Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
GRIN1
Protein-coding gene in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIN1 gene.[5][6]
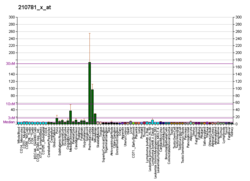
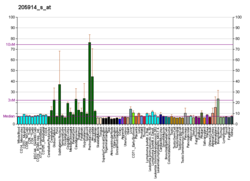
The protein encoded by this gene is a critical subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily which are heteromeric protein complexes with multiple subunits arranged to form a ligand-gated ion channel. These subunits play a key role in the plasticity of synapses, which is believed to underlie memory and learning. The gene consists of 21 exons and is alternatively spliced, producing transcript variants differing in the C-terminus. The sequence of exon 5 is identical in vertebrates, with exon 5 splicing demonstrated in human, mouse and rat.[7][8][9][10] Cell-specific factors are thought to control expression of different isoforms, possibly contributing to the functional diversity of the subunits.[6]
Remove ads
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads