Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Hyponitrite
Ion, and compounds containing the ion From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In chemistry, hyponitrite may refer to the anion N
2O2−
2 ([ON=NO]2−), or to any ionic compound that contains it. In organic chemistry, it may also refer to the group −O−N=N−O−, or any organic compound with the generic formula R1−O−N=N−O−R2, where R1 and R2 are organic groups.[1] Such compounds can be viewed as salts and esters of hyponitrous acid.
An acid hyponitrite is an ionic compound with the anion HN
2O−
2 ([HON=NO]−).
Remove ads
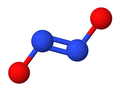
Hyponitrite ion
Hyponitrite exhibits cis–trans isomerism.[2]
The trans (E) form is generally found in hyponitrite salts such as sodium hyponitrite (Na
2N
2O
2) and silver(I) hyponitrite (Ag
2N
2O
2).
The cis (Z) form of sodium hyponitrite can be obtained too, but it is more reactive than the trans form.[2] The cis hyponitrite anion is nearly planar and almost symmetric, with lengths of about 140 pm for N−O bond and 120 pm for the N−N bond, and O−N−N angles of about 119°.[3]
Reactions
The hyponitrite ions can act as a bidentate ligand in either bridging or chelating mode. There is a bridging cis-hyponitrite group in the red dinuclear form of nitrosyl pentammine cobalt(III) chloride, [Co(NH3)5NO]Cl2.[4]
Hyponitrite can reduce elemental iodine to hydroiodic acid:[4]
- N
2O2−
2 + 3 I
2 + 3 H
2O → NO−
3 + NO−
2 + 6 HI
Remove ads
Hyponitrite esters
Organic trans-hyponitrites R1−O−N=N−O−R2 can be obtained by reacting trans silver(I) hyponitrite Ag
2N
2O
2 with various alkyl halides. For example, reaction with tert-butyl chloride yields trans di-tert-butyl hyponitrite.[5][6][7][8]
Other alkyl radicals reported in the literature include ethyl,[9] and benzyl.[10][11][12] These compounds can be a source of alkoxyl radicals.[13]
See also
Other nitrogen oxyanions include
- nitrate, NO−
3 - nitrite, NO−
2 - peroxonitrite, (peroxynitrite), OONO−
- peroxonitrate, HNO−
4 - trioxodinitrate, (hyponitrate), [ON=NO2]2−
- nitroxylate, [O2N−NO2]4−
- orthonitrate, NO3−
4
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads