Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Free trade agreements of New Zealand
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
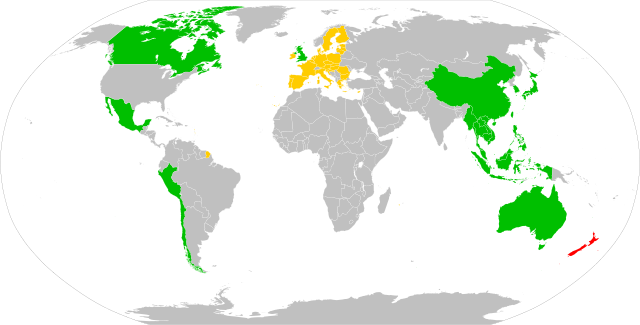
New Zealand is party to 14 free trade agreements (FTAs) worldwide. Together they accounted for over 70% of New Zealand's trade in 2023.[1]
History
Summarize
Perspective
Prior to the mid-twentieth century, New Zealand's trade was dominated by the United Kingdom which provided preferential trade quotas to her former colony.[2] As the United Kingdom attempted to join the European Economic Community in the 1960s and move away from trade with former colonies, New Zealand sought to diversify international trade. Following this, New Zealand signed its first bilateral free trade agreement in 1965 with the New Zealand-Australia Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (later superseded by Closer Economic Relations in 1983).[3] When the United Kingdom eventually joined the European Economic Community in 1973, exceptions for New Zealand allowed the United Kingdom's preferential trade offerings to be phased out until the 1990s.[2]
Economic liberalisation in the 1970s made New Zealand into a market economy dependent on international trade especially in tourism and agricultural sectors. New Zealand has since welcomed foreign investment and has been praised as one of the most business-friendly countries in the world.[4]
Since the 1990s, New Zealand has pursued free trade agreements as part of international trade policy with a goal (as of 2024) of 90% of exports covered by FTAs by 2030.[5][6] New Zealand signed bilateral free trade agreements throughout the Asia-Pacific region through the 2000s including with significant trading partners China and the ASEAN bloc. Free trade agreements have expanded in the 2010s and 2020s with New Zealand's participation in wide multilateral FTAs including the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
Remove ads
Free trade agreements in force
Summarize
Perspective
New Zealand has bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements with the following blocs and countries:
Bilateral agreements
 Australia: Closer Economic Relations (1983)[7]
Australia: Closer Economic Relations (1983)[7] China: New Zealand–China Free Trade Agreement (2008)[8]
China: New Zealand–China Free Trade Agreement (2008)[8] European Union: New Zealand-European Union Free Trade Agreement (2024)[9]
European Union: New Zealand-European Union Free Trade Agreement (2024)[9] Hong Kong: Hong Kong–New Zealand Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (2011)[10][11]
Hong Kong: Hong Kong–New Zealand Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (2011)[10][11] Malaysia: Malaysia–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (2009)[12][13]
Malaysia: Malaysia–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (2009)[12][13] Singapore: New Zealand and Singapore Closer Economic Partnership (2001)[14]
Singapore: New Zealand and Singapore Closer Economic Partnership (2001)[14] South Korea: NZ-Korea Free Trade Agreement (2015)[15]
South Korea: NZ-Korea Free Trade Agreement (2015)[15] Taiwan: Agreement between New Zealand and the Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu on Economic Cooperation (2013)[16][17]
Taiwan: Agreement between New Zealand and the Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu on Economic Cooperation (2013)[16][17] Thailand: New Zealand and Thailand Closer Economic Partnership (2005)[18]
Thailand: New Zealand and Thailand Closer Economic Partnership (2005)[18] United Kingdom: New Zealand–United Kingdom Free Trade Agreement (2023)[19][20]
United Kingdom: New Zealand–United Kingdom Free Trade Agreement (2023)[19][20]
Multilateral agreements
- Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership (TPSEP) (2005),[21] with:
- ASEAN Australia NZ FTA (2009),[22] with:
- Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) (2018),[23] with:
- PACER Plus (2020),[24] with:
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) (2022),[25] with:
Remove ads
Agreements not yet in force
- Agreement on Climate Change, Trade and Sustainability (ACCTS), negotiations concluded in 2024 but have not yet been signed,[26][27] with:
 United Arab Emirates: New Zealand-United Arab Emirates Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (NZ-UAE CEPA) (2024)[28]
United Arab Emirates: New Zealand-United Arab Emirates Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (NZ-UAE CEPA) (2024)[28] Gulf Cooperation Council: Negotiations began in 2007 and concluded in 2009 but never signed.[29] Agreed to resume negotiating in 2022.[30] Signed in October 2024.[31]
Gulf Cooperation Council: Negotiations began in 2007 and concluded in 2009 but never signed.[29] Agreed to resume negotiating in 2022.[30] Signed in October 2024.[31]
Free trade agreements under negotiation
New Zealand is negotiating bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements with the following blocs and countries:[32]
Pacific Alliance: Free trade agreement negotiating since 2017.[33]
 India: India–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement – negotiating since 2007 with the establishment of a JSG (Joint Study Group) looking at the feasibility of an Indian-NZ FTA.[34]
India: India–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement – negotiating since 2007 with the establishment of a JSG (Joint Study Group) looking at the feasibility of an Indian-NZ FTA.[34]- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity, under negotiation since 2021[35] with:
Remove ads
Abandoned or superseded proposals
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP): signed and ratified but never entered into force, superseded by the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership.
 Japan: Conducted a feasibility study in 2008.[36] Superseded as Japan joined the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership.
Japan: Conducted a feasibility study in 2008.[36] Superseded as Japan joined the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership. Mercosur: New Zealand-Mercosur Free Trade Agreement. Negotiations began in 2010[37][38][39] and ended without a deal before 2024.[32]
Mercosur: New Zealand-Mercosur Free Trade Agreement. Negotiations began in 2010[37][38][39] and ended without a deal before 2024.[32] Russia,
Russia,  Belarus and
Belarus and  Kazakhstan: Russia-Kazakhstan-Belarus Free Trade Agreement – negotiations began in 2010[40] and were later suspended.[41]
Kazakhstan: Russia-Kazakhstan-Belarus Free Trade Agreement – negotiations began in 2010[40] and were later suspended.[41] United States: New Zealand–United States Free Trade Agreement.[21] Negotiations began in 2008 but were ended in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (which the United States would withdraw from).
United States: New Zealand–United States Free Trade Agreement.[21] Negotiations began in 2008 but were ended in favour of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (which the United States would withdraw from).
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads