynamo Dresden, which had a tradition in UEFA club competitions up to the early 1990s. Dynamo Dresden won eight titles in the DDR-Oberliga. Currently, the club is a member of the 2. Bundesliga after some seasons in the Bundesliga and 3. Liga.[173]
In the early 20th century, the city was represented by Dresdner SC, who were one of Germany's most successful clubs in football. Their best performances came during World War II, when they were twice German champions, and twice Cup winners. Dresdner SC is a multisport club. While its football team plays in the sixth-tier Landesliga Sachsen, its volleyball section has a team in the women's Bundesliga. Dresden has a third football team SC Borea Dresden.
ESC Dresdner Eislöwen is an ice hockey club playing in the second-tier ice hockey league DEL2.
Dresden Monarchs are an American football team in the German Football League.
The Dresden Titans are the city's top basketball team. Due to good performances, they have moved up several divisions and currently play in Germany's second division ProA. The Titans' home arena is the Margon Arena.
Since 1890, horse races have taken place and the Dresdener Rennverein 1890 e.V. are active and one of the big sporting events in Dresden.[174]
Major sporting facilities in Dresden are the Rudolf-Harbig-Stadion, the Heinz-Steyer-Stadion and the EnergieVerbund Arena for ice hockey.
Remove ads
Quality of life
According to the 2017 Global Least & Most Stressful Cities Ranking, Dresden was one of the least stressful cities in the world. It was ranked 15th out of 150 cities worldwide and above Düsseldorf, Leipzig, Dortmund, Cologne, Frankfurt, and Berlin.[175]
Notable people
Public service
- Augustus II the Strong (1670–1733), Elector of Saxony and King of Poland.[176]
- Augustus III of Poland (1696–1763), Elector of Saxony and King of Poland.[177]
- Frederick Augustus I of Saxony (1750–1827), King of Saxony.[178]
- Anthony of Saxony (1755–1836), King of Saxony
- Count Heinrich von Bellegarde (1756–1845), Generalfeldmarschall and statesman.[179]
- Johann Adolf, Freiherr von Thielmann (1765–1824), Prussian cavalry soldier.[180]
- Wilhelm Adolf Becker (1796–1846), classical scholar.[181]
- Frederick Augustus II of Saxony (1797–1854), King of Saxony.[182]
- John, King of Saxony (1801–1873), King of Saxony.[183]
- Edwin Freiherr von Manteuffel (1809–1885), Prussian general field marshal.[184]
- Albert, King of Saxony (1828–1902), King of Saxony.[185]
- George, King of Saxony (1832–1904), King of Saxony.[186]
- Heinrich Gotthard Freiherr von Treitschke (1834–1896), historian, political writer and nationalist
- Ernst Brandes (1862–1935), German lawyer, estate manager and politician
- Frederick Augustus III of Saxony (1865–1932), King of Saxony
- Amelie Beese (1886–1925), aviator
- Max Immelmann (1890–1916), WWI fighter pilot, first pilot awarded the Pour le Mérite, known as the "Blue Max"
- Herbert Wehner (1906–1990), politician (SPD)
- Wolfgang Bergold (1913–1987), East German politician and diplomat
- Wolfgang Mischnick (1921–2002), politician (FDP)
- Peter Hoffmann (1930–2023), historian
- Gerhart Baum (born 1932), politician (FDP)
- Andreas von Bülow (born 1937), politician and writer
- Christine Bergmann (born 1939), politician (SPD)
- Katja Kipping (born 1978), politician (The Left)
Academics
- Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus (1651–1708), German mathematician, physicist, physician, and philosopher
- Christoph M. Kimmich (born 1939), German-American historian and eighth President of Brooklyn College
- Gert Jäger (born 1935), translation scholar
Arts
- August Buchner (1591–1661), influential Baroque poet
- August Joseph Pechwell (1757–1811), painter
- Theodor Körner (1791–1813), poet and soldier.[187]
- Moritz Hauptmann (1792–1868), music theorist, teacher and composer.[188]
- Ludwig Richter (1803–1884), painter.[189]
- Hans von Bülow (1830–1894), conductor, virtuoso pianist and composer.[190]
- Paul Miersch (1868–1956), composer
- Elsa Laura Wolzogen (1876–1945), composer
- Victor Klemperer (1881–1960), Jewish author of I Will Bear Witness
- Erich Kästner (1899–1974), author of books
- Carle Hessay (1911–1978), Canadian painter
- Siegfried Geißler (1929–2014), composer, conductor, hornist and politician
- Gerhard Richter (born 1932), painter
- Gernot Roll (1939–2020), cinematographer, film director and script writer
- Amalie Scholl (1823–1879), German composer
- Georgina Schubert (1840–1878), composer and singer
- Erik Simon (born 1950), German science fiction writer, editor of anthologies of science fiction, literary critic of science fiction, and translator
- Thomas Fritsch (1944–2021), film, television and dubbing actor
- Andrea Ihle (born 1953), operatic soprano
- Martha Irmler, ballet dancer
- Annette Jahns (1958–2020), operatic mezzo-soprano and contralto, and opera director
- Siarhei Mikhalok (born 1972), Belarusian rock musician and actor
Science and business
- Georg Bartisch (ca.1535 – 1607), eye surgeon and author of first German-language textbook of ophthalmology
- Carl Friedrich Wenzel (ca.1740 – 1793), chemist and metallurgist.[191]
- Georg Amadeus Carl Friedrich Naumann (1797–1873), mineralogist and geologist.[192]
- Otto Linné Erdmann (1804–1869), chemist, introduced vaccination into Saxony.[193]
- Ferdinand A. Lange (1815–1875), watchmaker, founder of A. Lange & Söhne
- Julius Hermann Moritz Busch (1821–1899), publicist; "Bismarck's Boswell".[194]
- Ernst Engel (1821–1896), statistician and economist; Engel curve & Engel's law.[195]
- Melitta Bentz (1873–1950), inventor of the coffee filter.
- Karl Reinisch (1921–2007), engineer
- Edith Schönert-Geiß (1933–2012), numismatist
- Marie Simon (1824–1877), nurse[196]
- Reinhart Heinrich (1946–2006), biophysicist
Sport
- Kurt Hitke (1889–1979), American racing driver
- Heinz Melkus (1928–2005), racing driver and founder of Melkus
- Curt Rottman (1886–1928), Olympic gymnast
- Matthias Sammer (born 1967), footballer and football coach
- Ad Santel (1887–1966), professional wrestler
- Helmut Schön (1915–1996), football coach
- Wolfgang Seidel (1926–1987), racing driver
- Fritz Wiessner (1900–1988), pioneer of free climbing
- Axel Tischer (born 1986), professional wrestler
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads