Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Gla domain
Protein family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation/gamma-carboxyglutamic (GLA) domain is a protein domain that contains post-translational modifications of many glutamate residues by vitamin K-dependent carboxylation to form γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla). Proteins with this domain are known informally as Gla proteins. The Gla residues are responsible for the high-affinity binding of calcium ions.[1][2]
The GLA domain binds calcium ions by chelating them between two carboxylic acid residues. These residues are part of a region that starts at the N-terminal extremity of the mature form of Gla proteins, and that ends with a conserved aromatic residue. This results in a conserved Gla-x(3)-Gla-x-Cys motif[3] that is found in the middle of the domain, and which seems to be important for substrate recognition by the carboxylase.
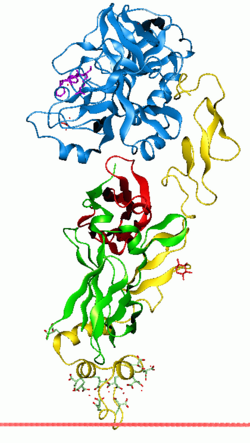
The 3D structures of several Gla domains have been solved.[4][5] Calcium ions induce conformational changes in the Gla domain and are necessary for the Gla domain to fold properly. A common structural feature of functional Gla domains is the clustering of N-terminal hydrophobic residues into a hydrophobic patch that mediates interaction with the cell surface membrane.[5]
At present, the following human Gla-containing proteins (Gla proteins) have been characterized to the level of primary structure:
- the blood coagulation factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, and X
- the anticoagulant proteins C and S, and the factor X-targeting protein Z.
- the bone Gla protein osteocalcin
- the calcification-inhibiting matrix Gla protein (MGP),
- the cell growth regulating "growth arrest specific gene 6" protein GAS6,
- periostin (a factor necessary for migration and adhesion of epithelial cells), plus
- two proline-rich Gla-proteins (PRGPs) and two transmembrane Gla proteins (TMGPs), the functions of which are unknown.[6][7][8]
In all cases in which their function was known, the presence of the Gla residues in these proteins turned out to be essential for functional activity.[9]
Remove ads
Functions
Summarize
Perspective
Coagulation and anticoagulation proteins
Gla domains are found in vertebrate coagulation proteins. There seems to be a single origin of these Gla domains.[10]
The Gla domain causes a binding affinity to phosphatidylserine, a membrane phospholipid, in most Gla coagulation proteins. The exceptions are FVII and protein C, which instead bind phosphatidic acid. In any case, in vertebrate coagulation proteins, the Gla domain anchor the proteins to a membrane, allowing the coagulation complexes to form.[11]
Control of mineralization and calcification
The bone Gla protein (osteocalcin) and the matrix Gla protein have diverged in a jawed vertebrate ancestor. In humans, the bone Gla protein mainly helps bone mineralization by collecting calcium ions and the matrix Gla protein prevents soft tissue calcification by binding away calcium ions.[12]
In invertebrates
A number of Gla domain proteins were found in Ciona intestinalis, which lacks a blood coagulation cascade. Despite the lack of blood coagulation, it has Gla proteins with domain architecture resembling that of factor IX and protein S. It also has a Gla protein that resembles PRGP1 and another that resembles the non-Gla vertebrate protein Jagged1.[13]
Remove ads
Human proteins containing this domain
- Coagulation proteins
- Thrombin (F2) (a.k.a. coagulation factor II; also its precursor prothrombin) – involved in coagulation
- Factor VII (F7) – involved in coagulation
- Factor IX (F9) – involved in coagulation
- Factor X (F10) – involved in coagulation
- Protein C (PROC) – roles in regulating anticoagulation, inflammation, cell death, and maintaining the permeability of blood vessel walls
- Protein S (PROS1) – involved in coagulation
- Protein Z (PROZ) – involved in coagulation
- Calcium-managing proteins
- Osteocalcin (BGLAP) – involved in bone mineralization.
- Matrix gla protein (MGP) – inhibitor of calcification of soft tissue and plays a role in bone organization
- Other regulatory proteins
- GAS6 – thought to be involved in the stimulation of cell proliferation
- Transthyretin (TTR) previously known as prealbumin — carries thyroxine (T4) in blood and into cerebral spinal fluid
- Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 (ITIH2) – plays a role in pancreas islets and many other cells
- Periostin – a factor necessary for cell migration (embryonic development, and immune responses) and adhesion of epithelial cells, over-expressed in some cancers
- Proline-rich/transmembrane Gla proteins
Remove ads
Subfamilies
- Coagulation factor, Gla region InterPro: IPR002383
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads