Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
IRF3
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor.[5]
Remove ads
Function
Summarize
Perspective
IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family.[5] IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. IRF3 has been further characterized and shown to contain several functional domains including a nuclear export signal, a DNA-binding domain, a C-terminal IRF association domain and several regulatory phosphorylation sites.[6] IRF3 is found in an inactive cytoplasmic form that upon serine/threonine phosphorylation forms a complex with CREBBP.[7] The complex translocates into the nucleus for the transcriptional activation of interferons alpha and beta, and further interferon-induced genes.[8]
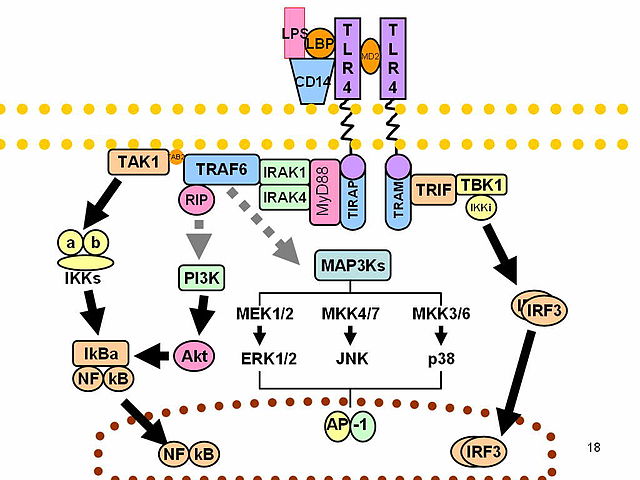
IRF3 plays an important role in the innate immune system's response to viral infection.[9] Aggregated MAVS have been found to activate IRF3 dimerization.[10] A 2015 study shows phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING and TRIF at a conserved pLxIS motif recruits and specifies IRF3 phosphorylation and activation by the Serine/threonine-protein kinase TBK1, thereby activating the production of type-I interferons.[11] Another study has shown that IRF3-/- knockouts protect from myocardial infarction.[12] The same study identified IRF3 and the type I IFN response as a potential therapeutic target for post-myocardial infarction cardioprotection.[12]
Remove ads
Interactions
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads